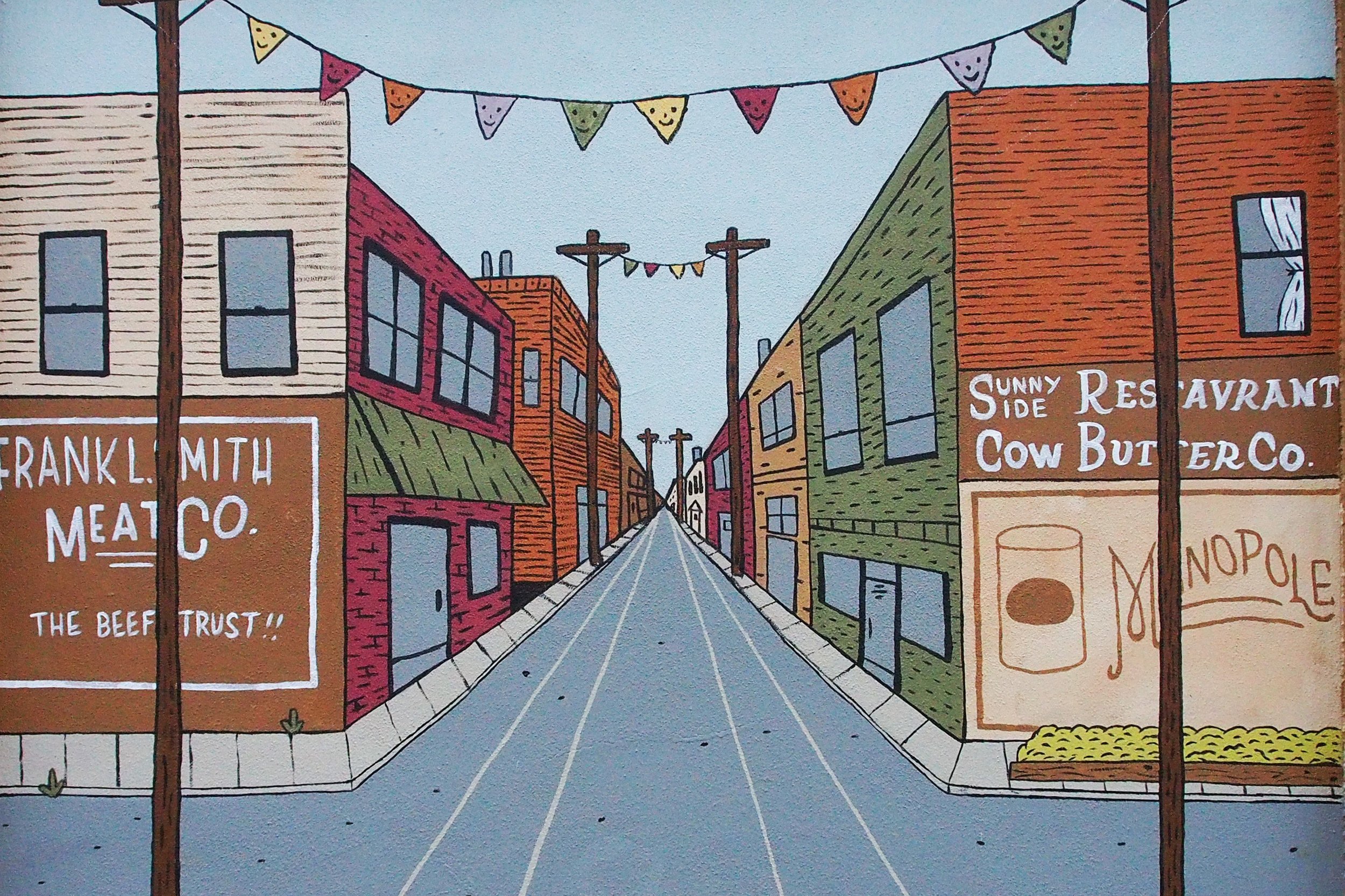
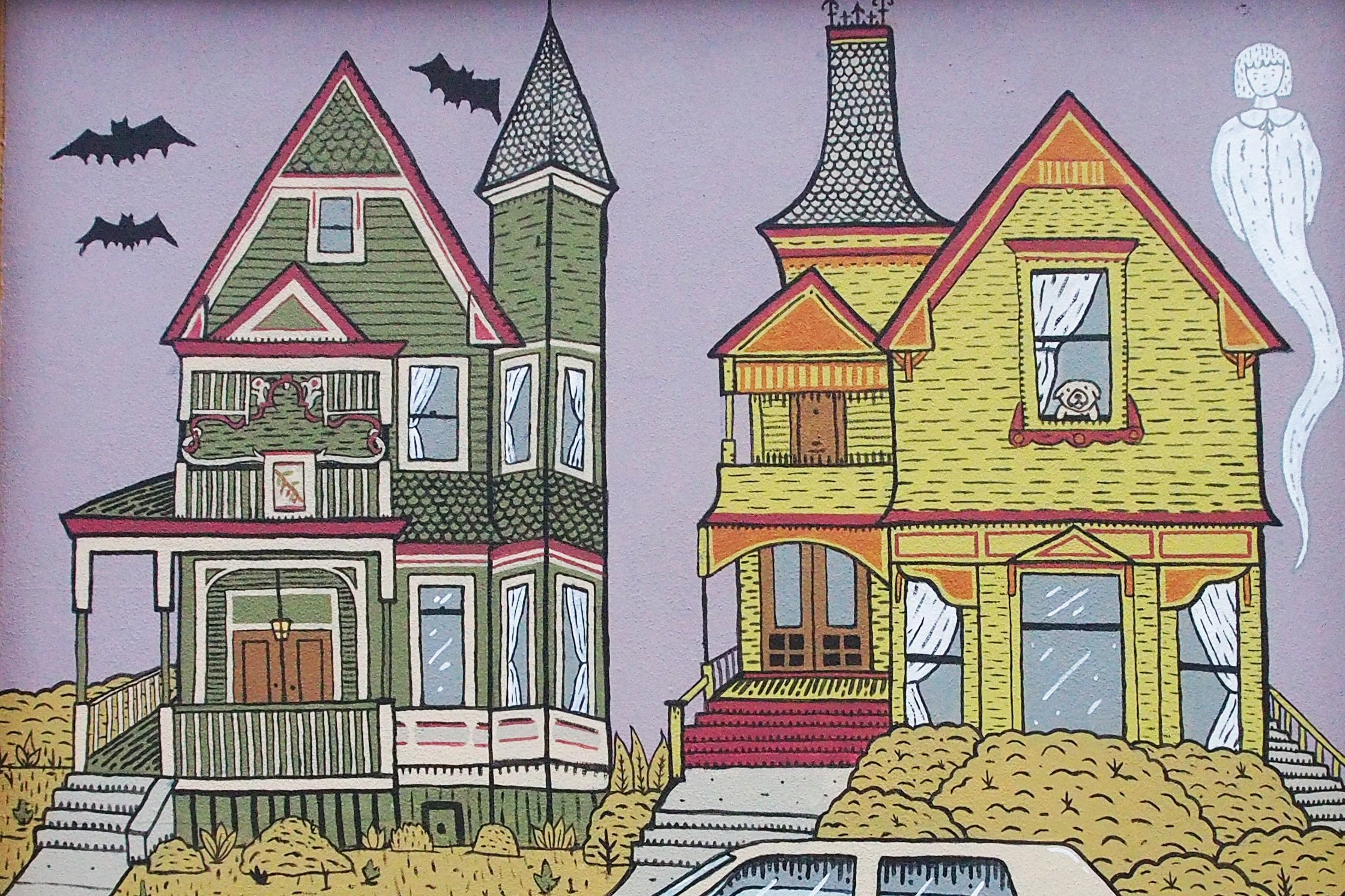
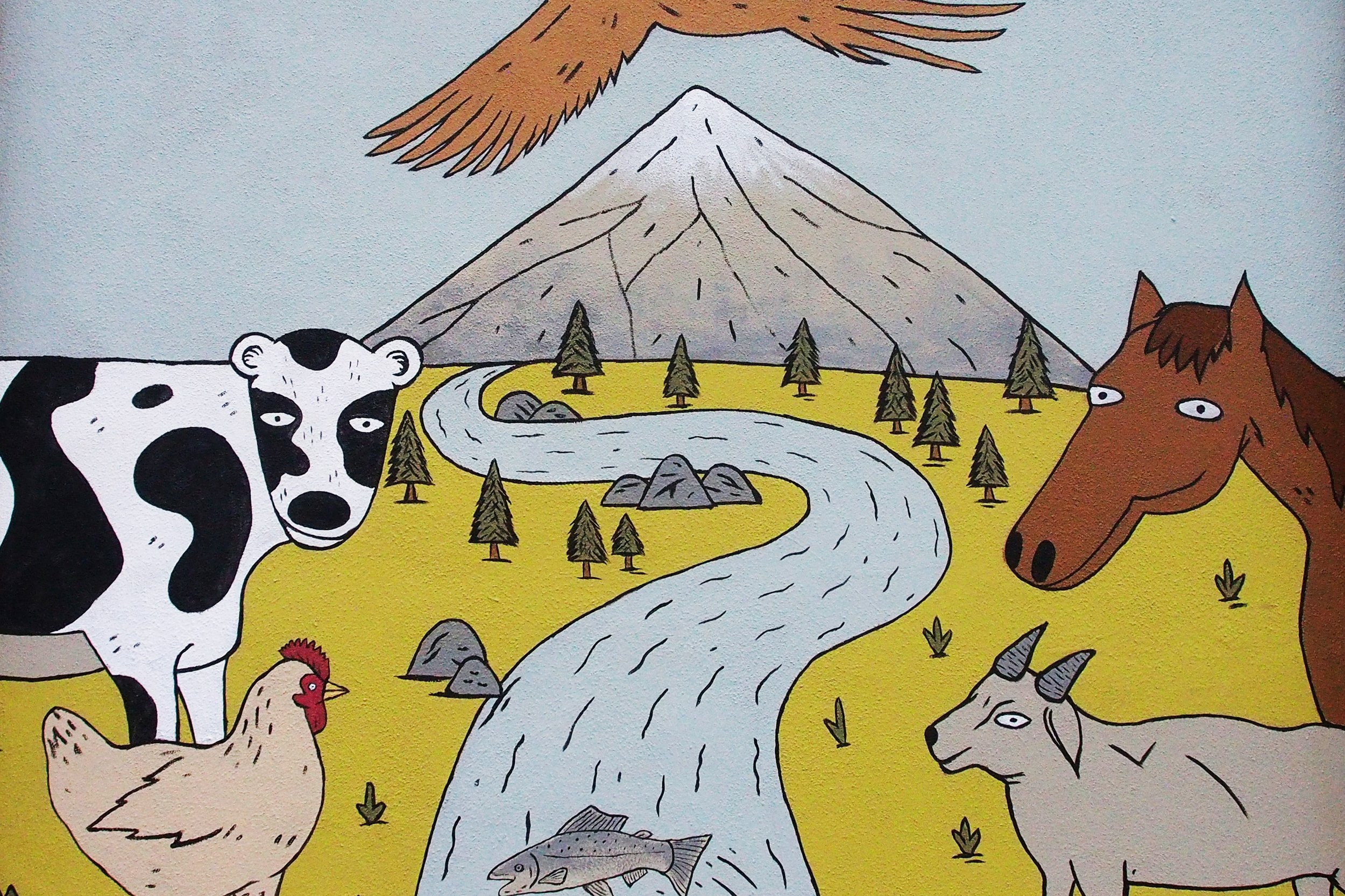
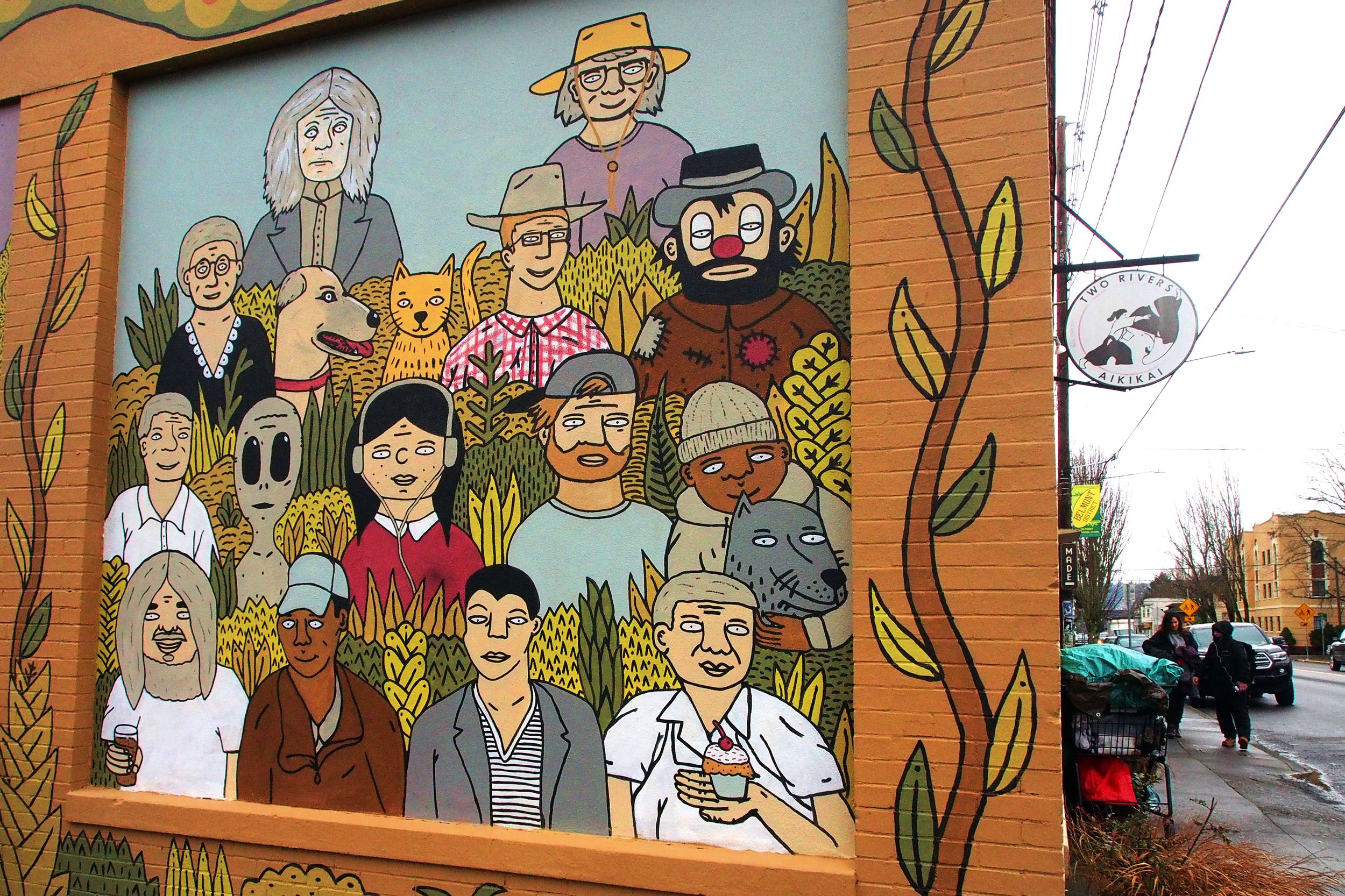
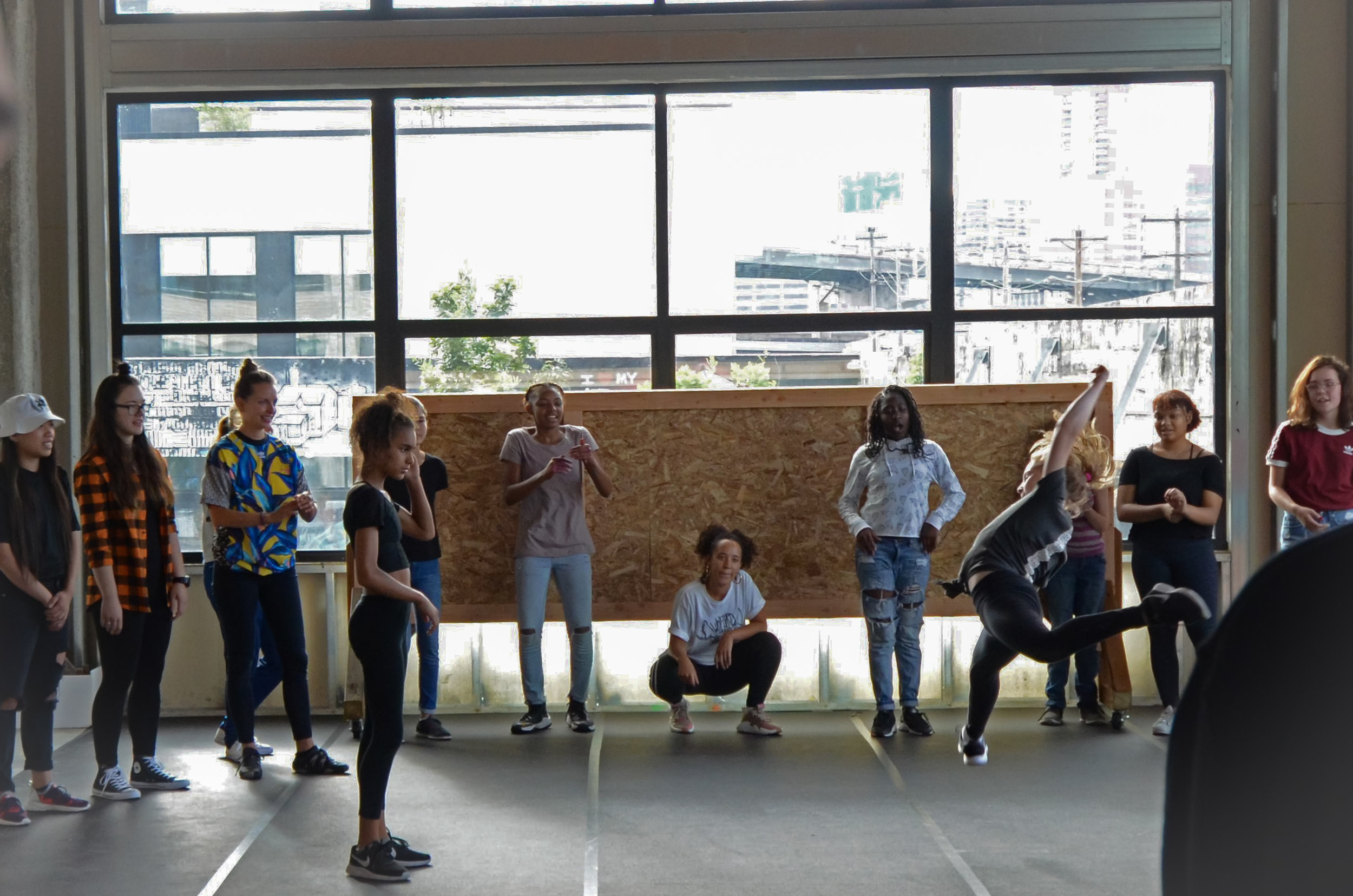
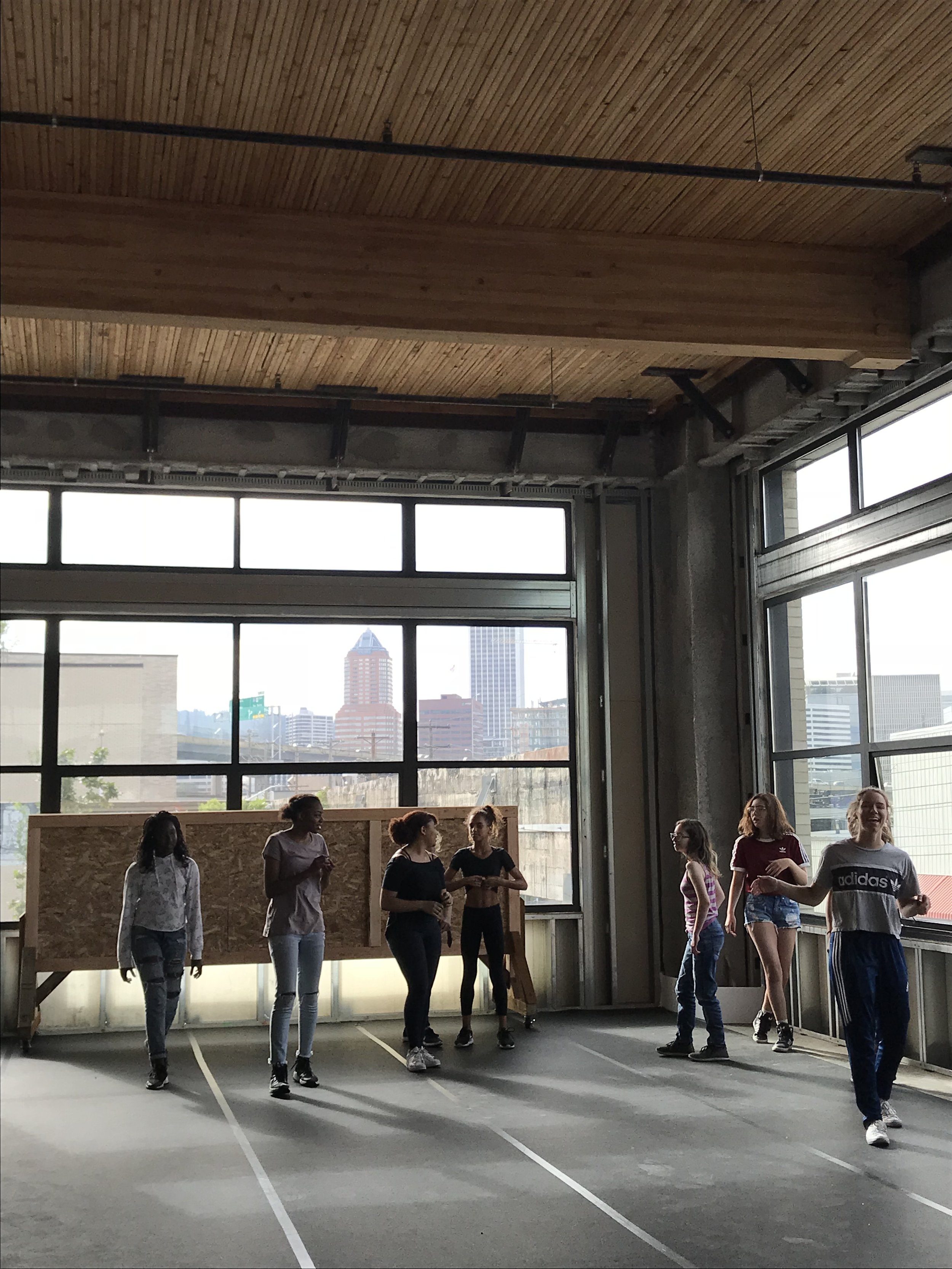
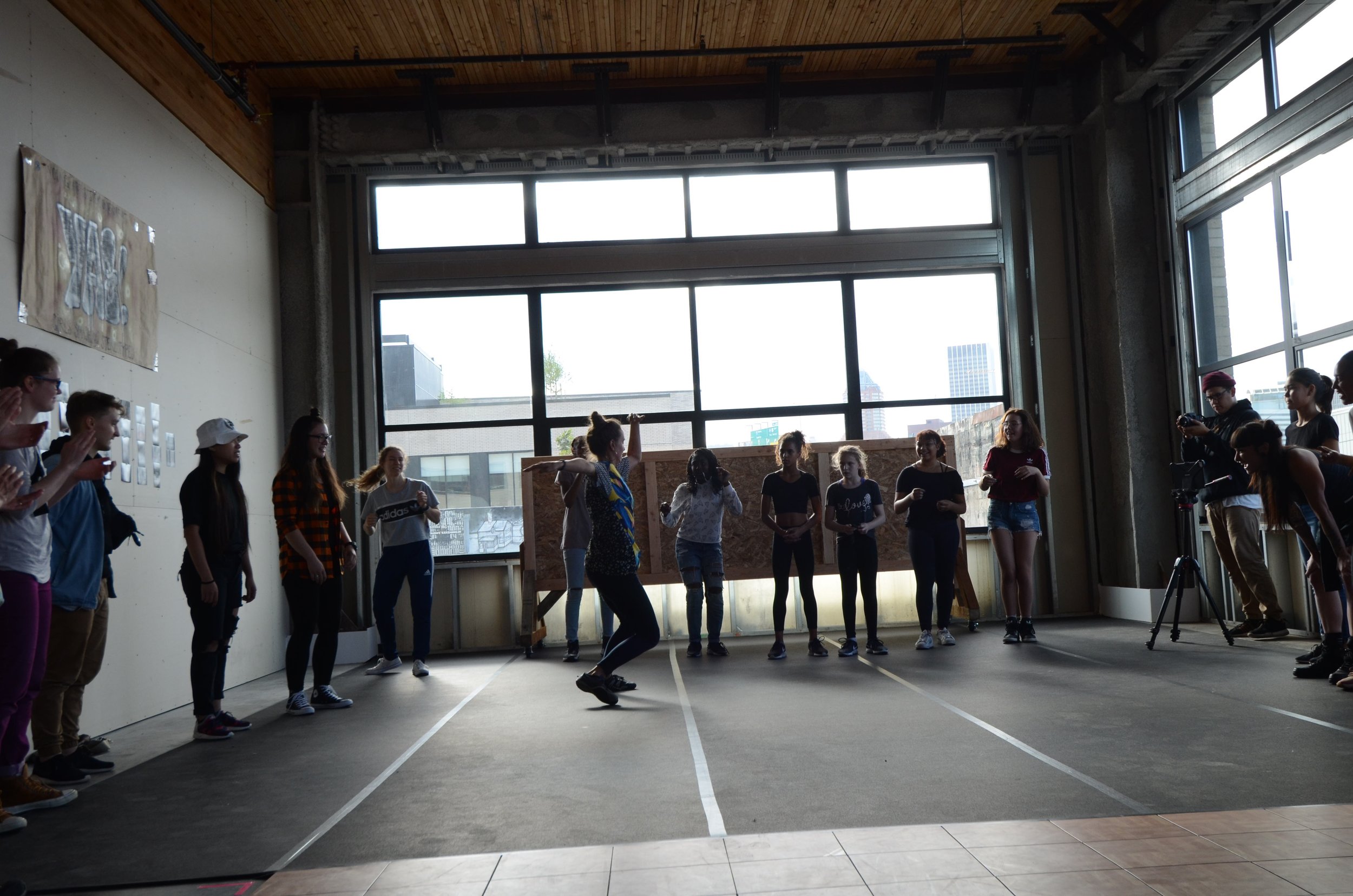
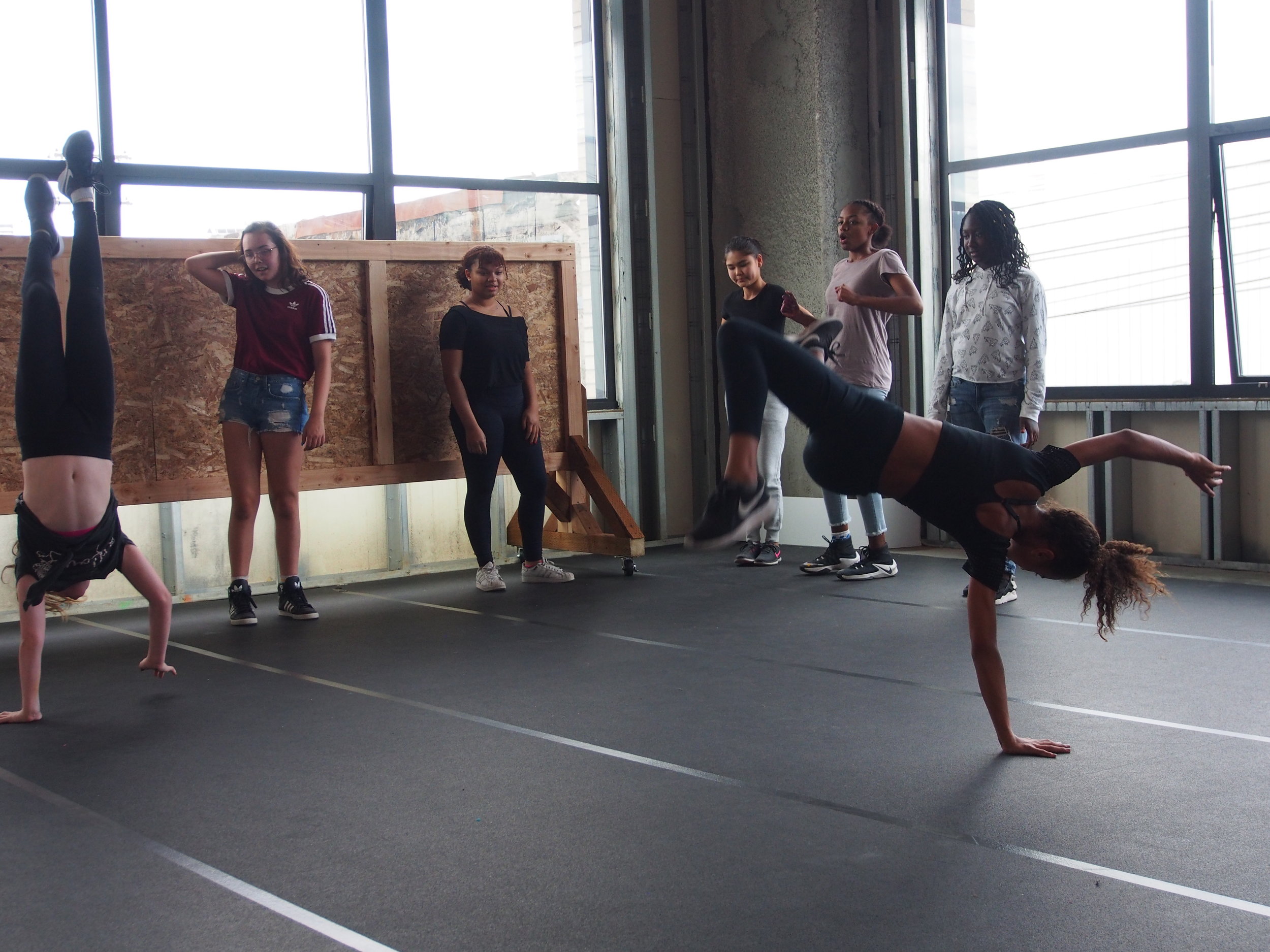
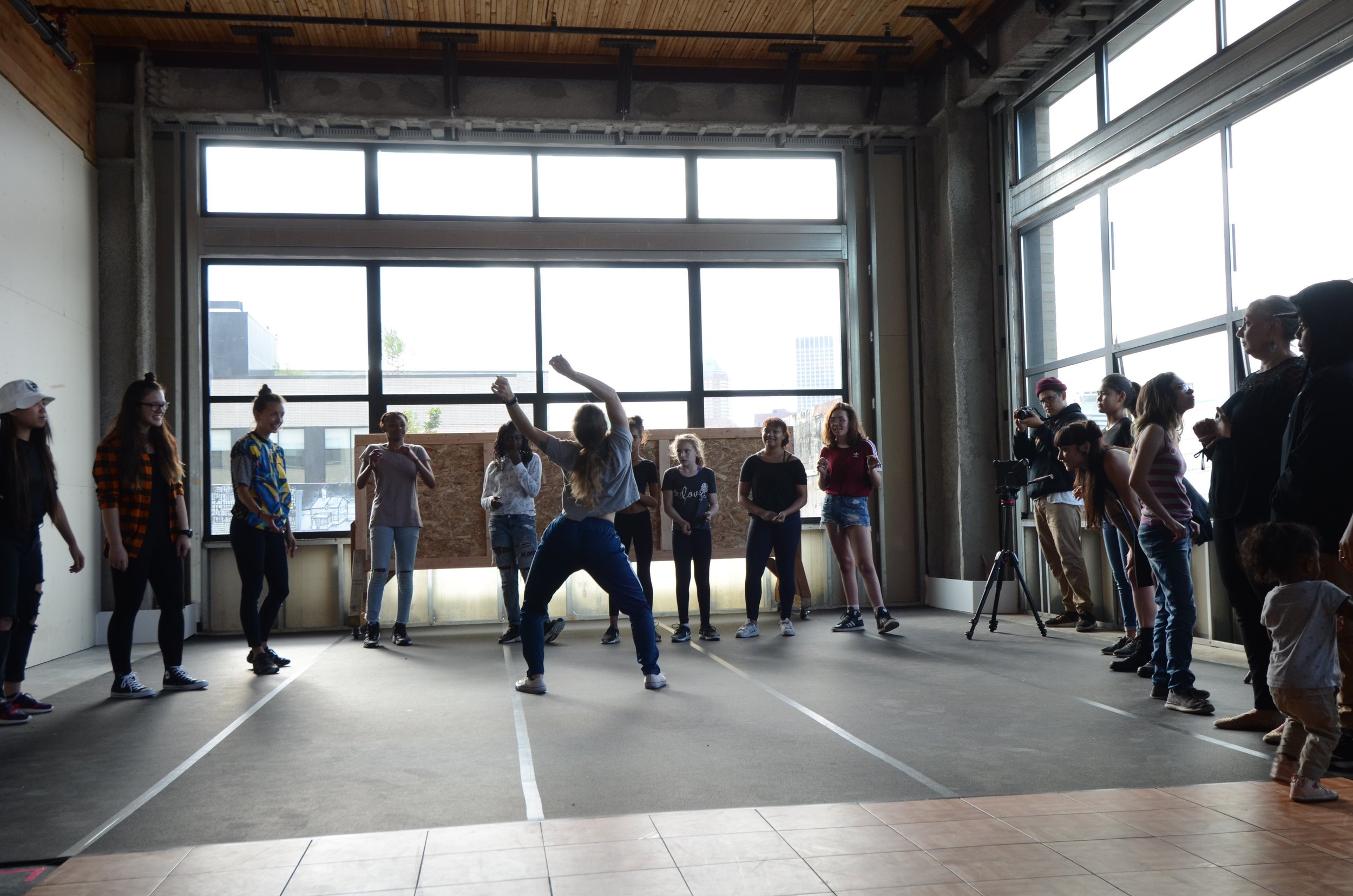
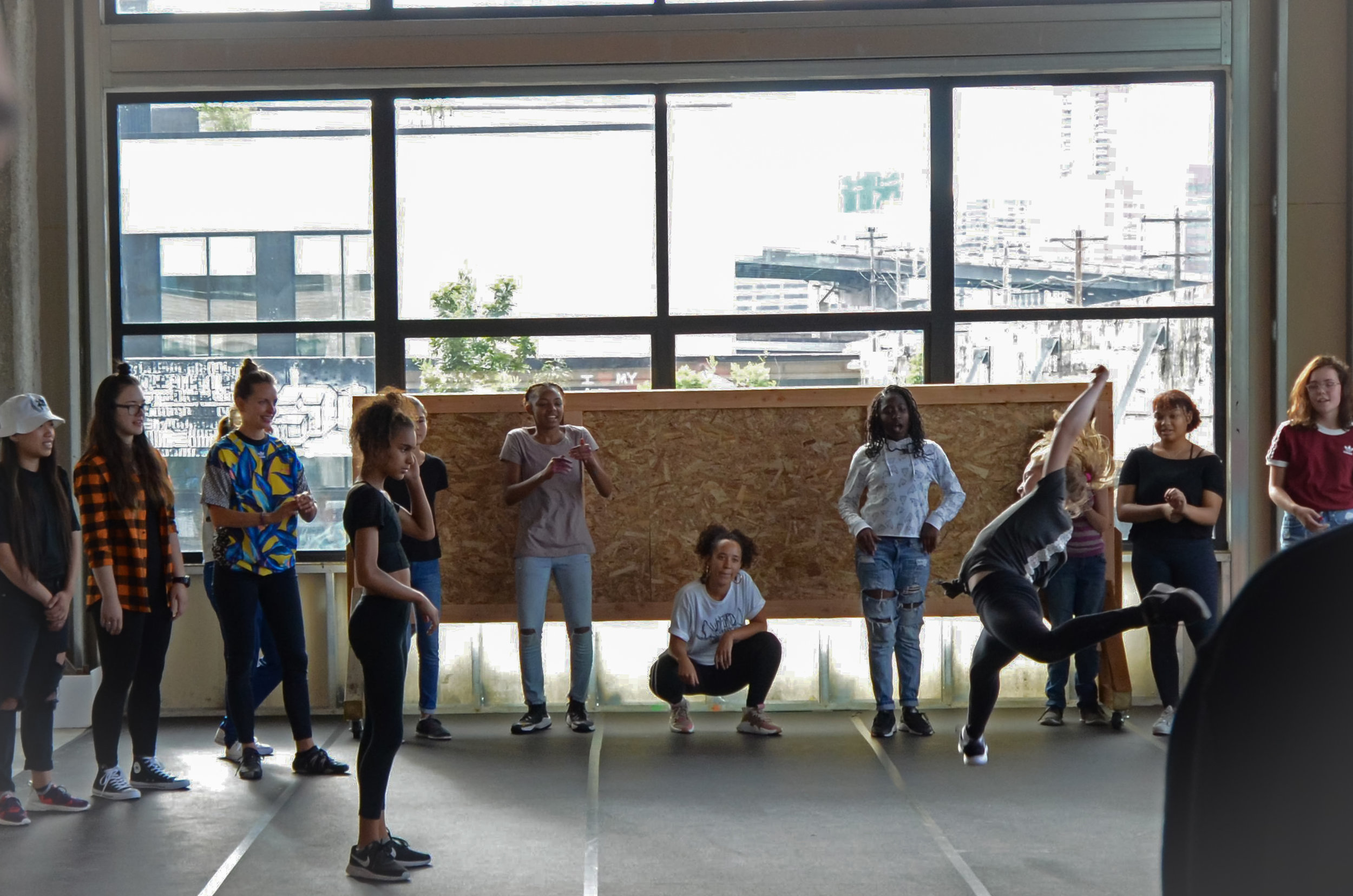
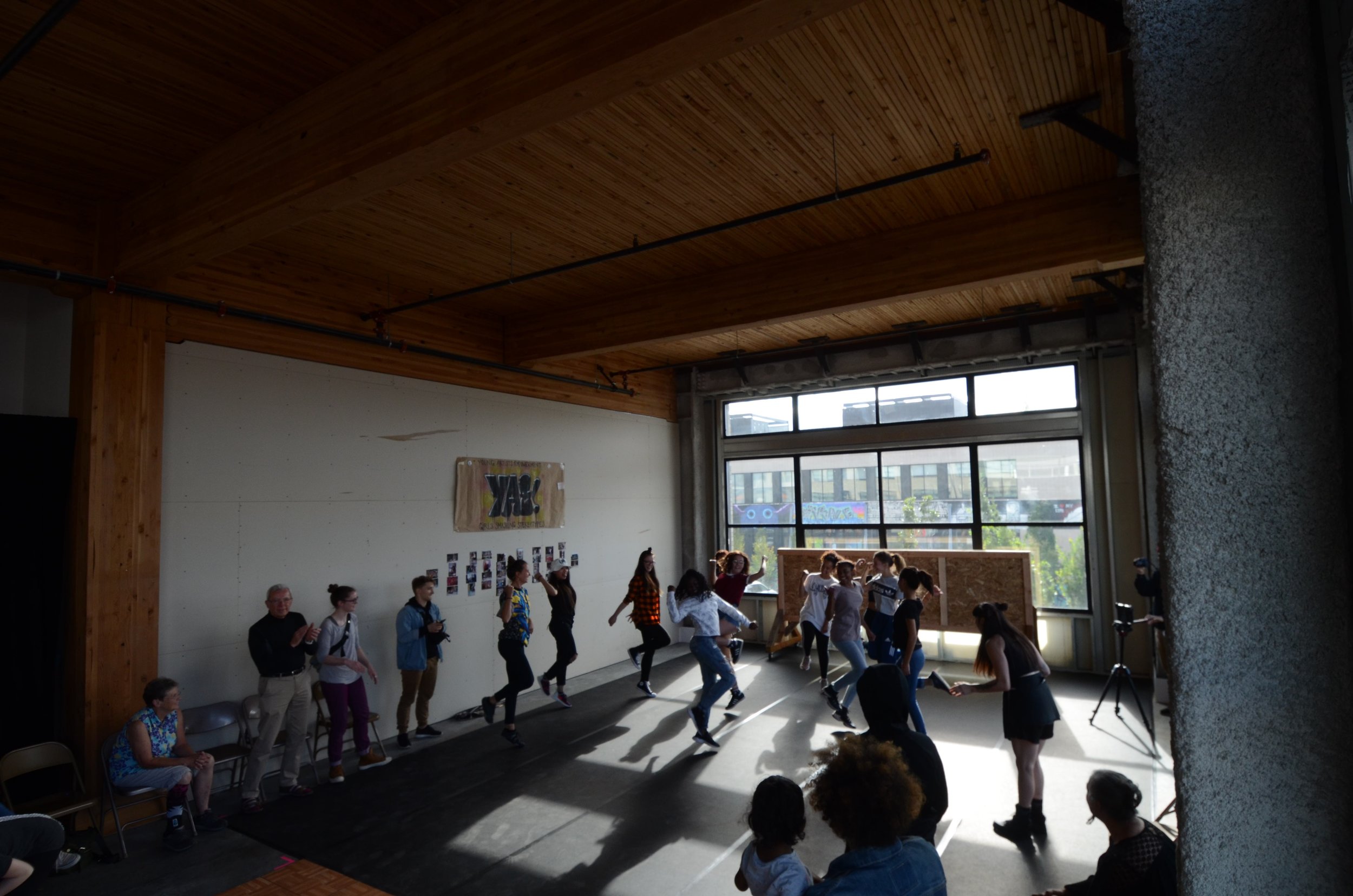
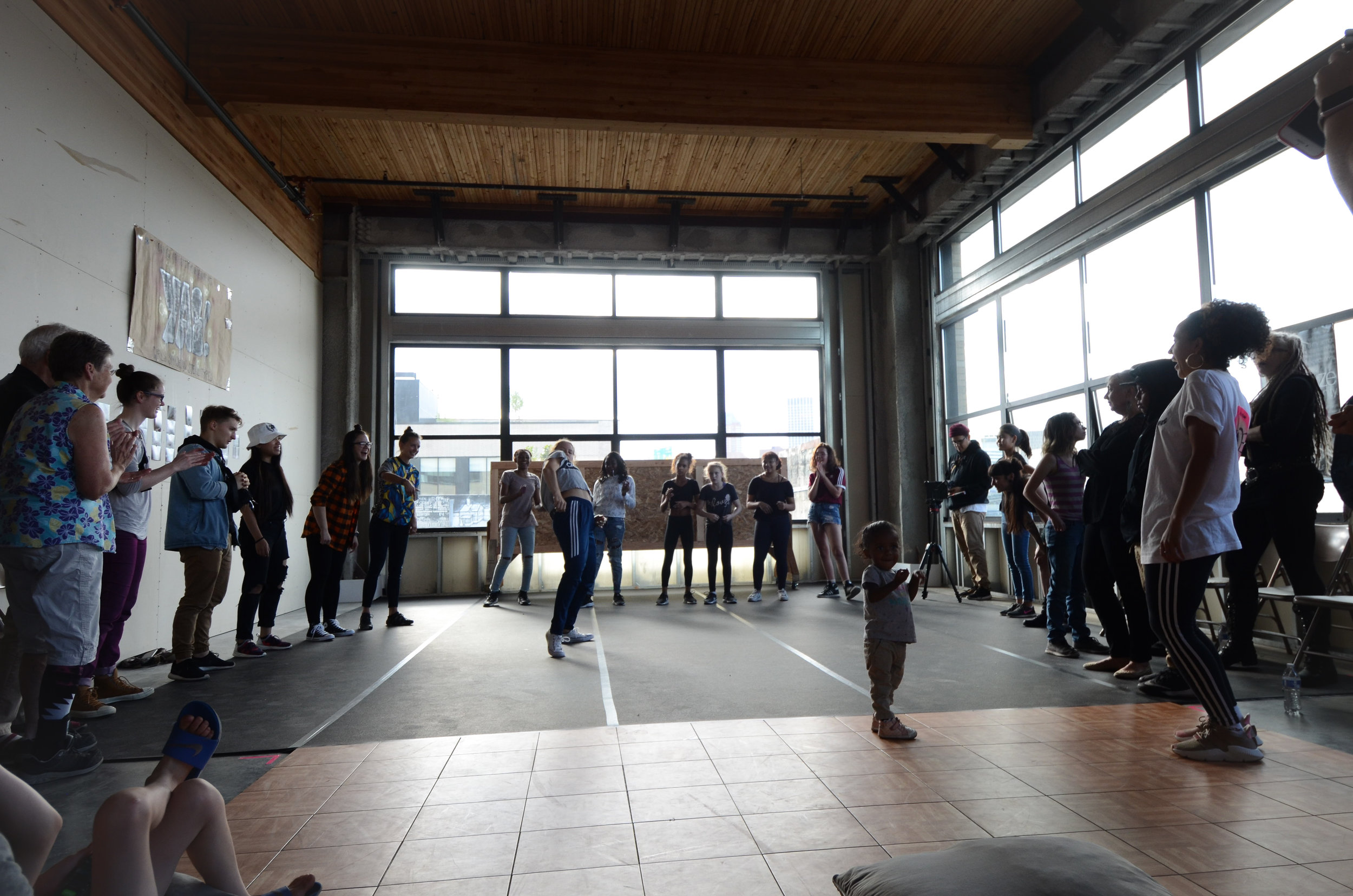
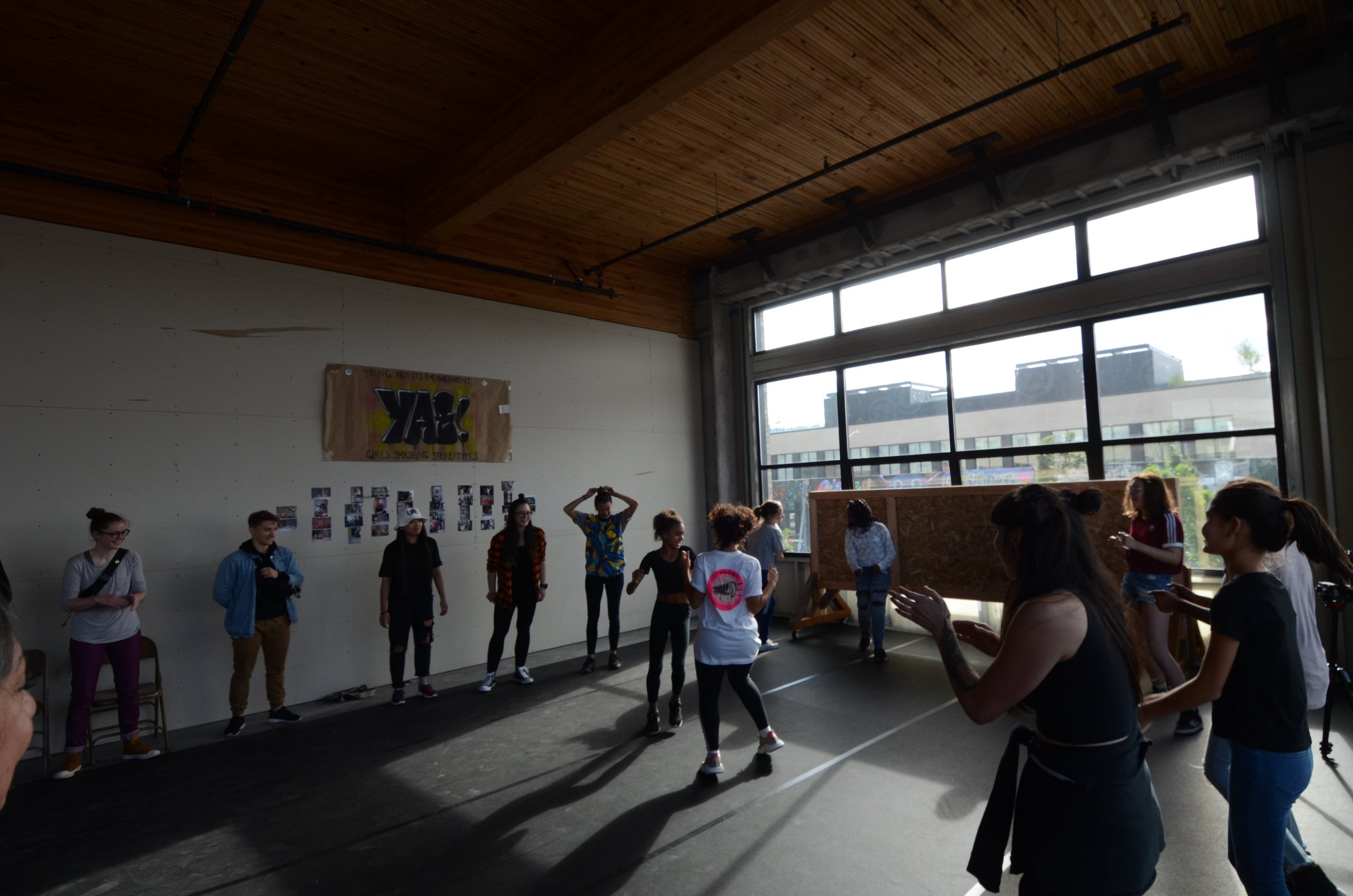
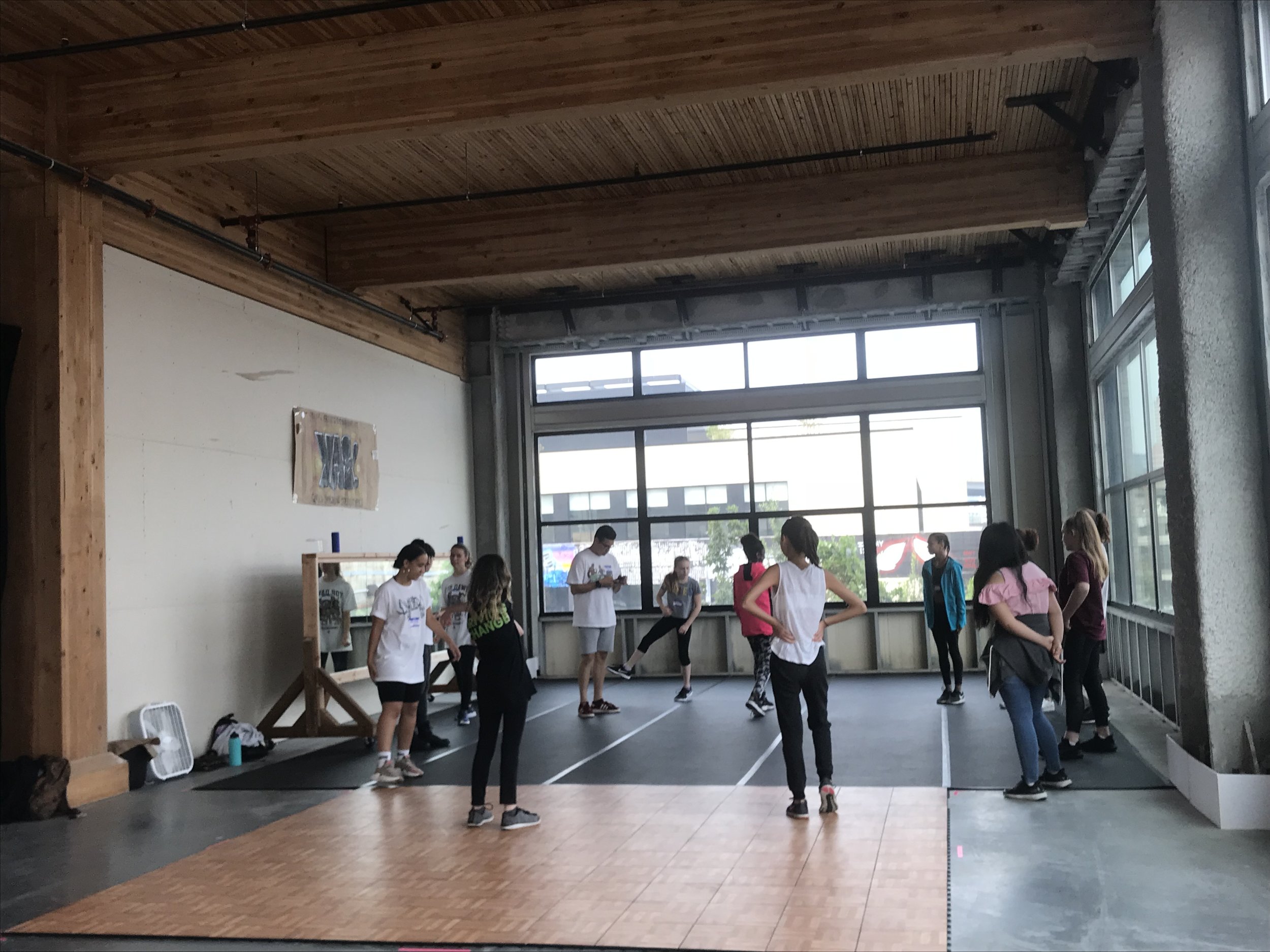
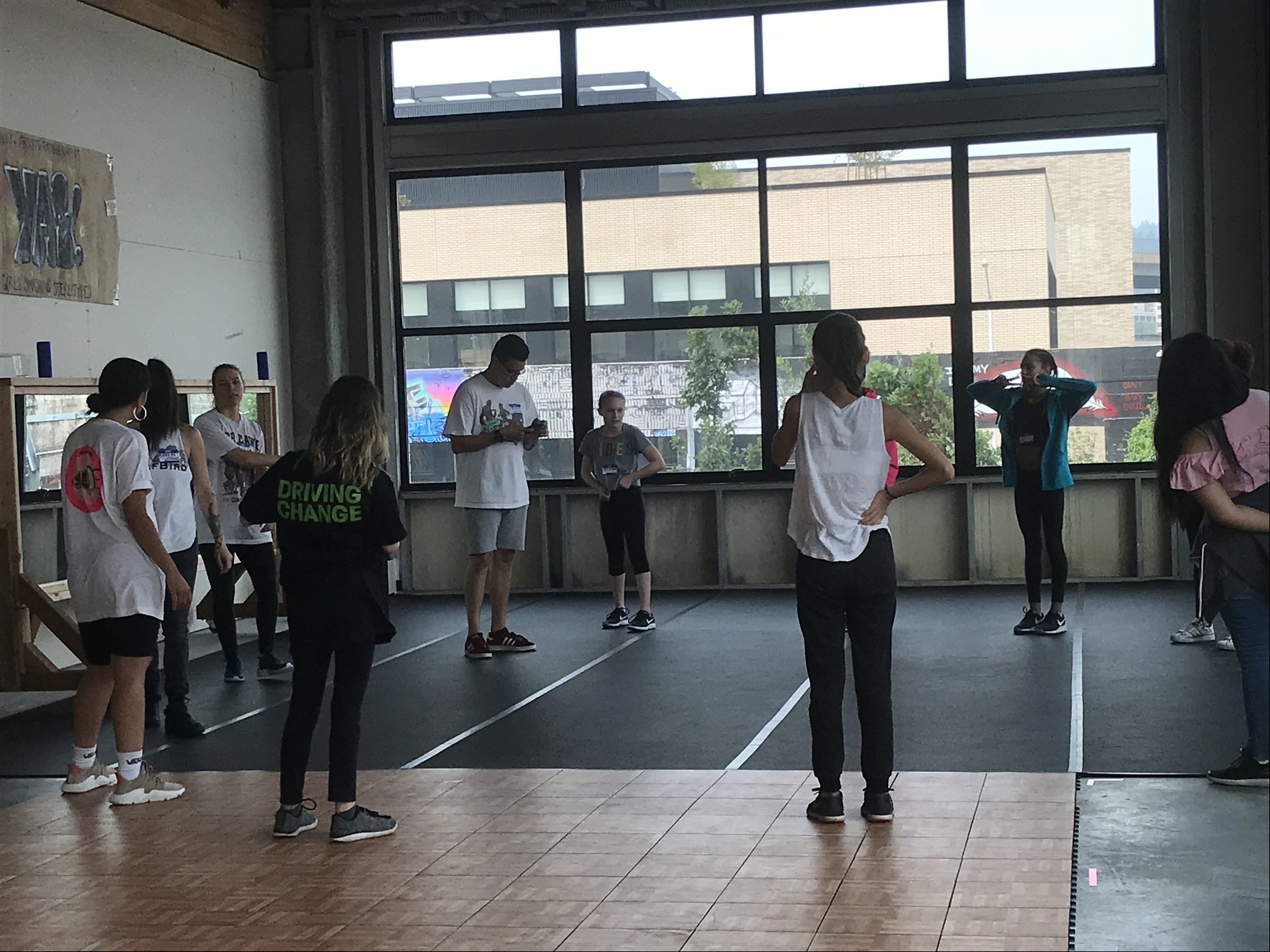
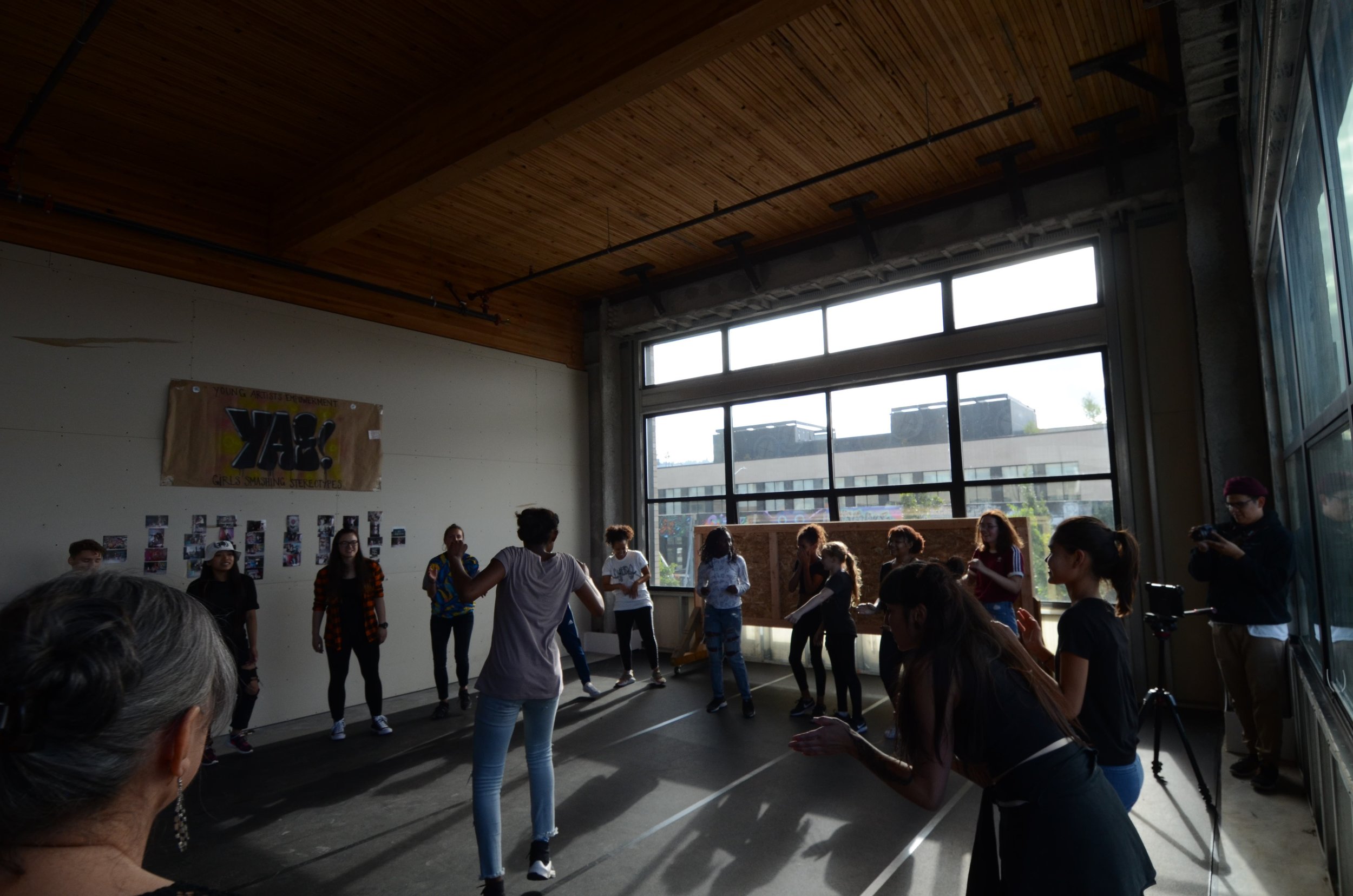
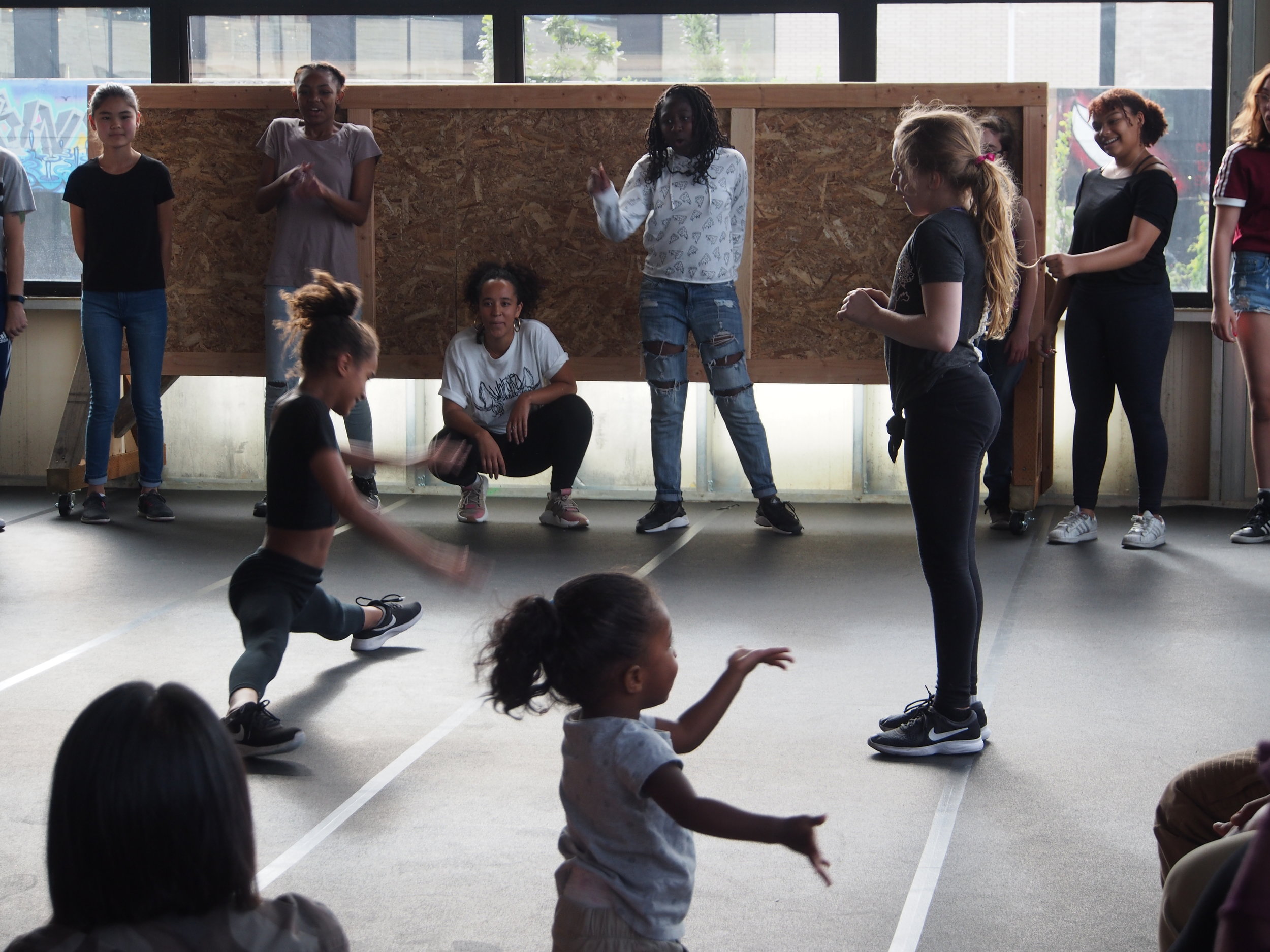
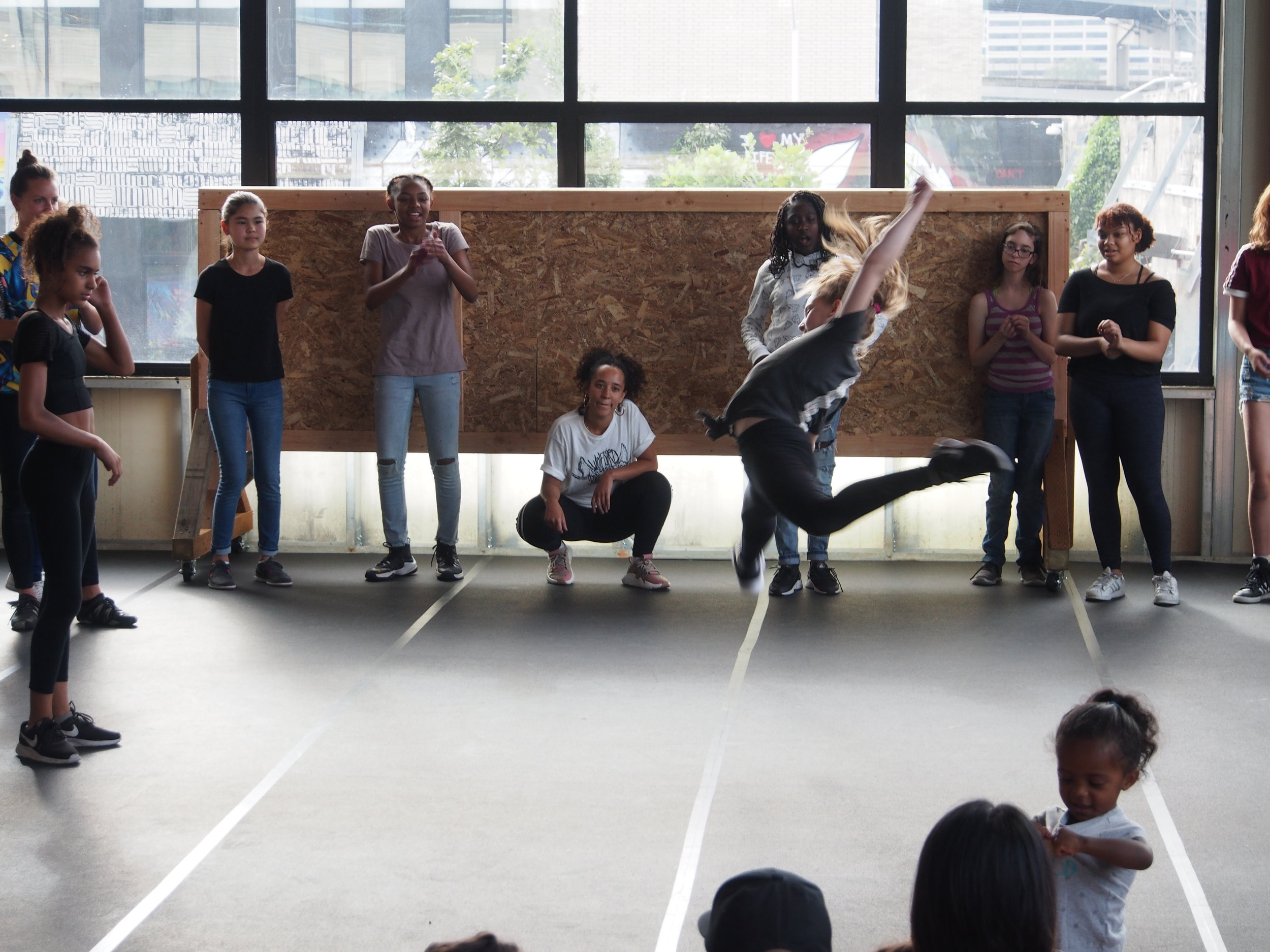
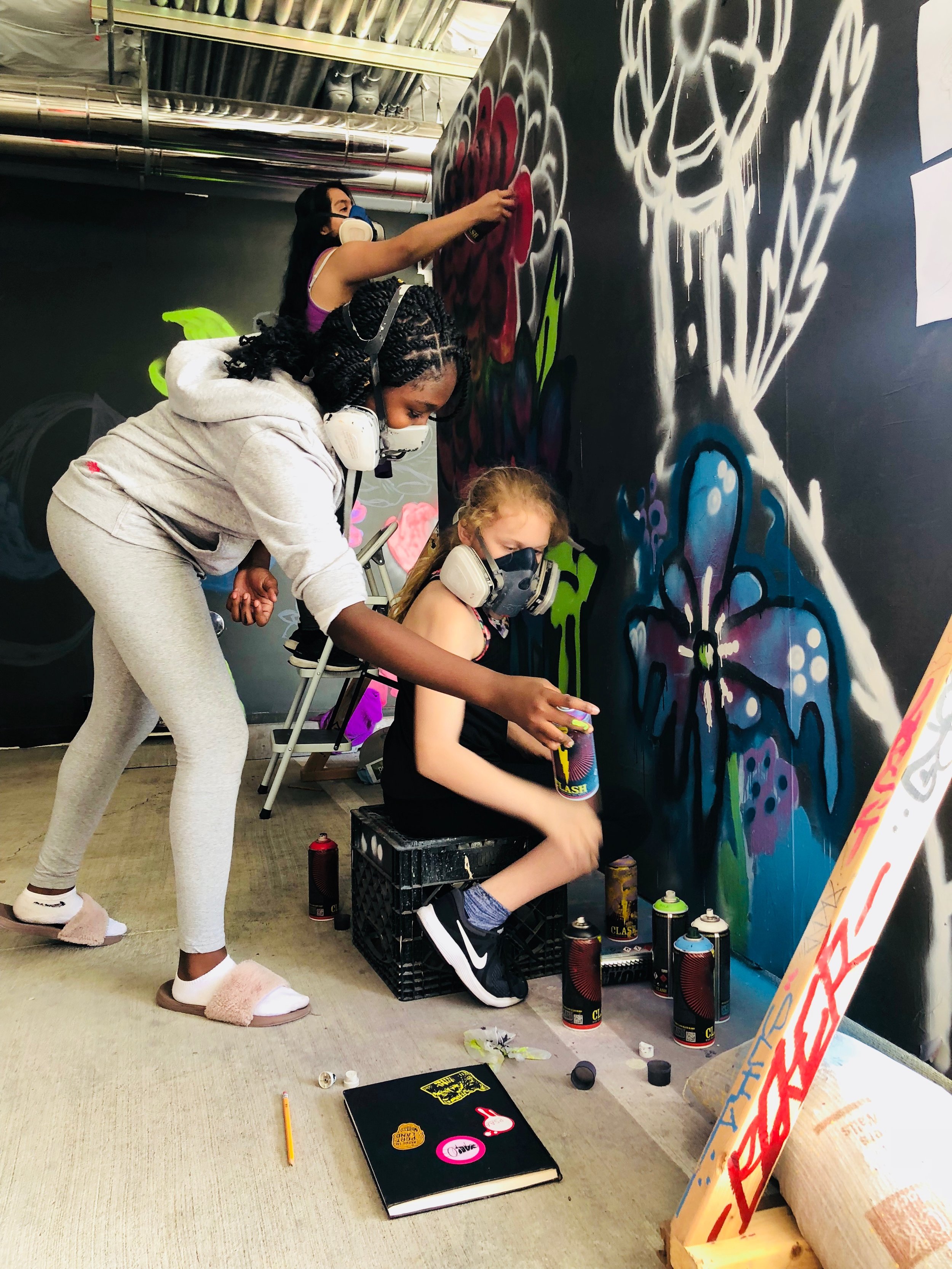
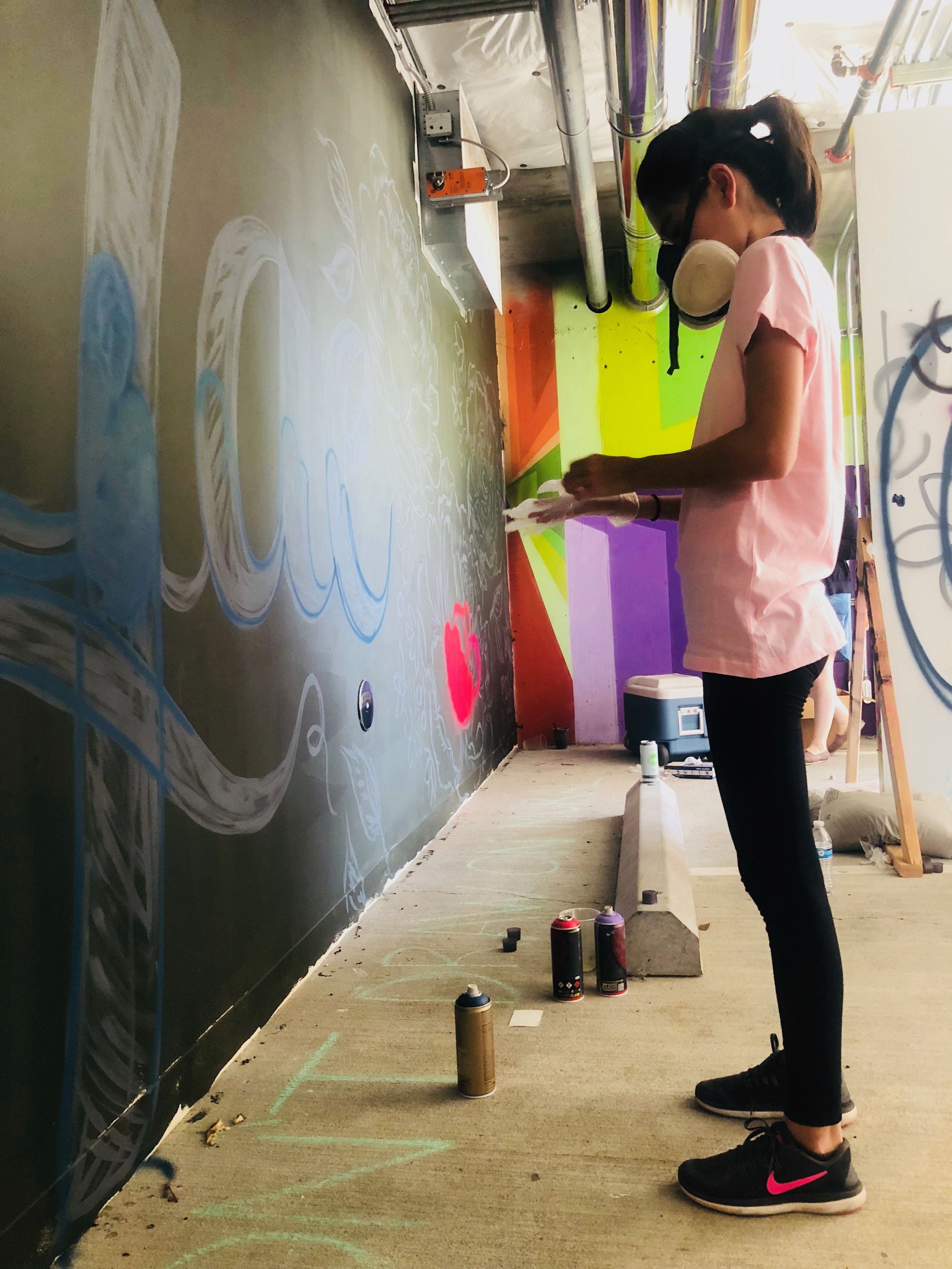
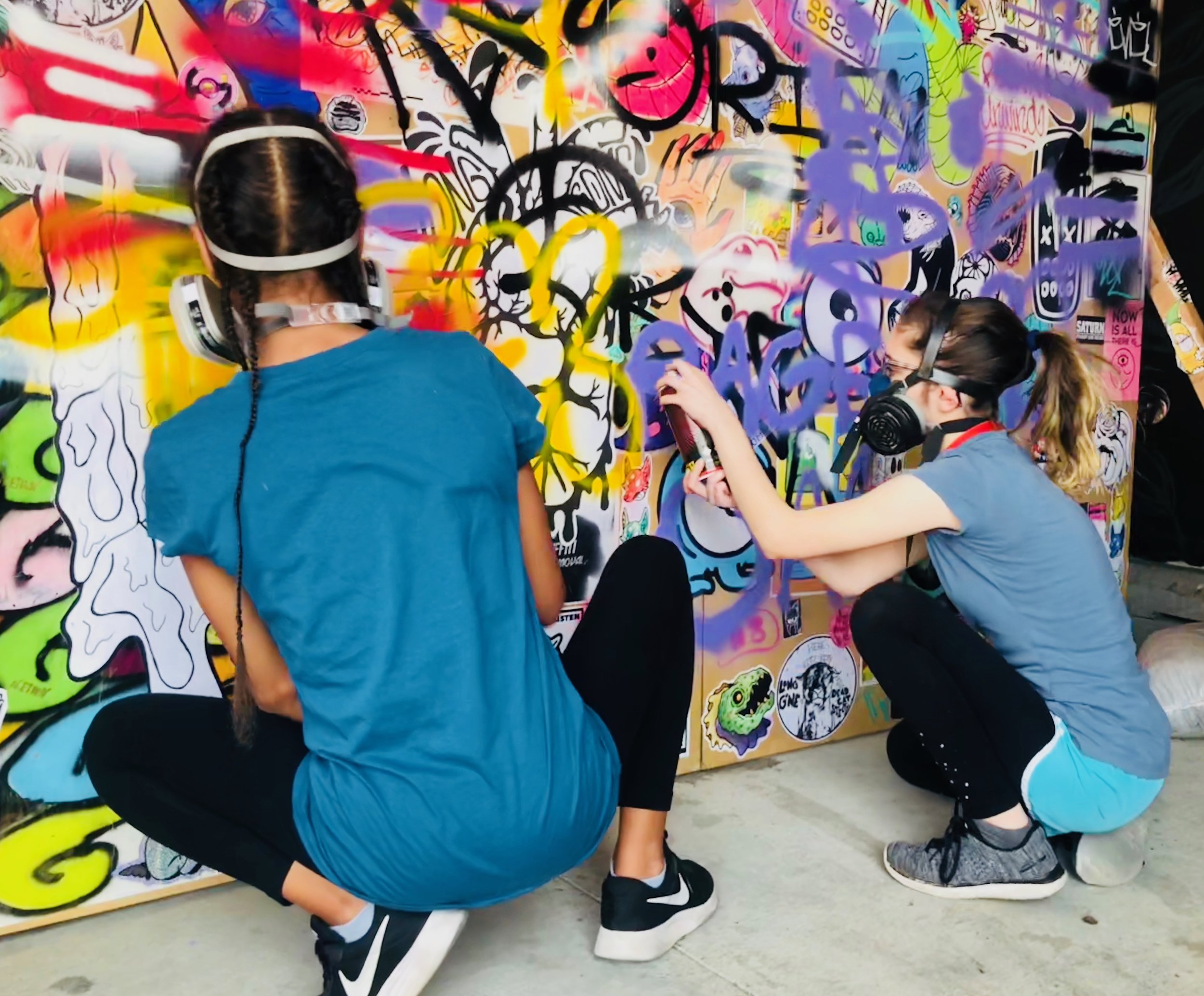
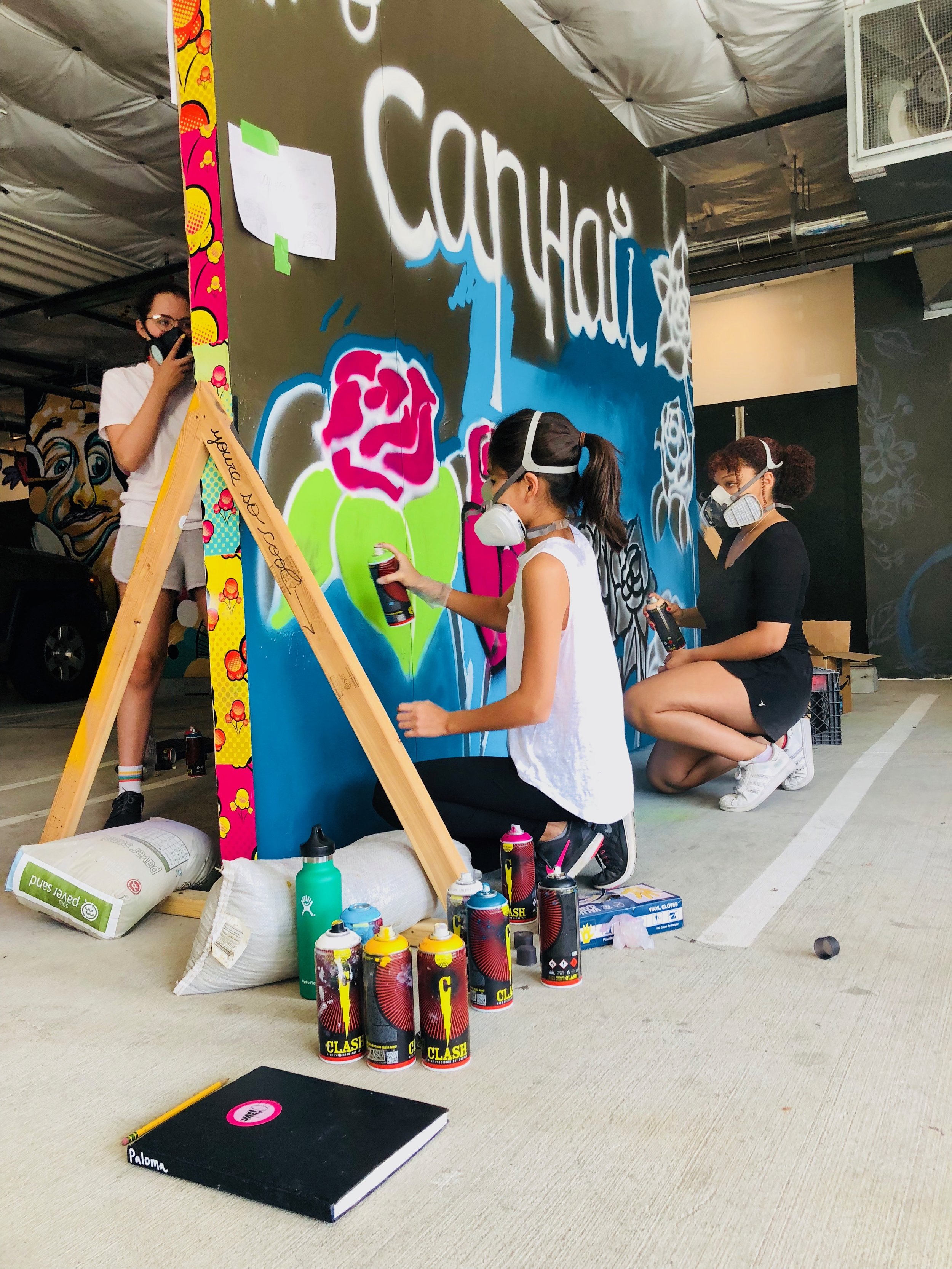
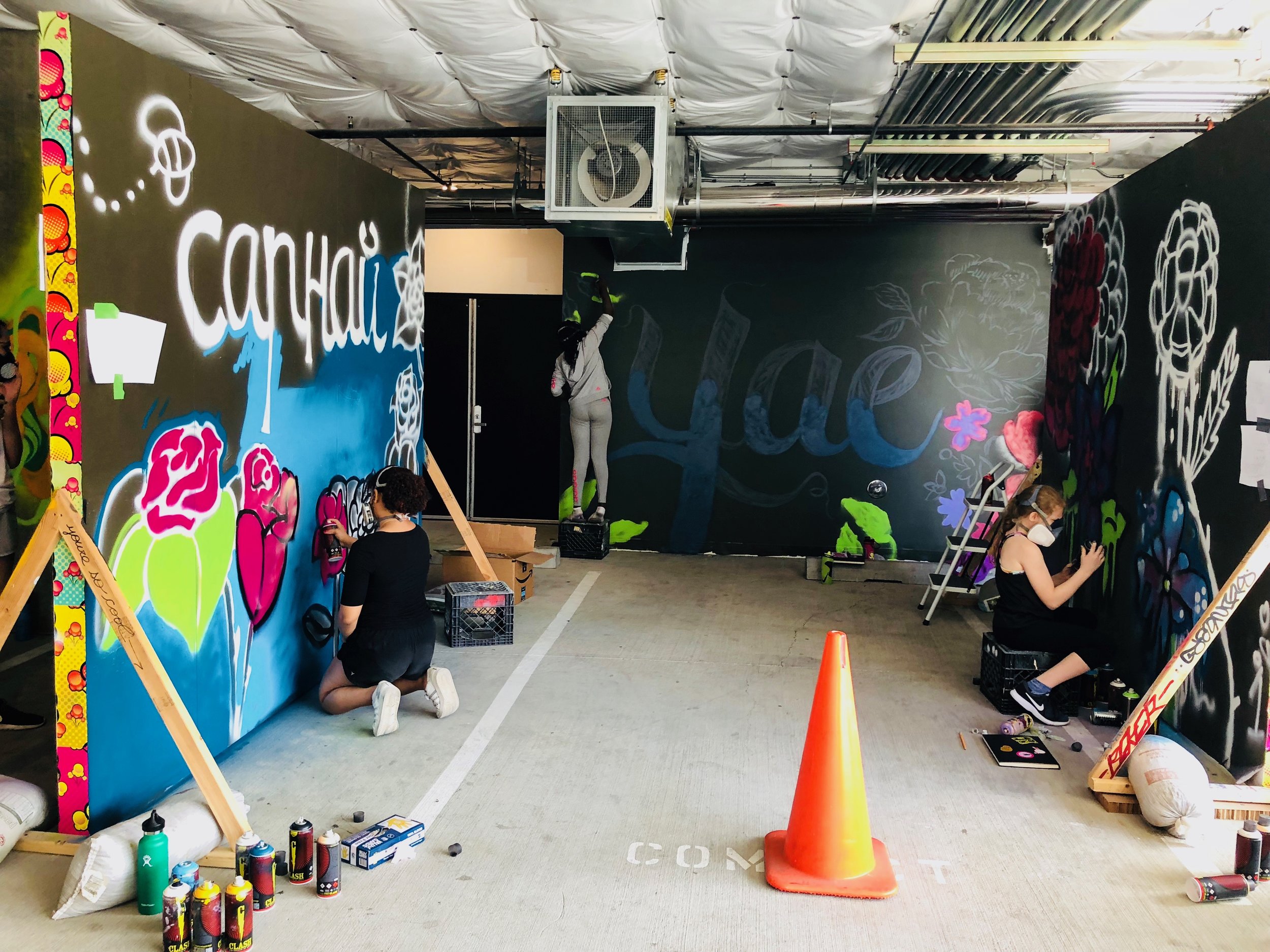
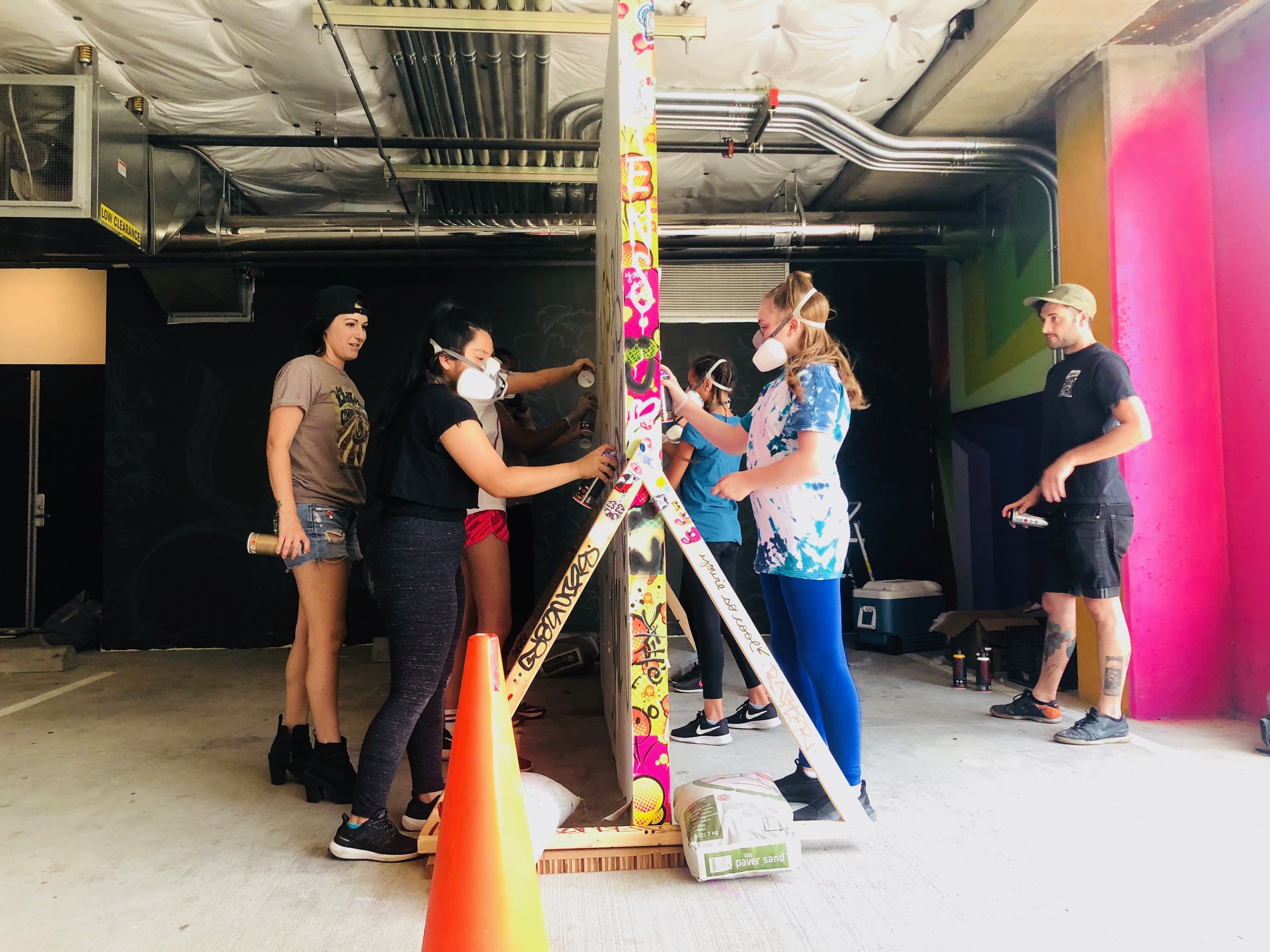
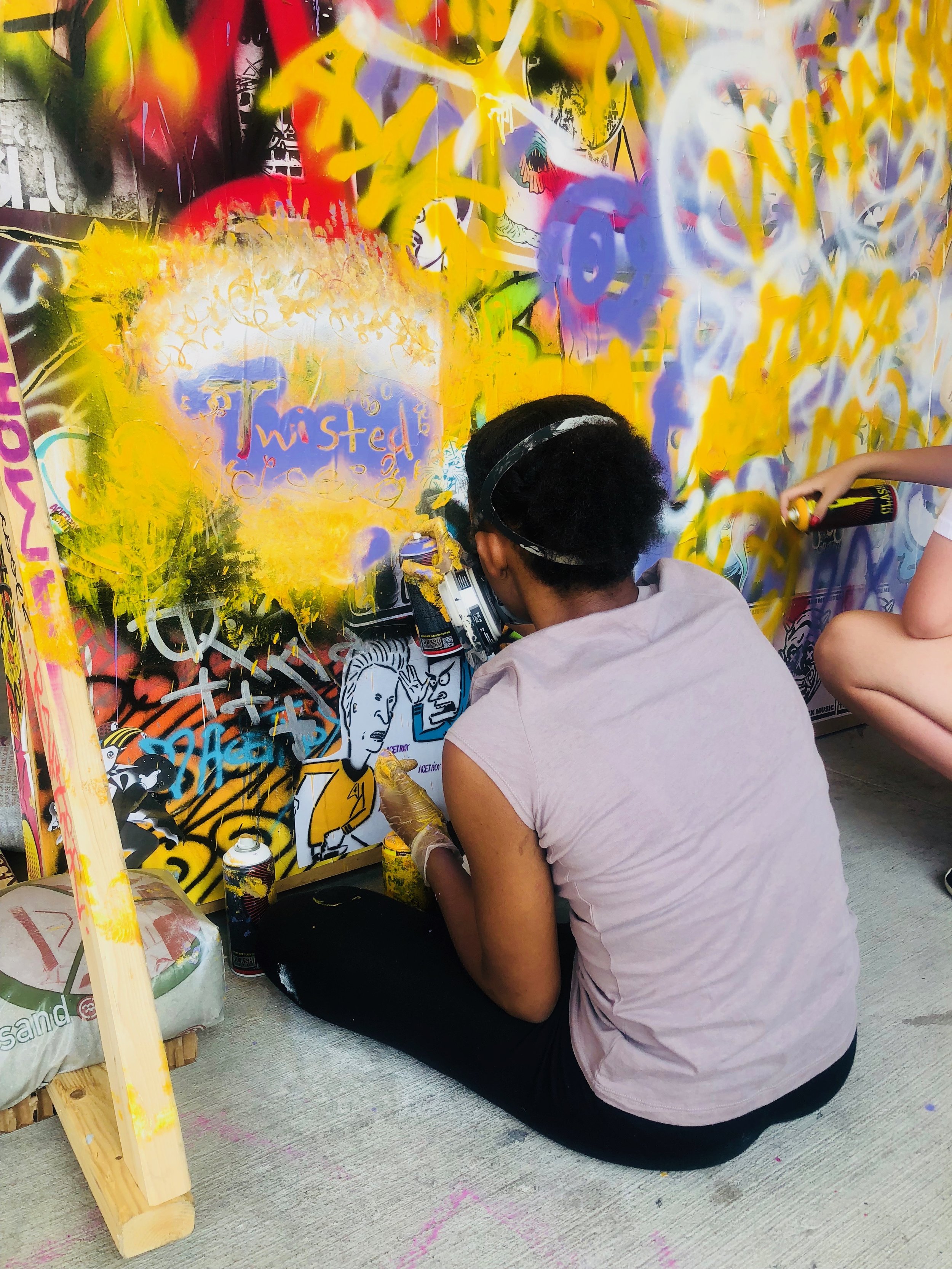
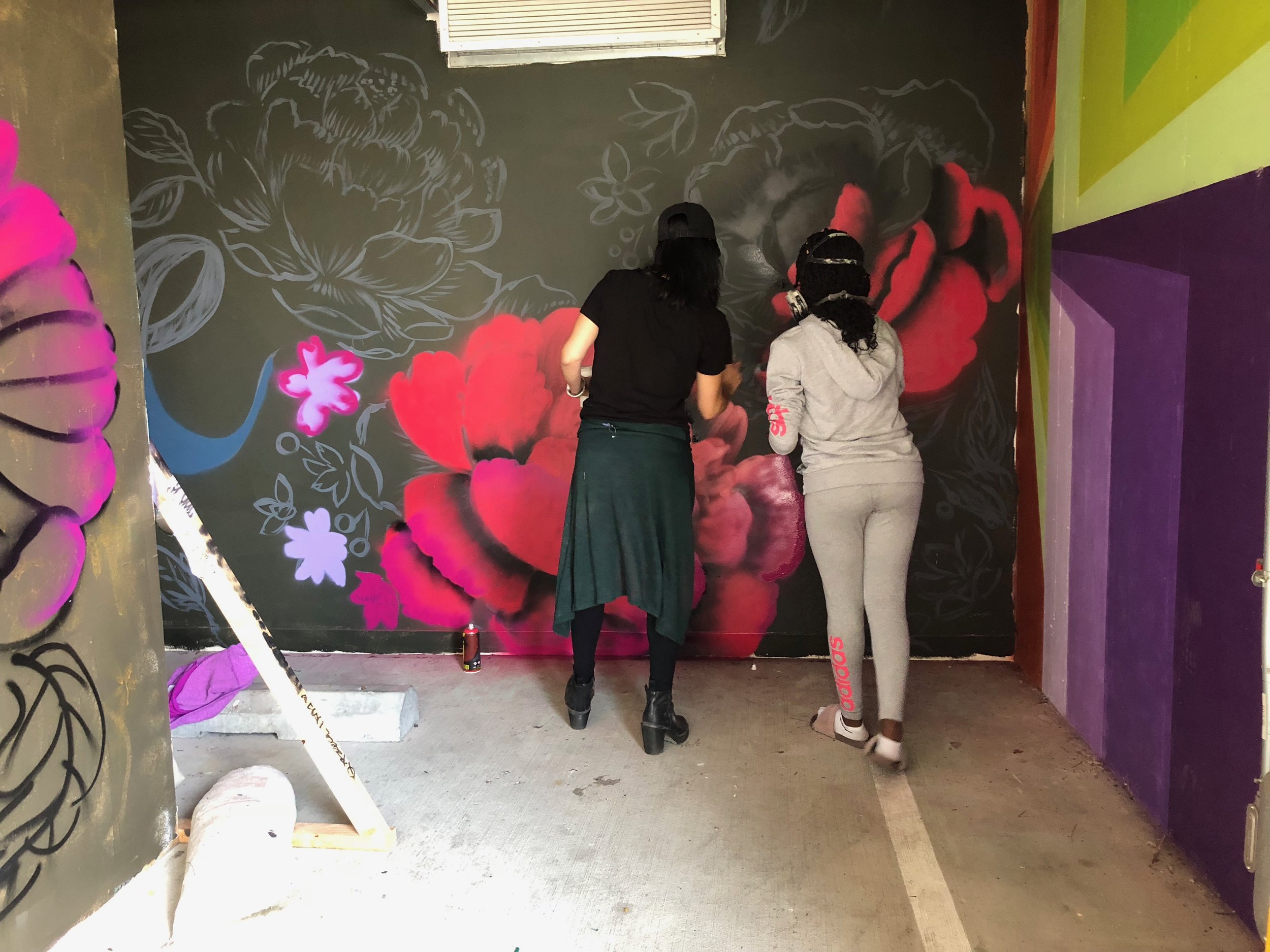
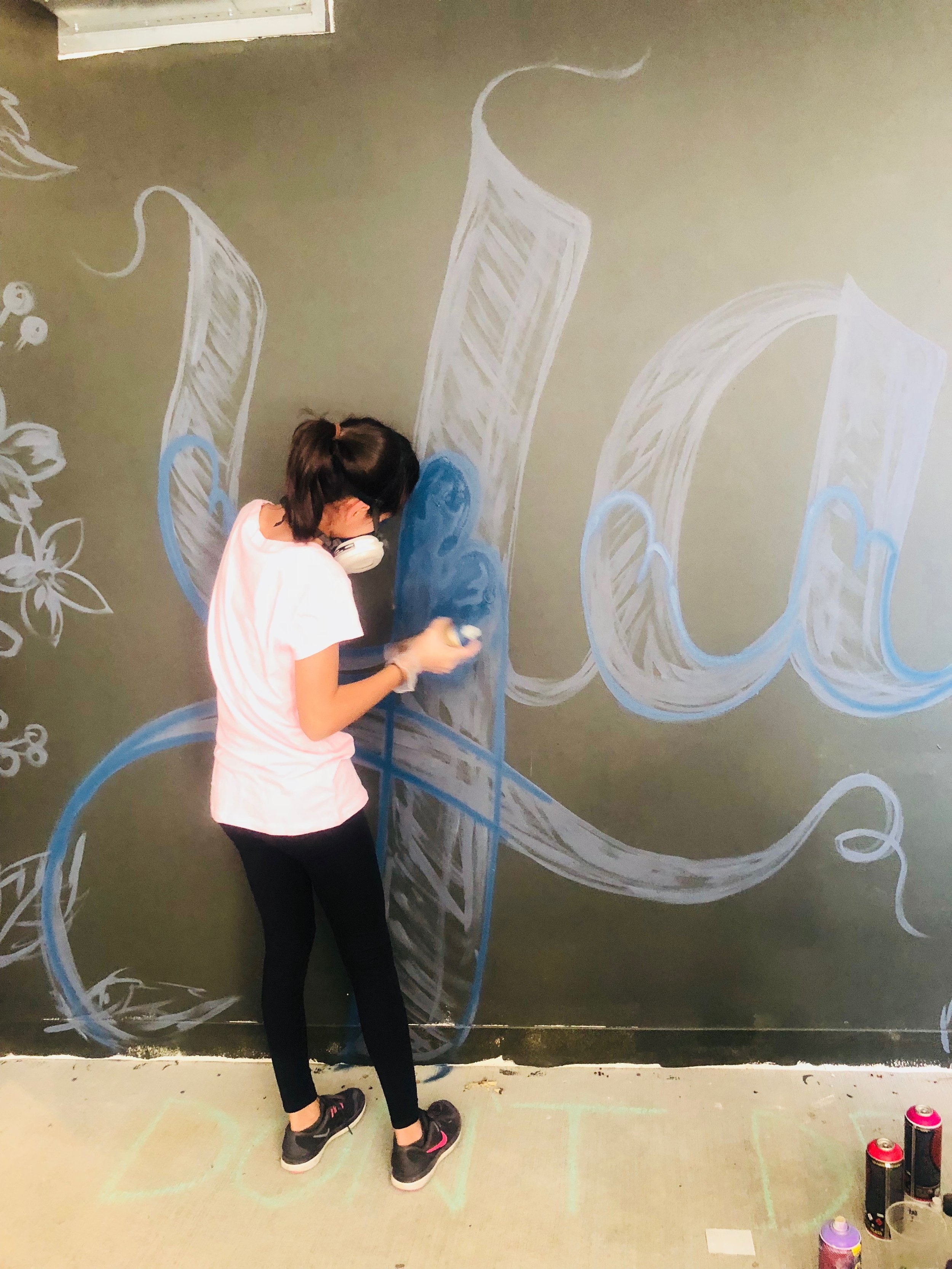
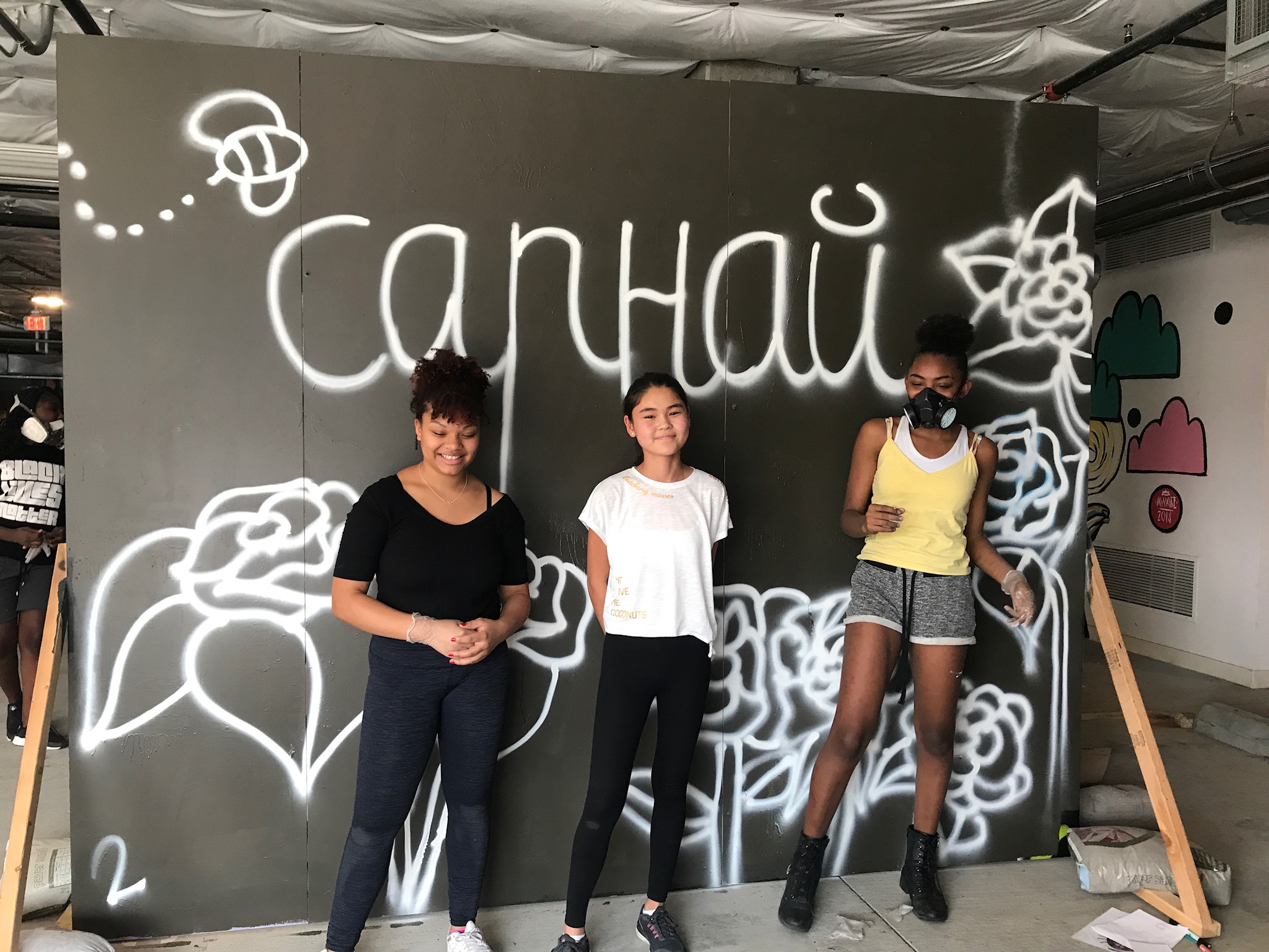
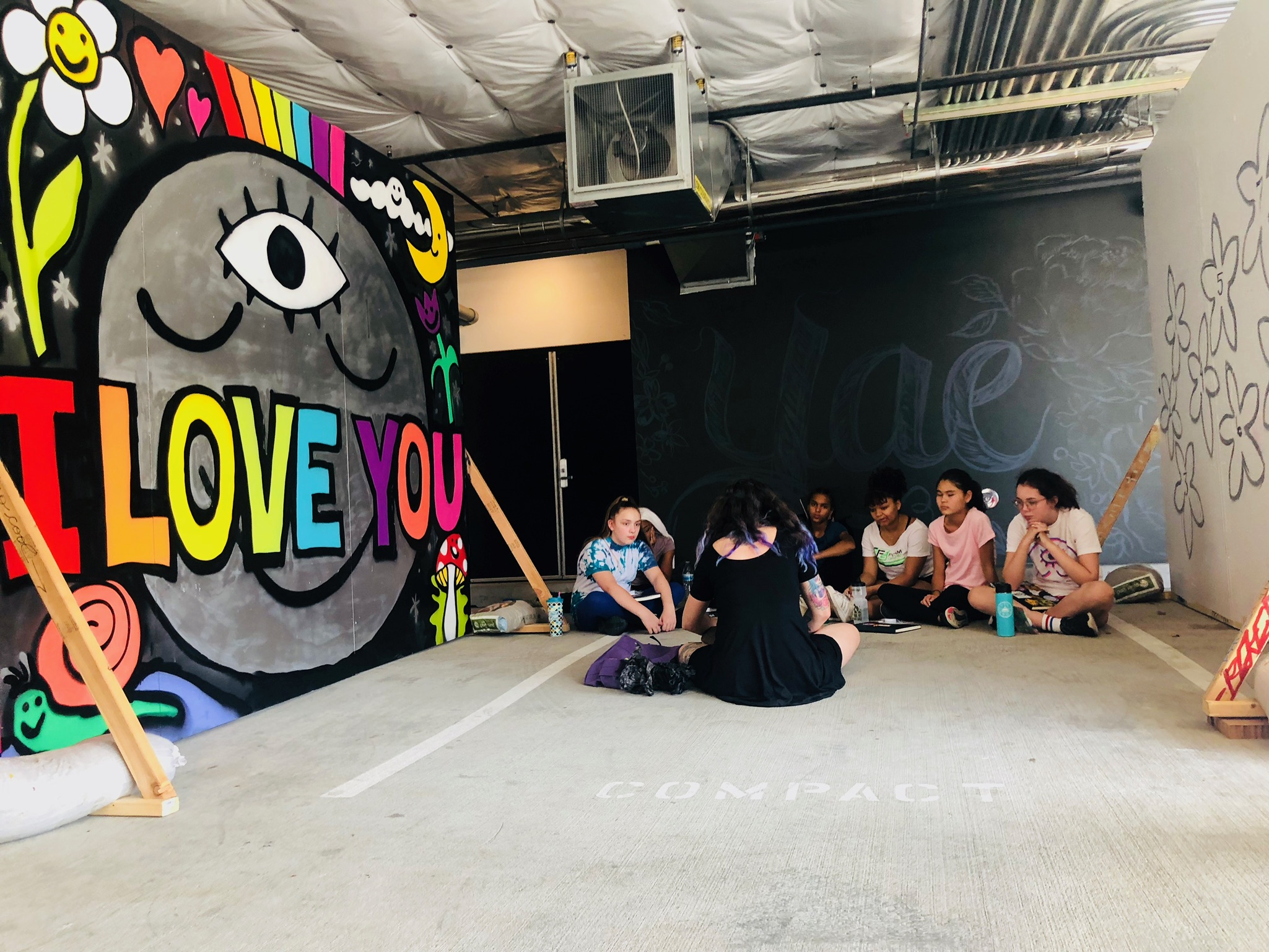
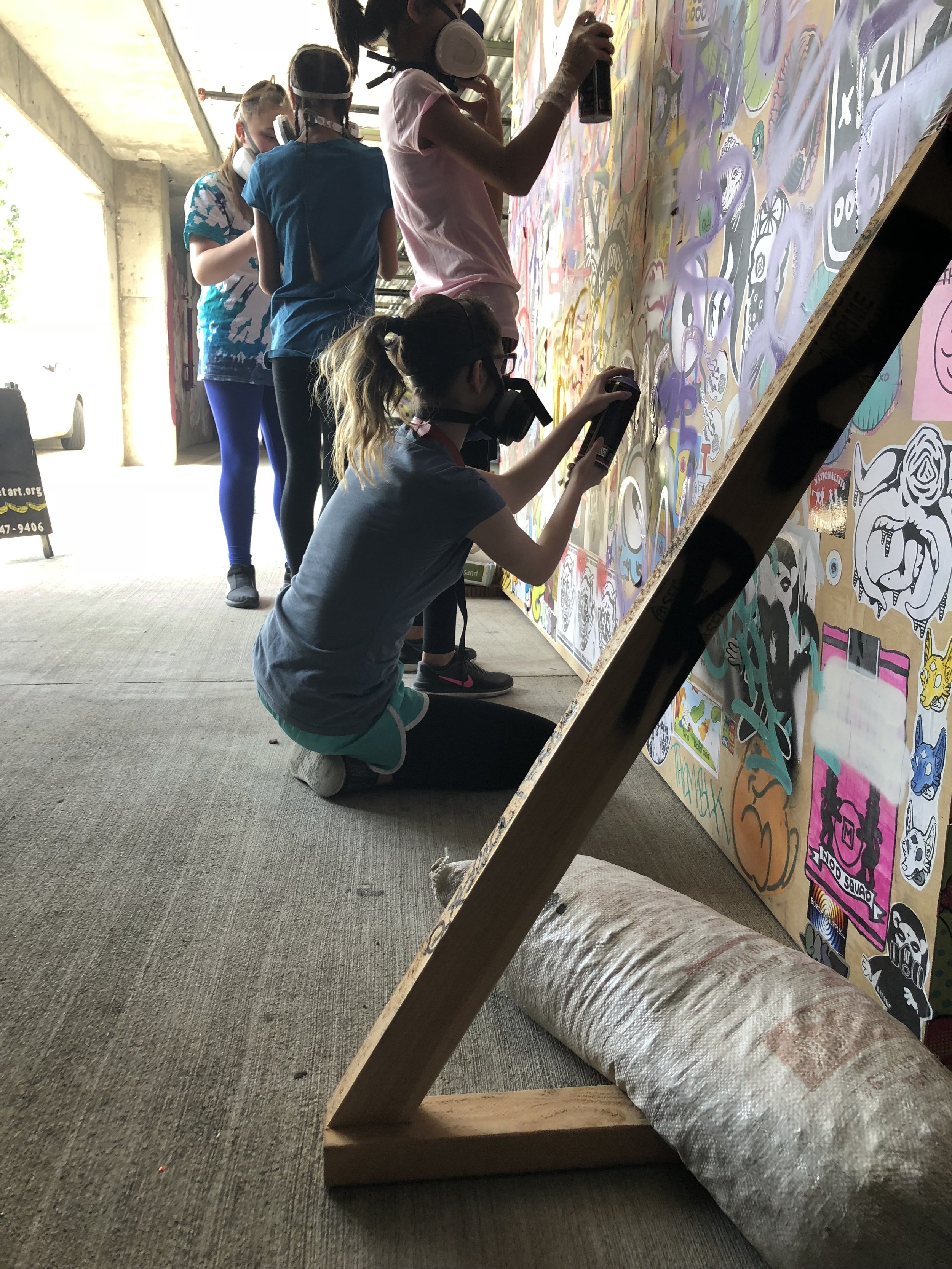
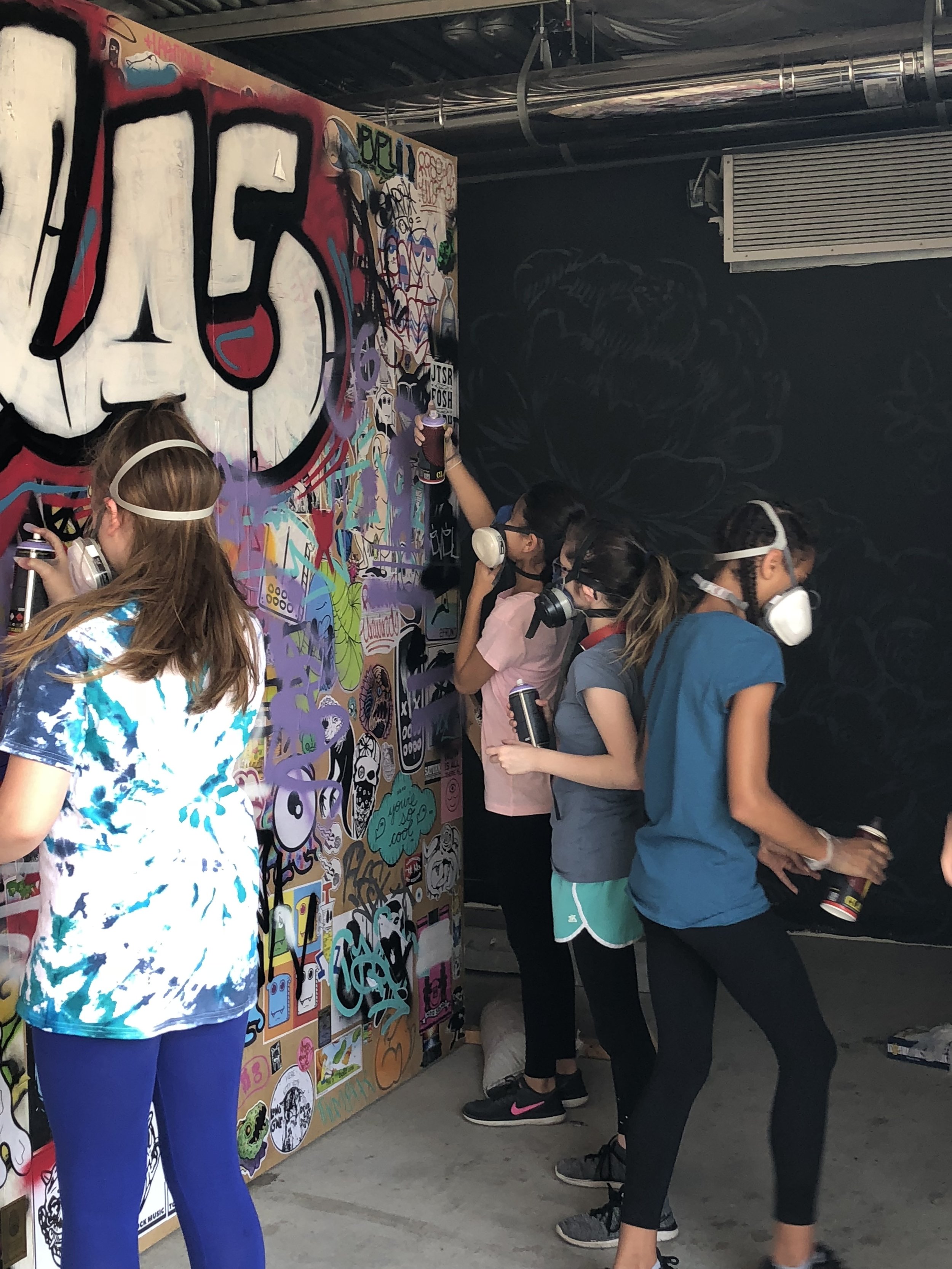
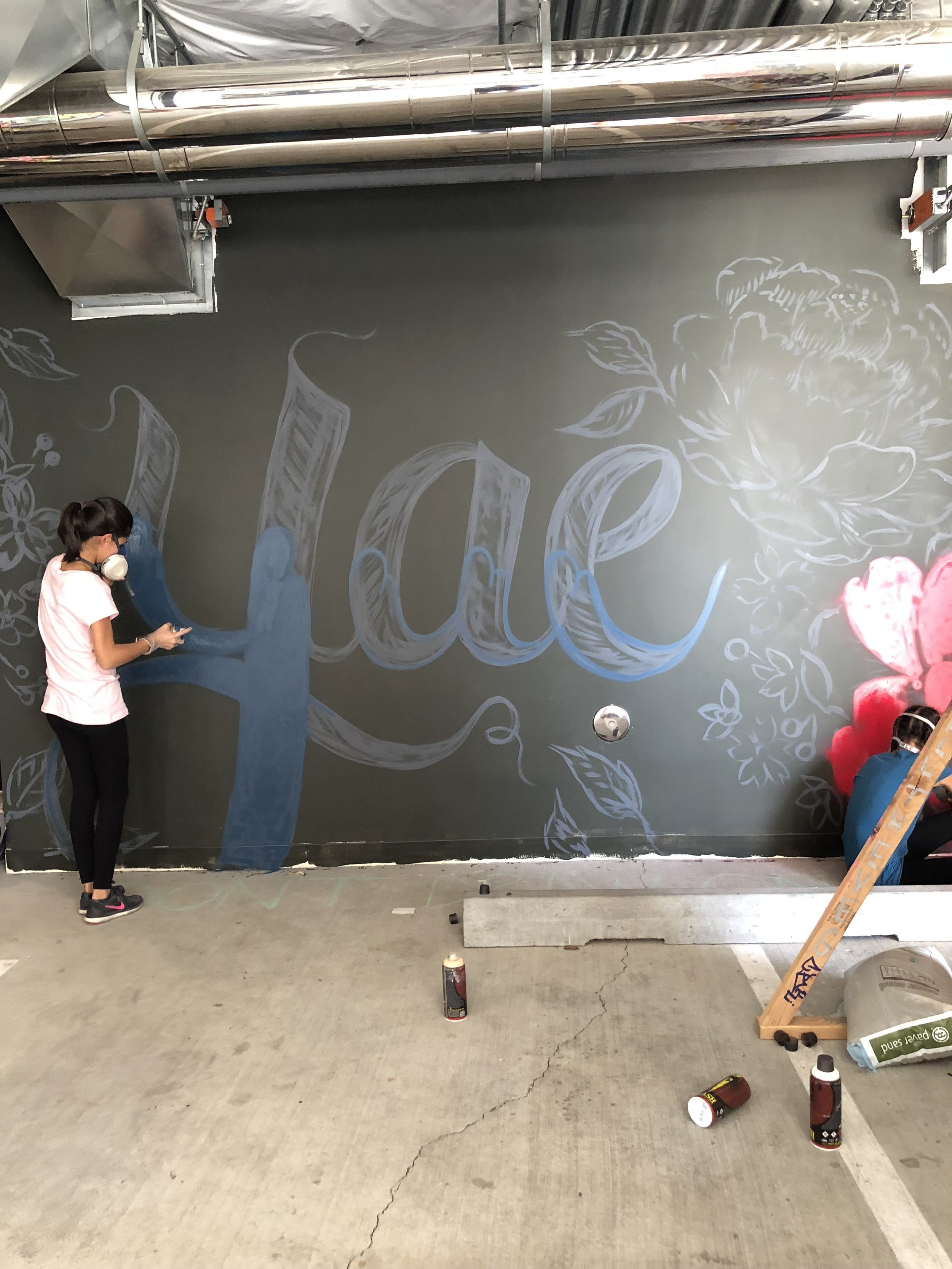
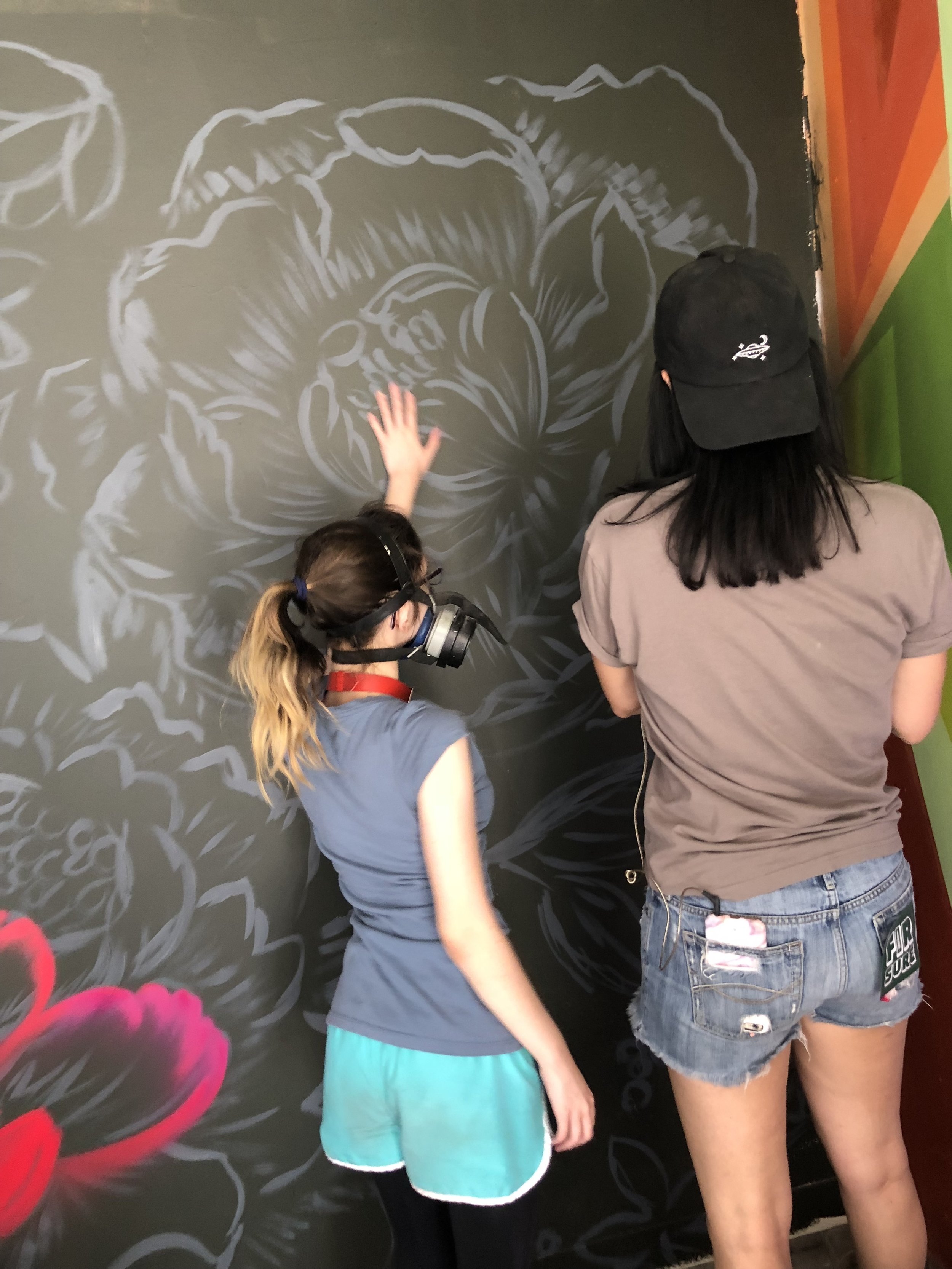
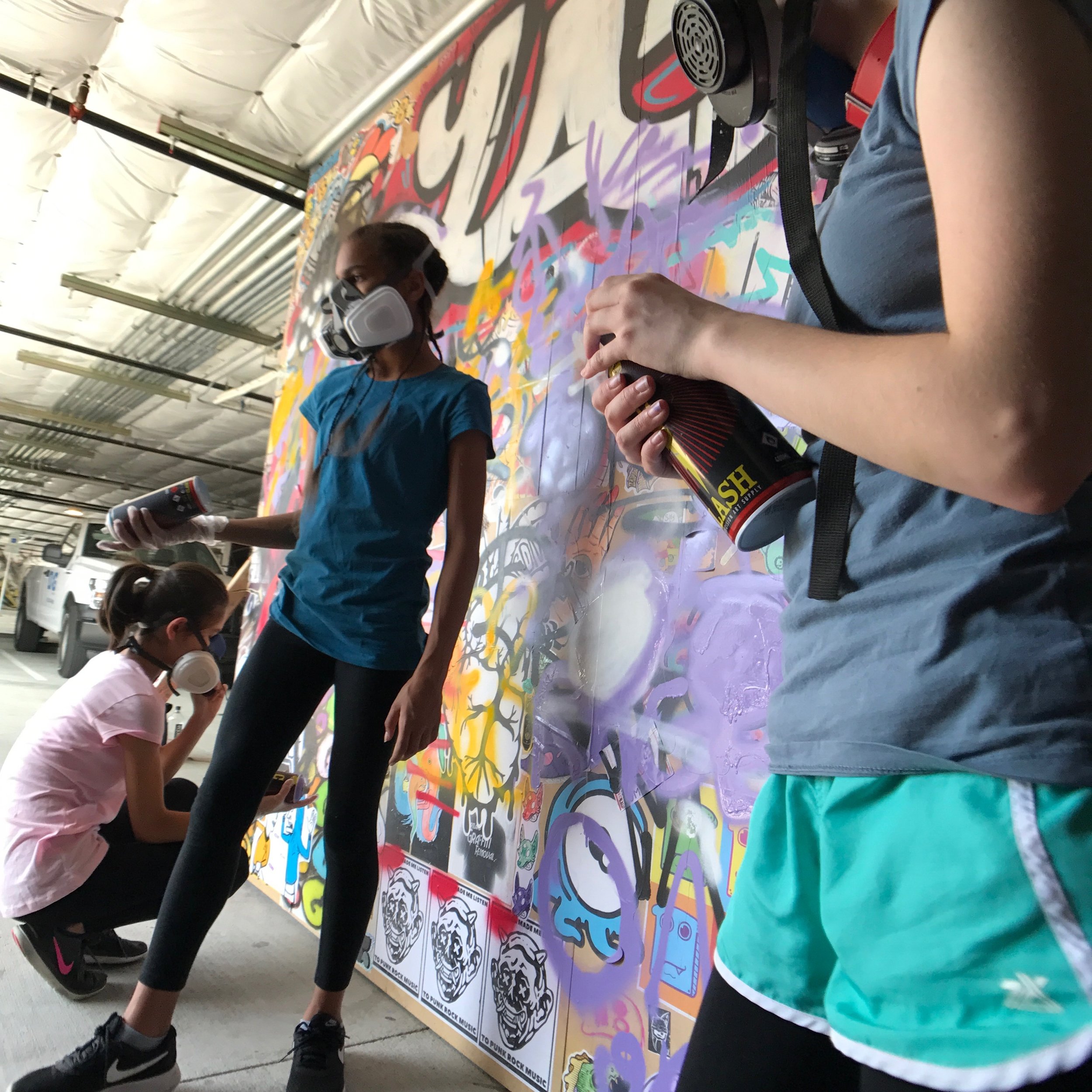
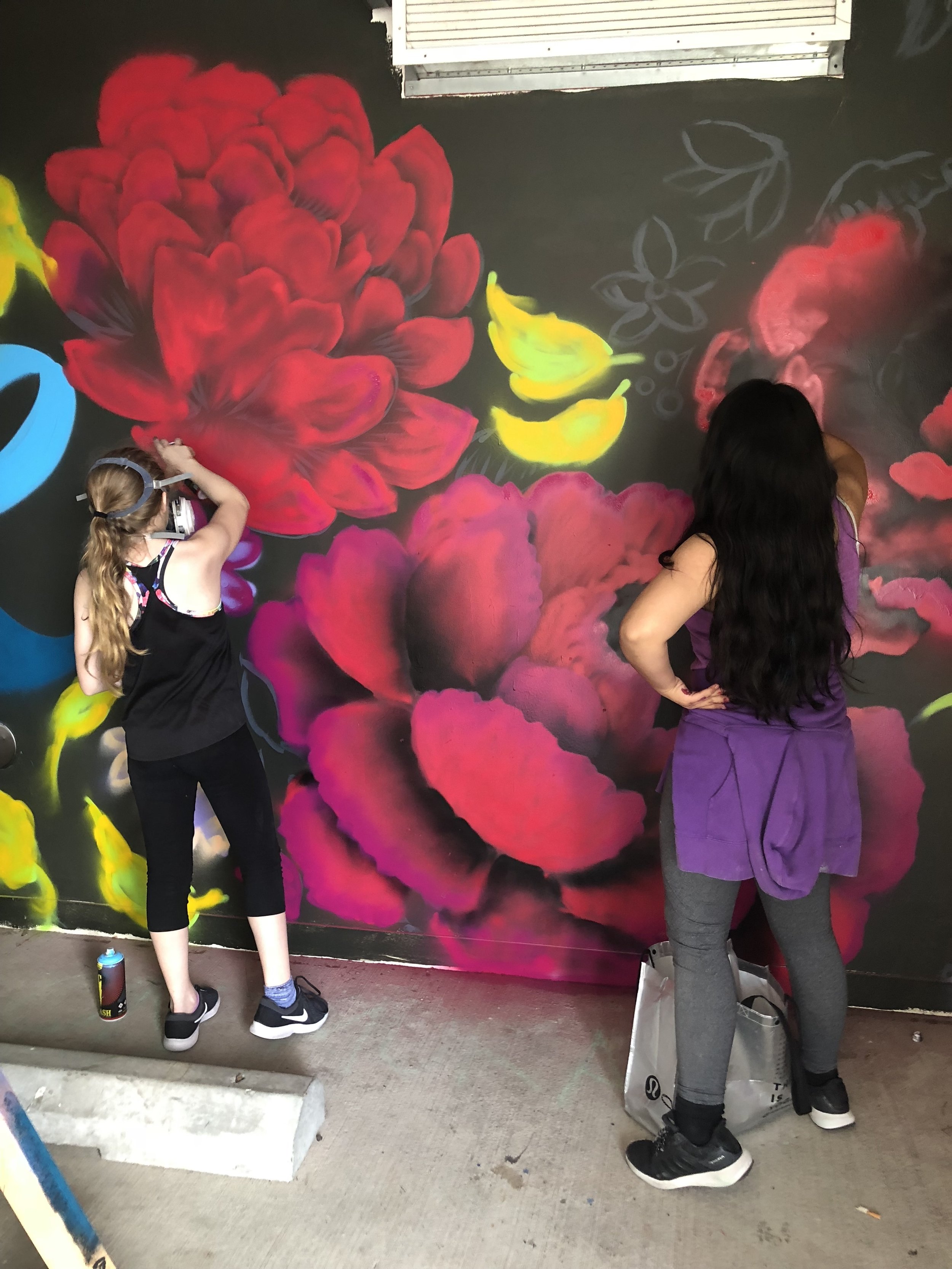
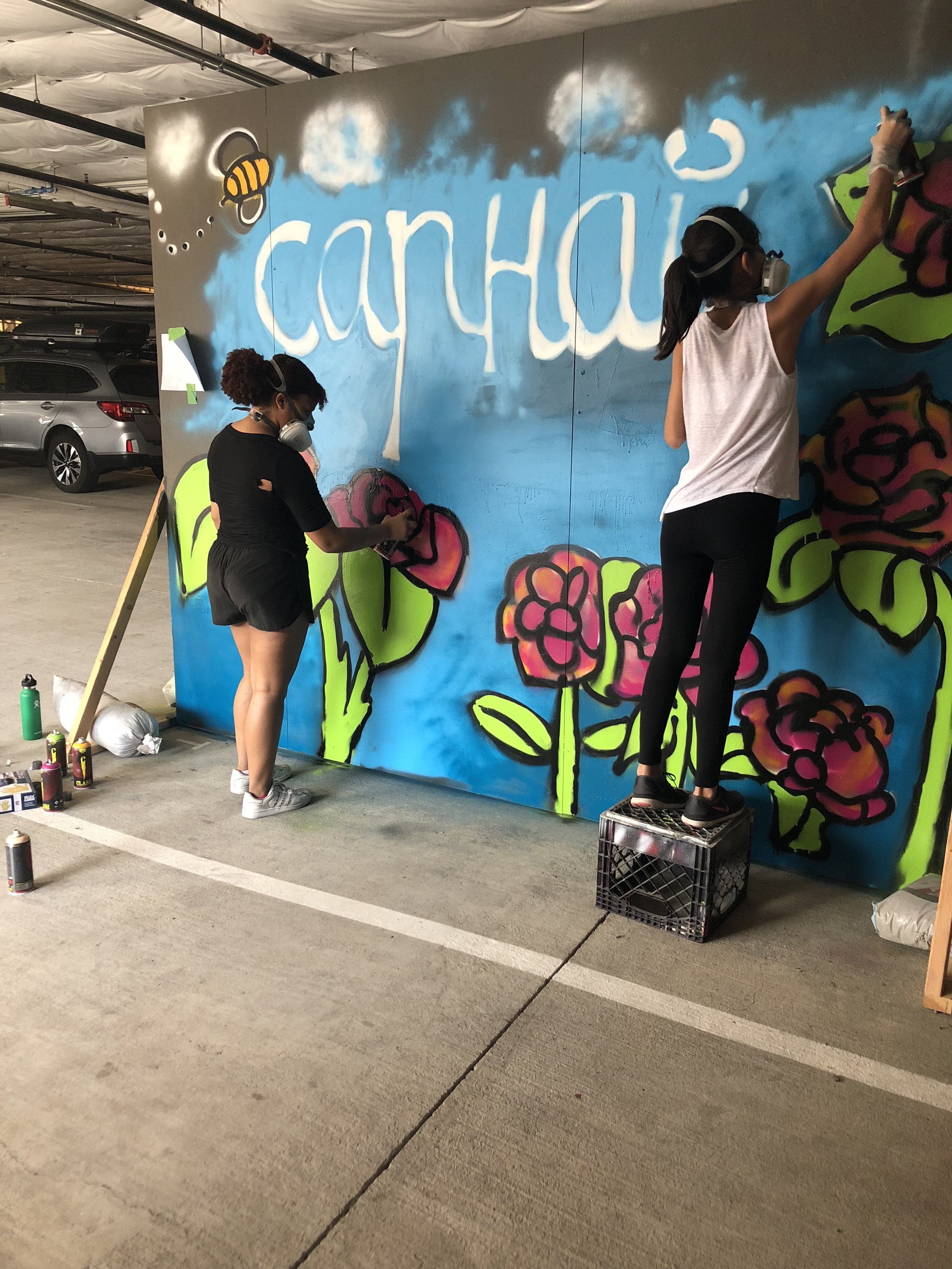
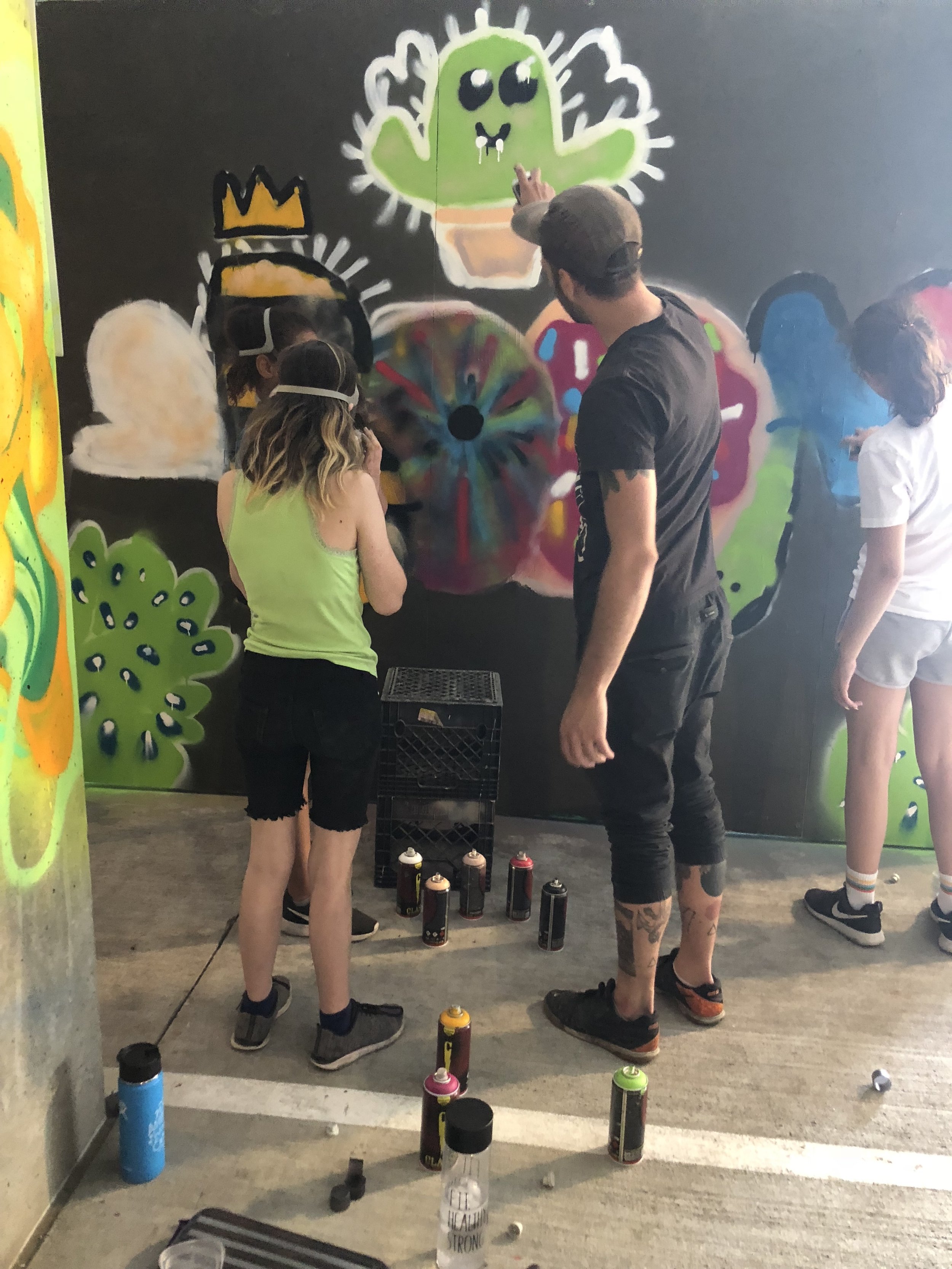
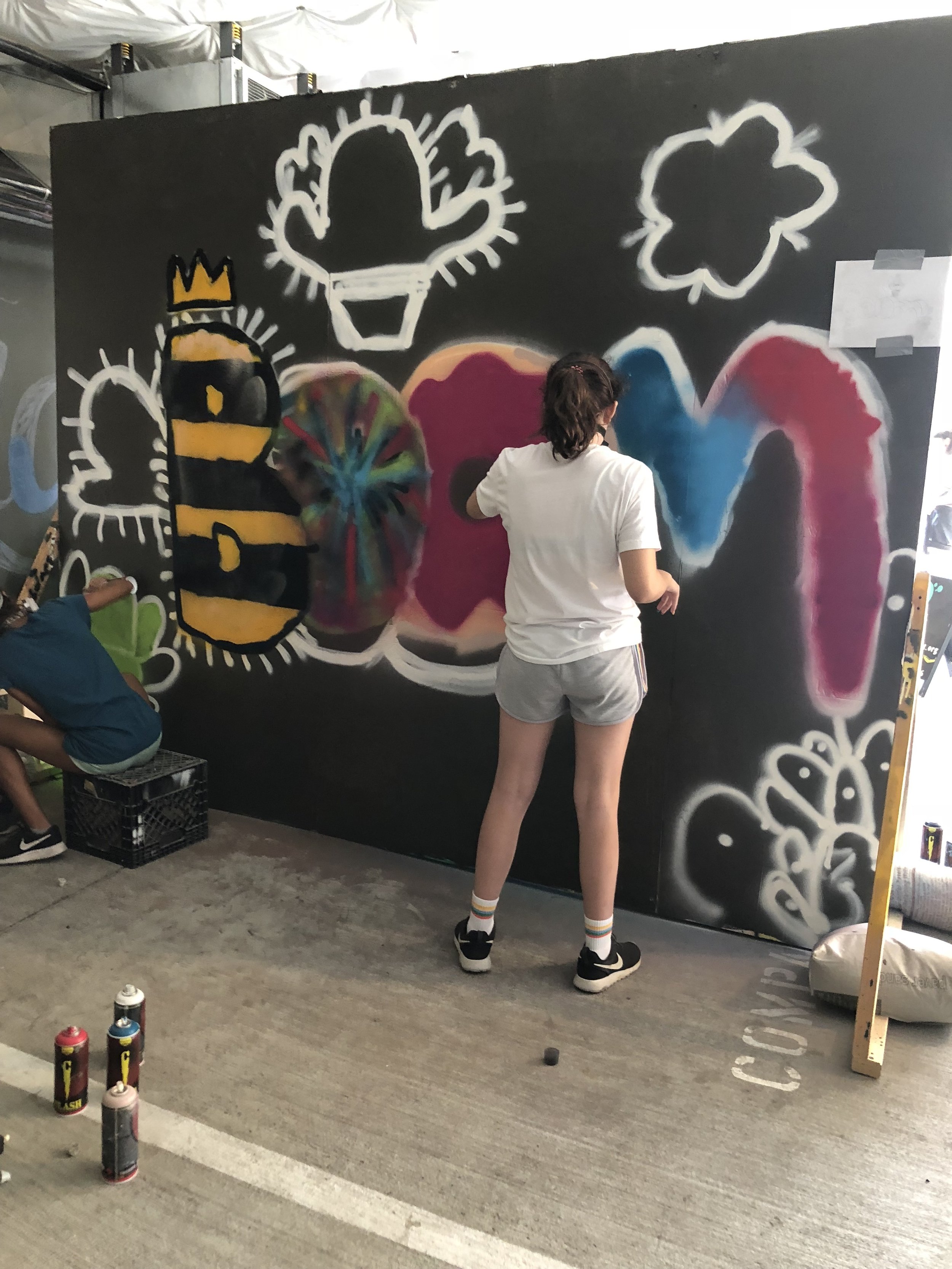
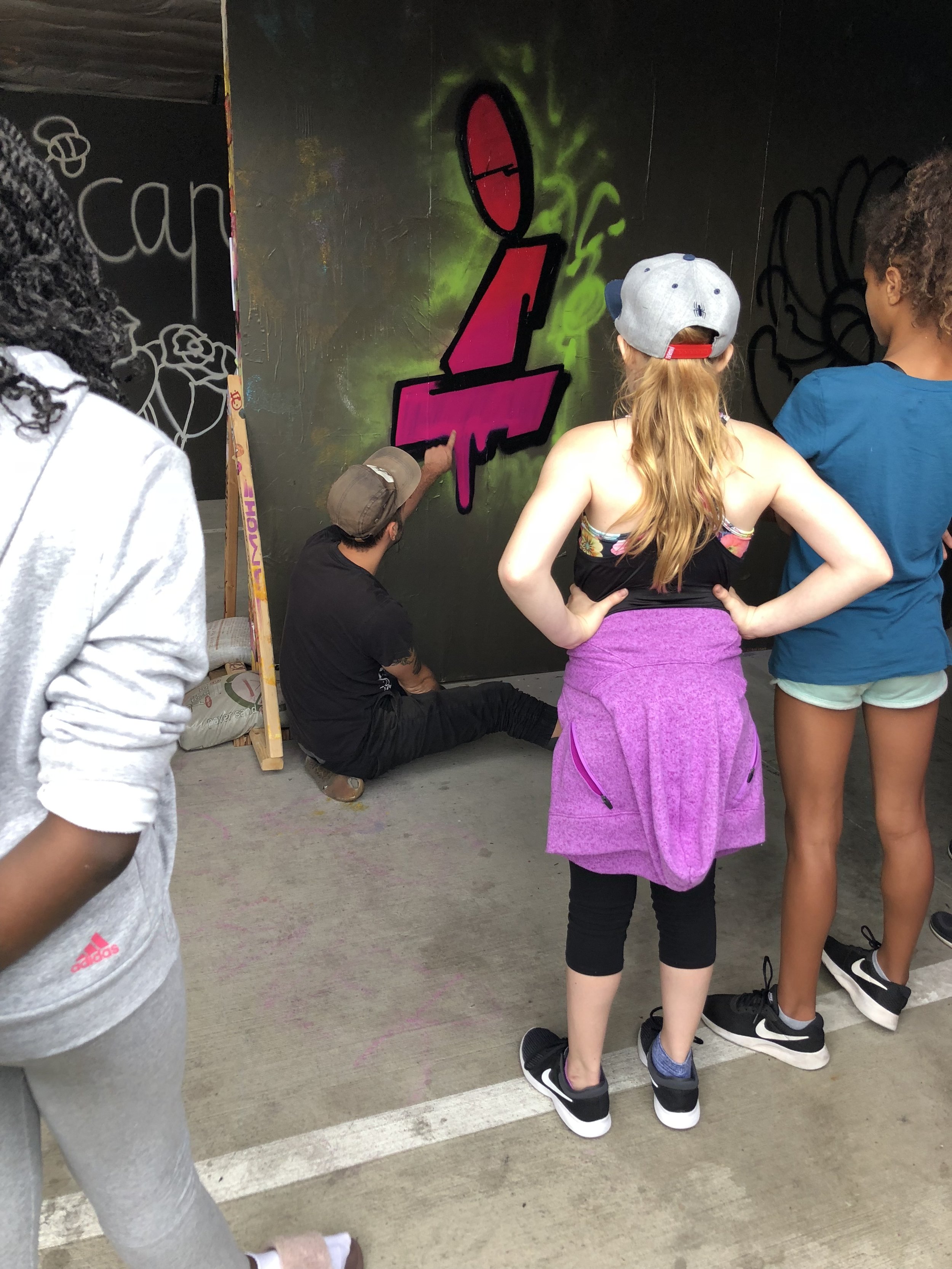
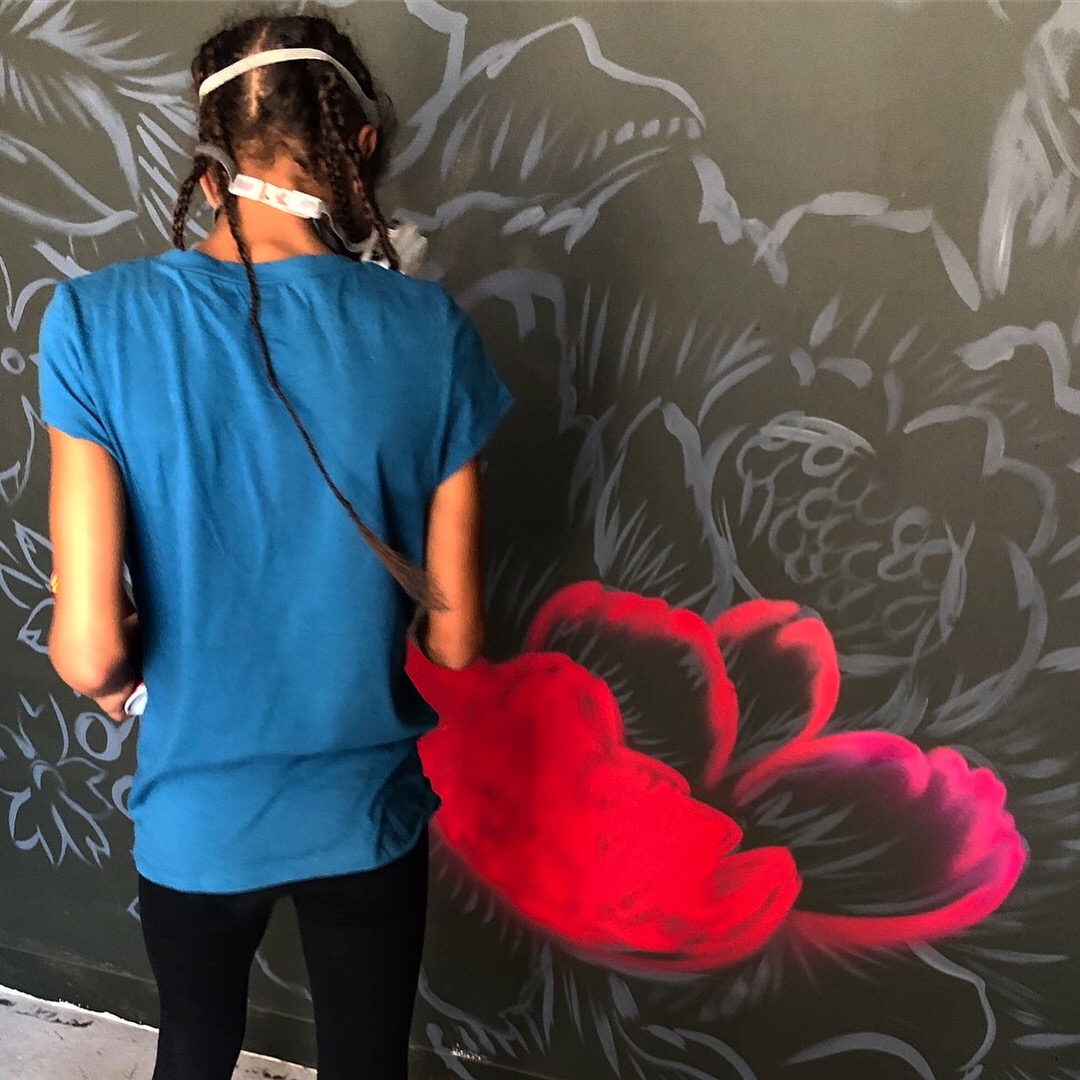
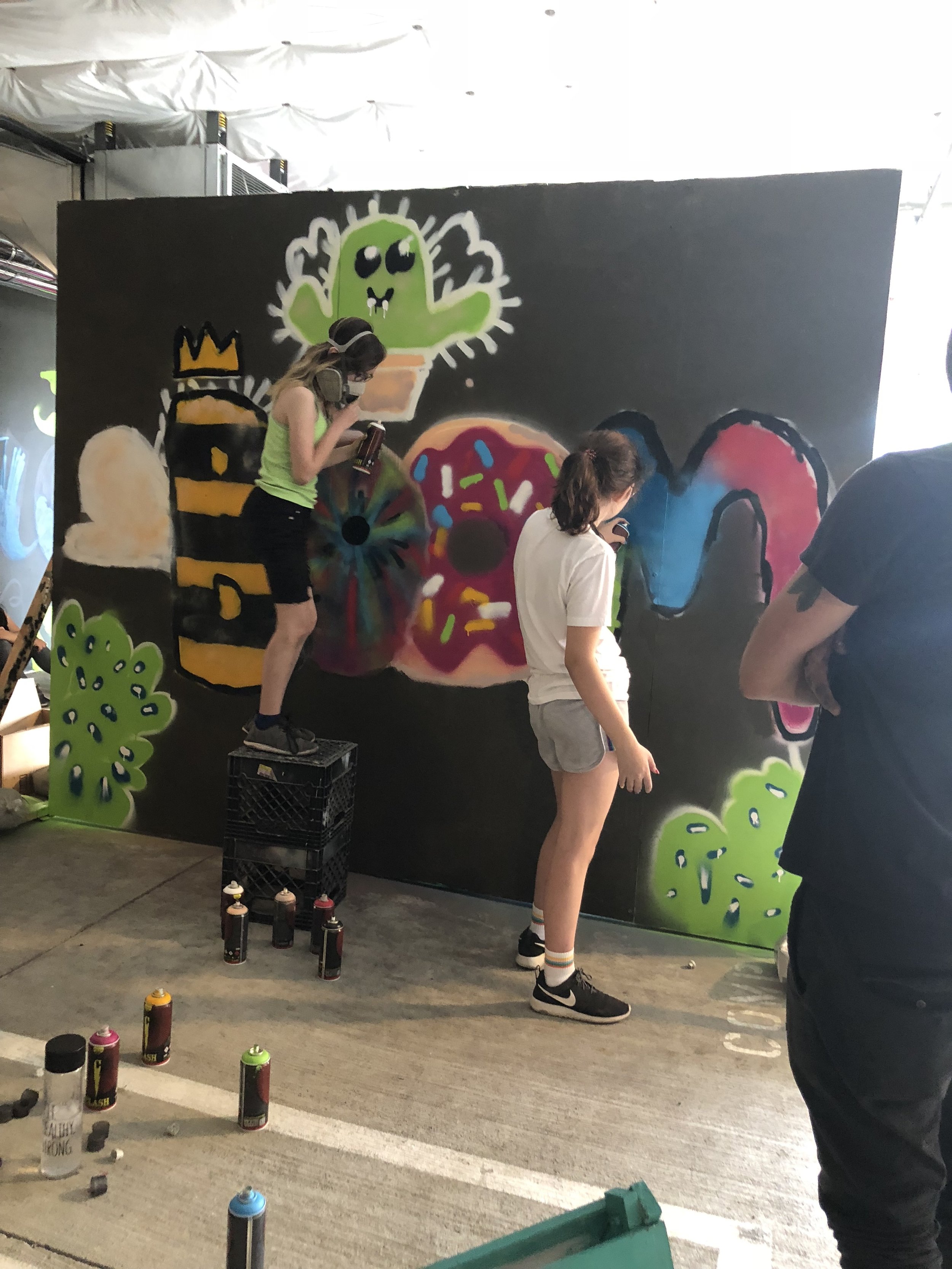
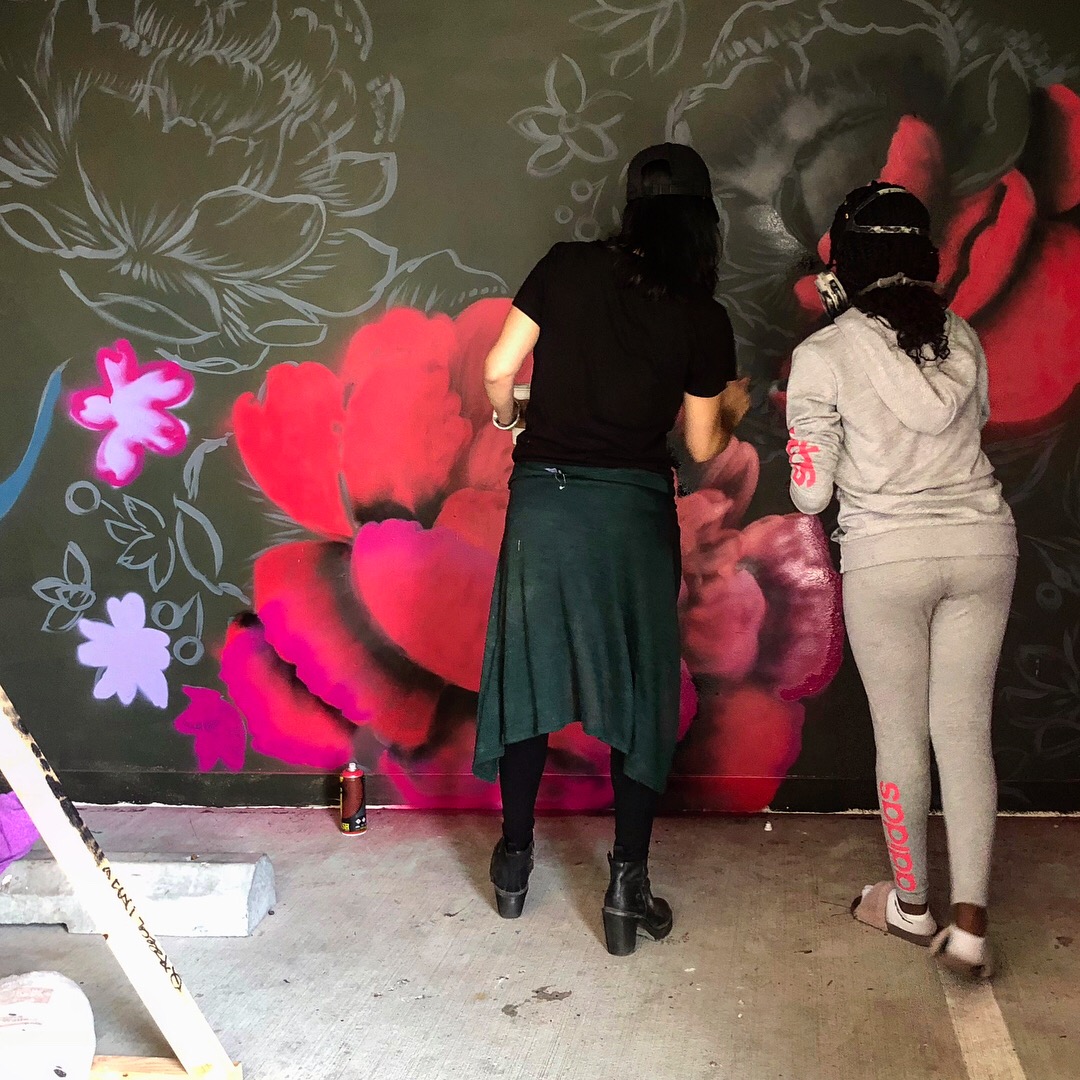
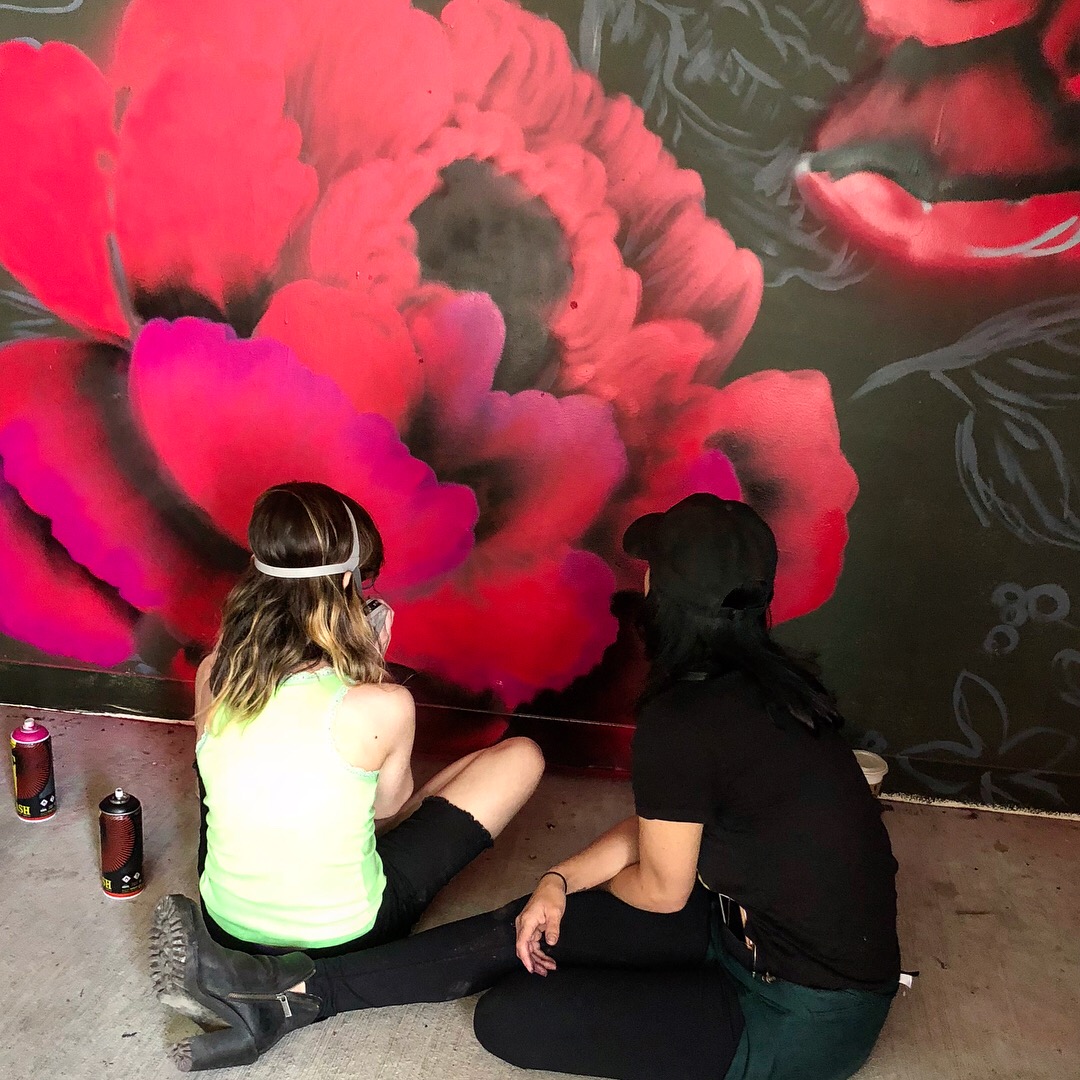
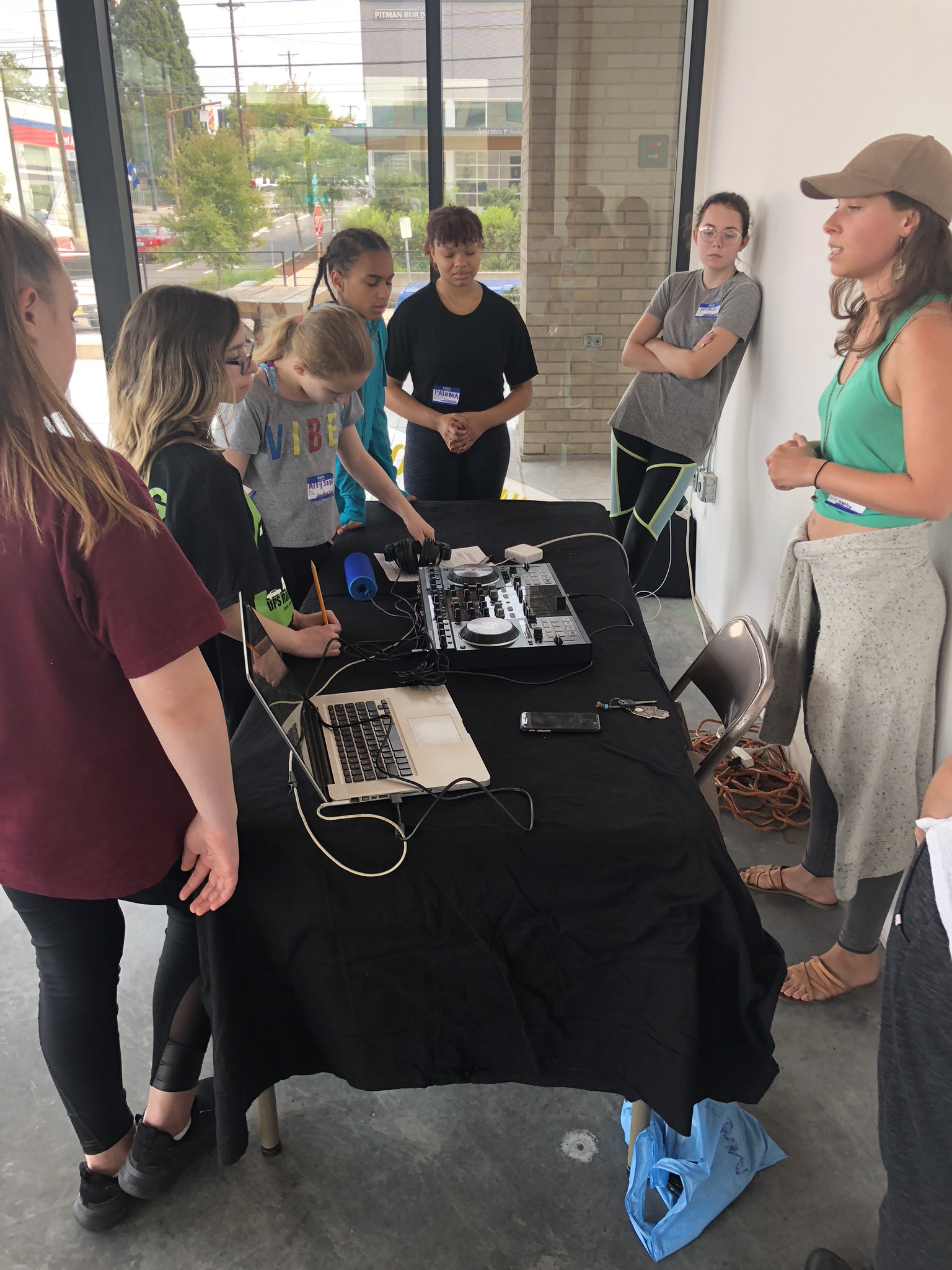
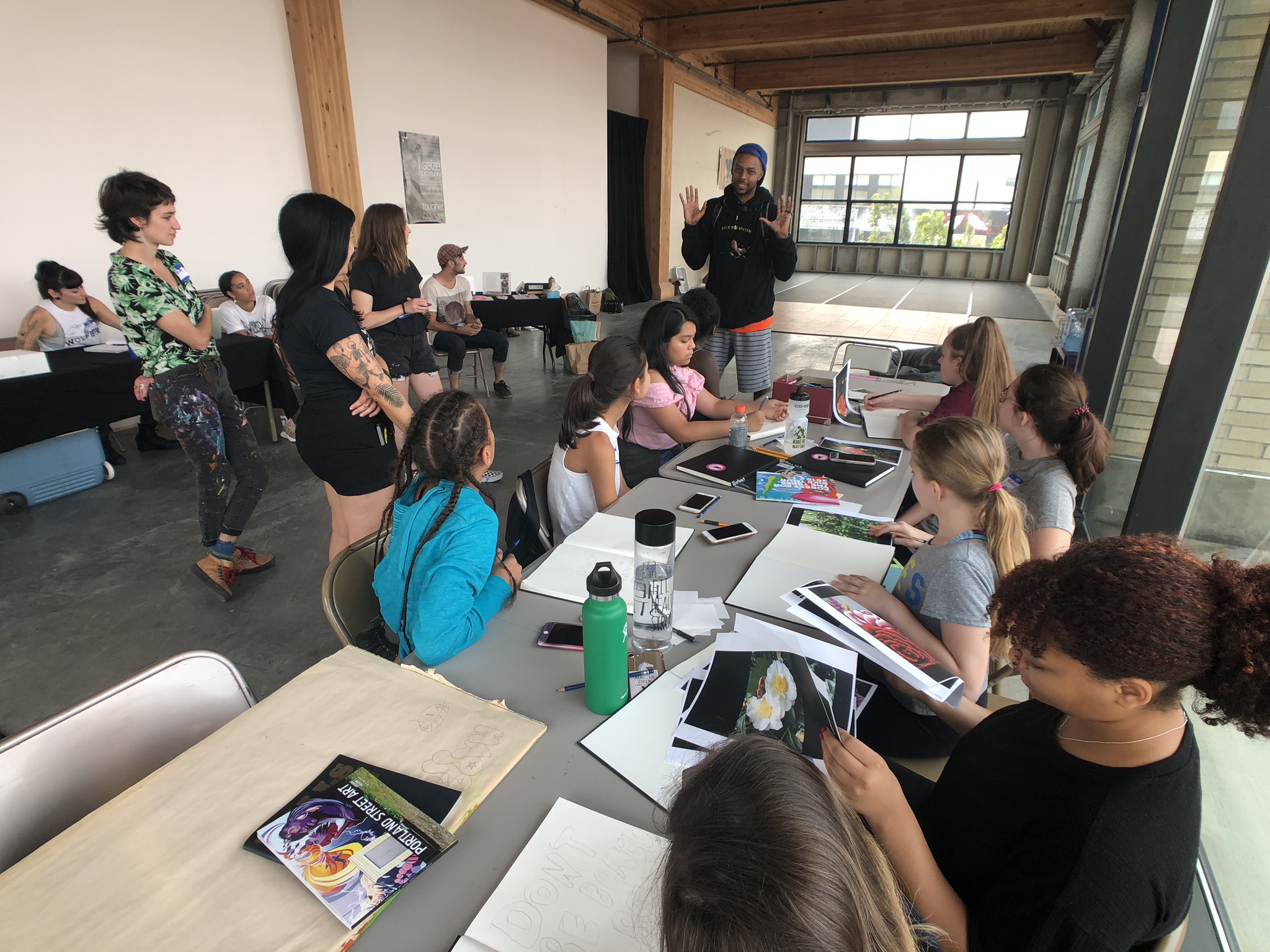
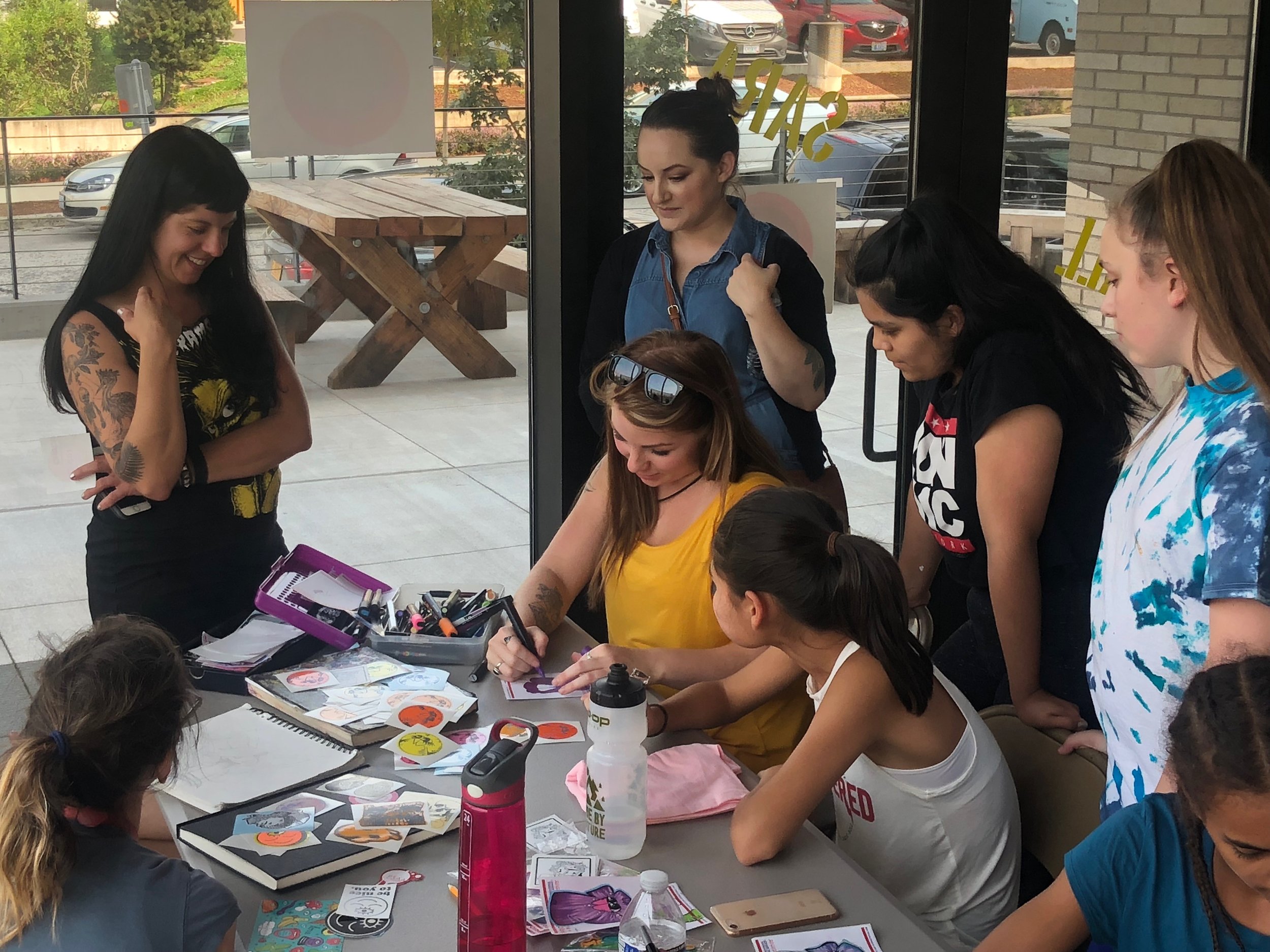
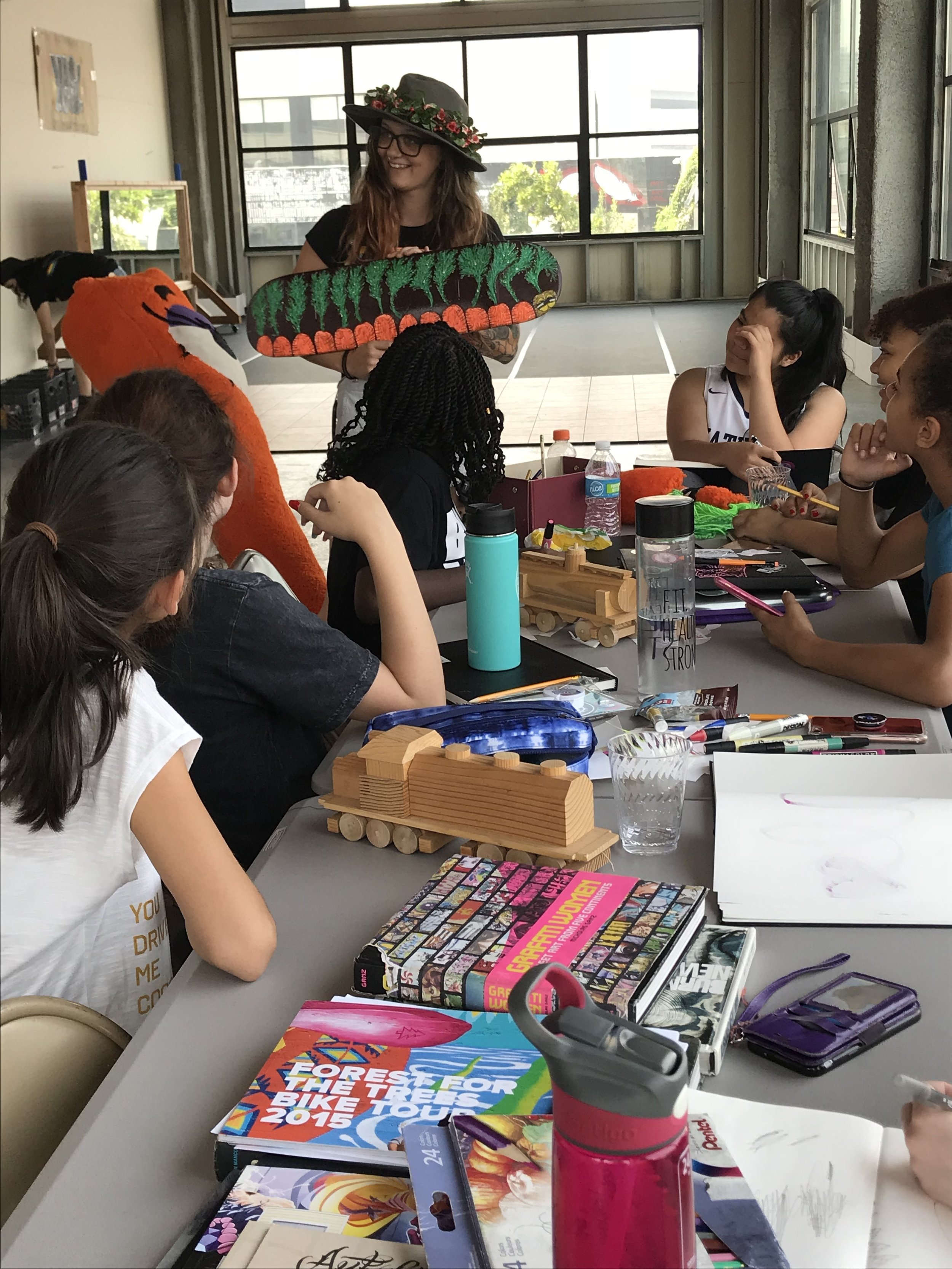
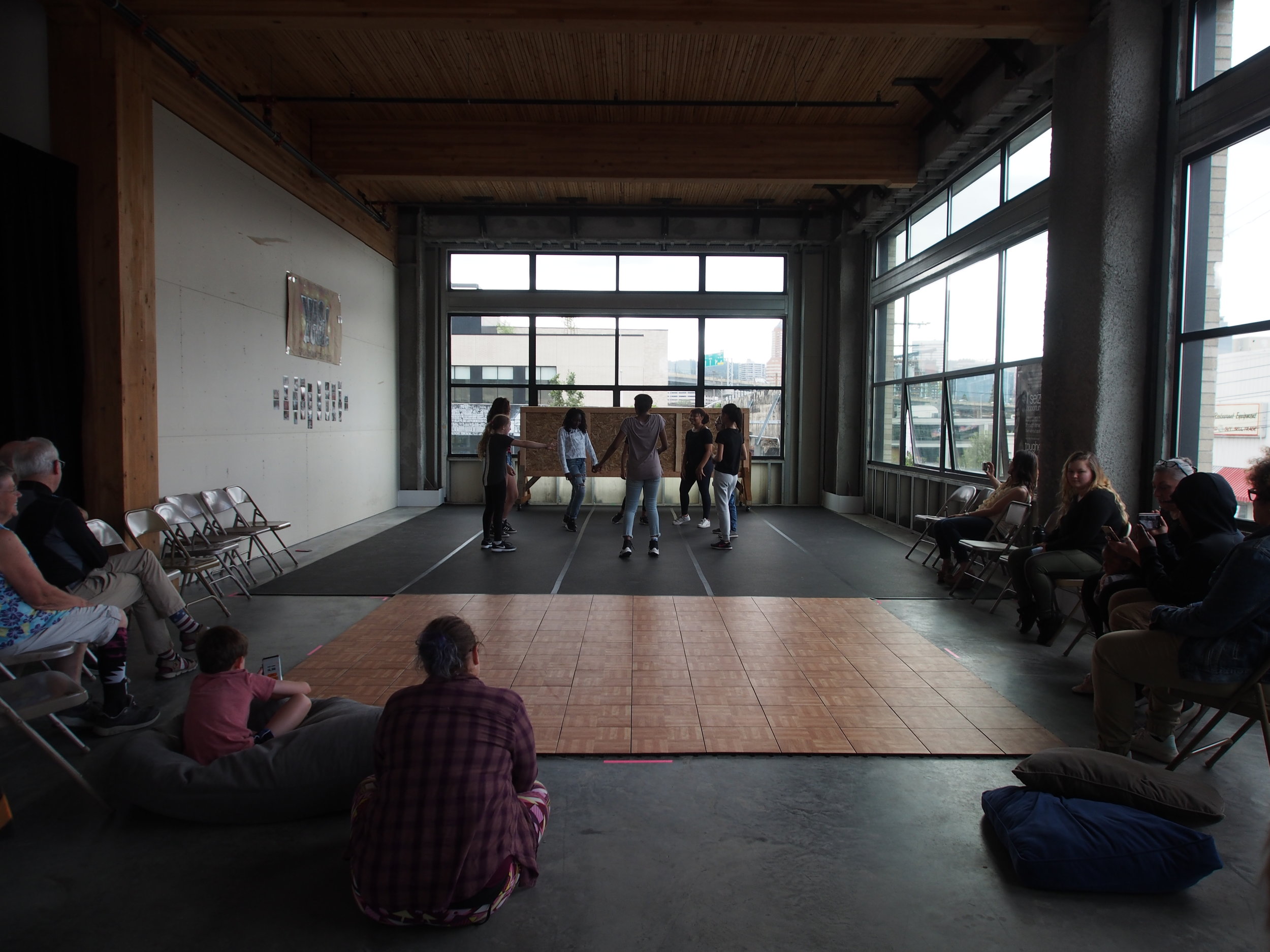
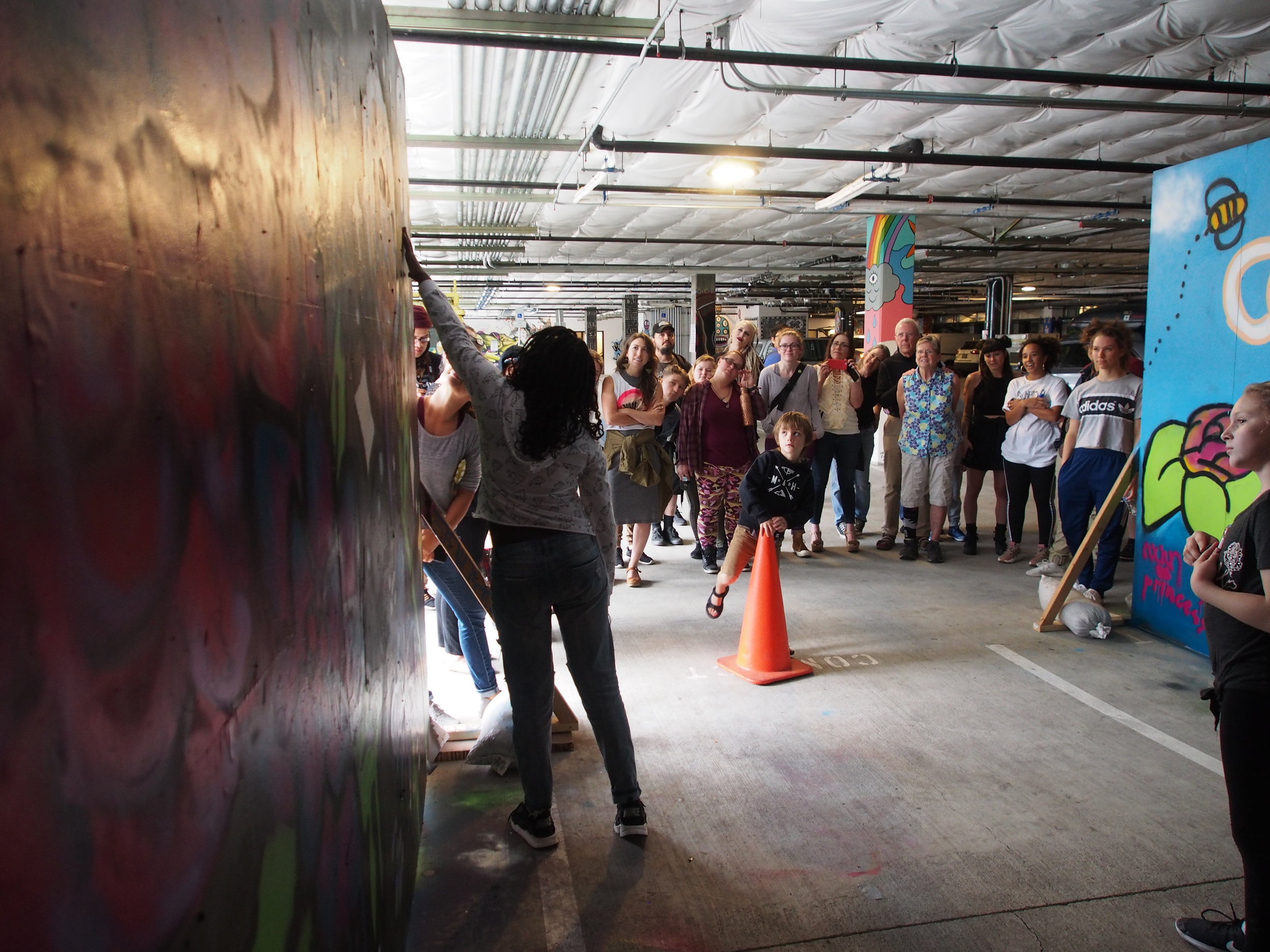
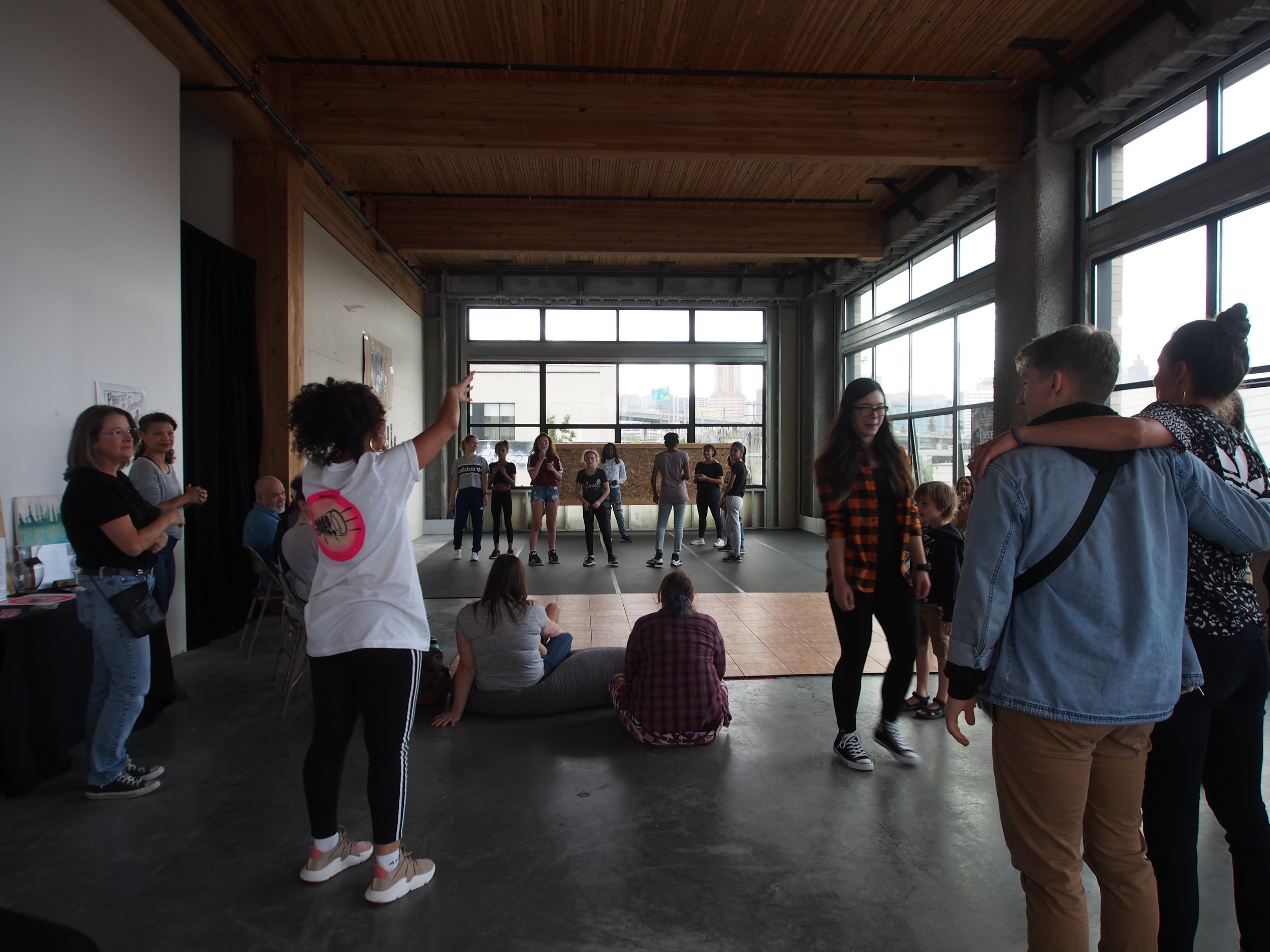
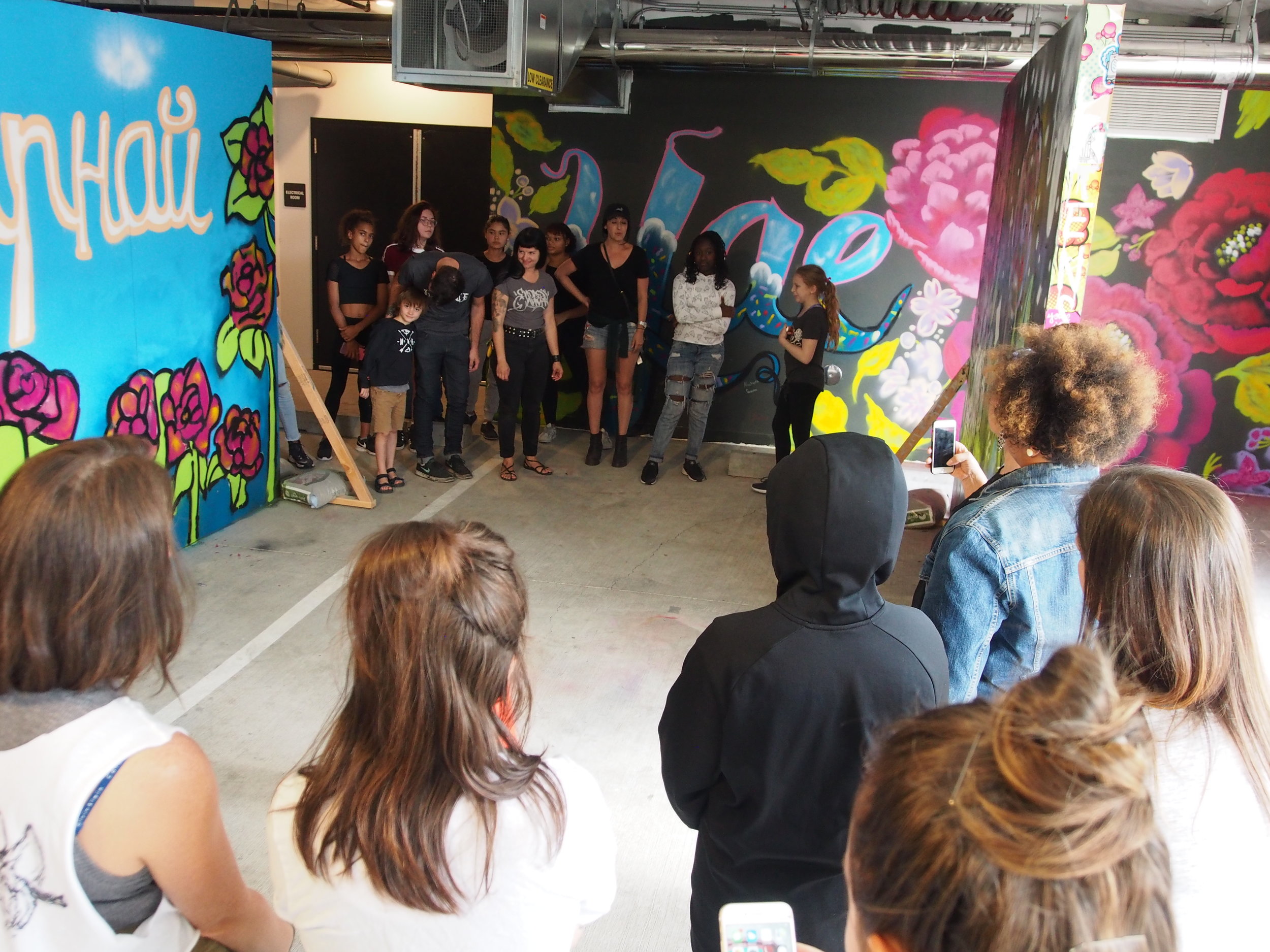
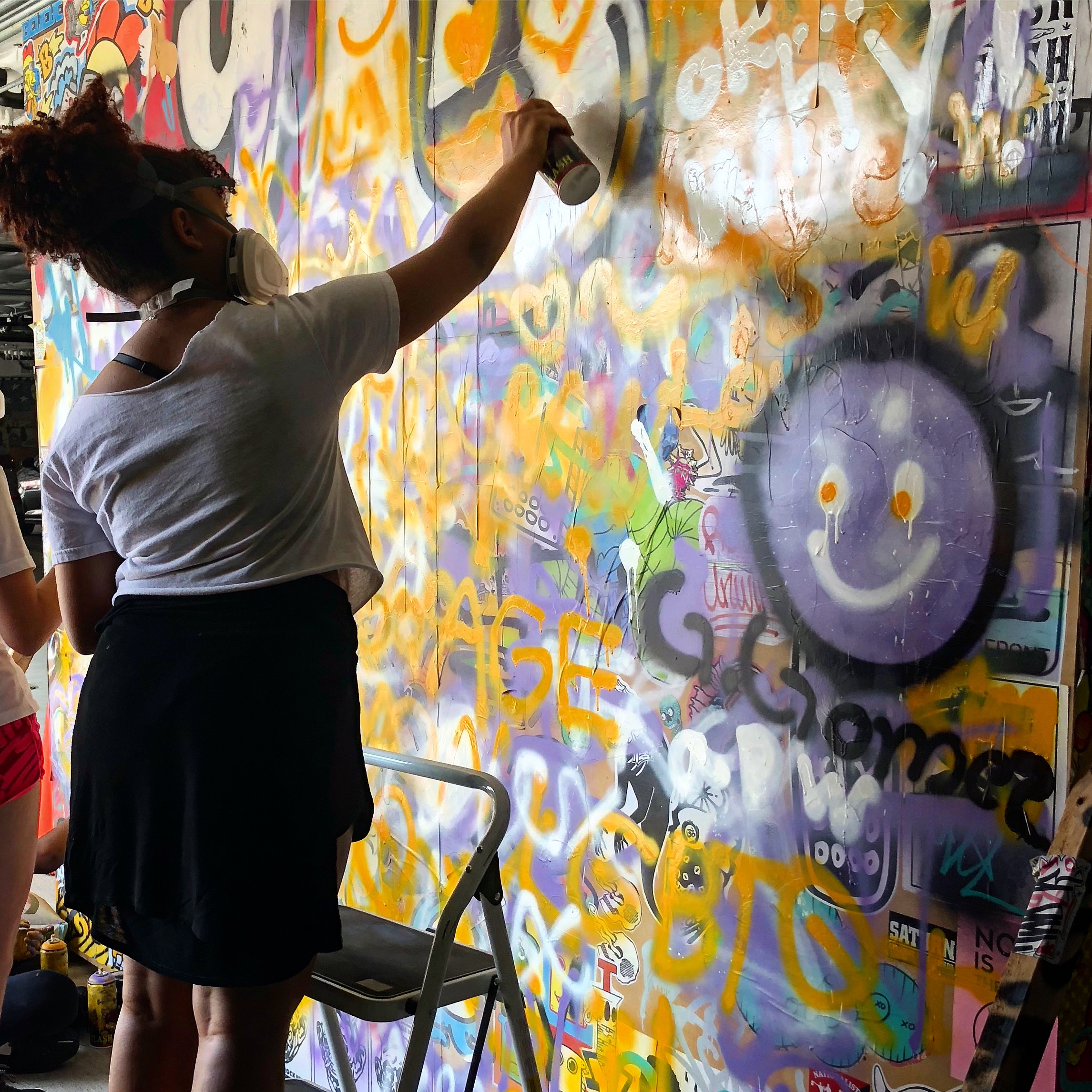In 1888, Thaddeus “Thad” F. Fisher and his wife Phoebe escaped the city and built a house just off Belmont at the edge of the city. Thad was a prominent Woodsmen of the World, a man of earnest endeavor who bore the respect of all who knew him (Multnomah County Archives). The house was built in the high style of Queen Anne, popular during the late 1800s. They planted plum and apple trees which still stand to this day. Highly ornamental in design, the house included intricate woodwork, intersecting cross gables, a 3-story tower, and a steeply pitched irregular roof. A large veranda coils around half the main house. Set back and slightly higher than the street, the ‘life’ of the house is thrust upward into the sky, establishing a sense of continuity between the house and the surrounding overgrown setting. On almost a daily basis, people take pause on the sidewalk looking at the house, pointing, talking, and sometimes asking questions. Old neighborhood residents often stop by to reminisce and tell tales of the house’s past.
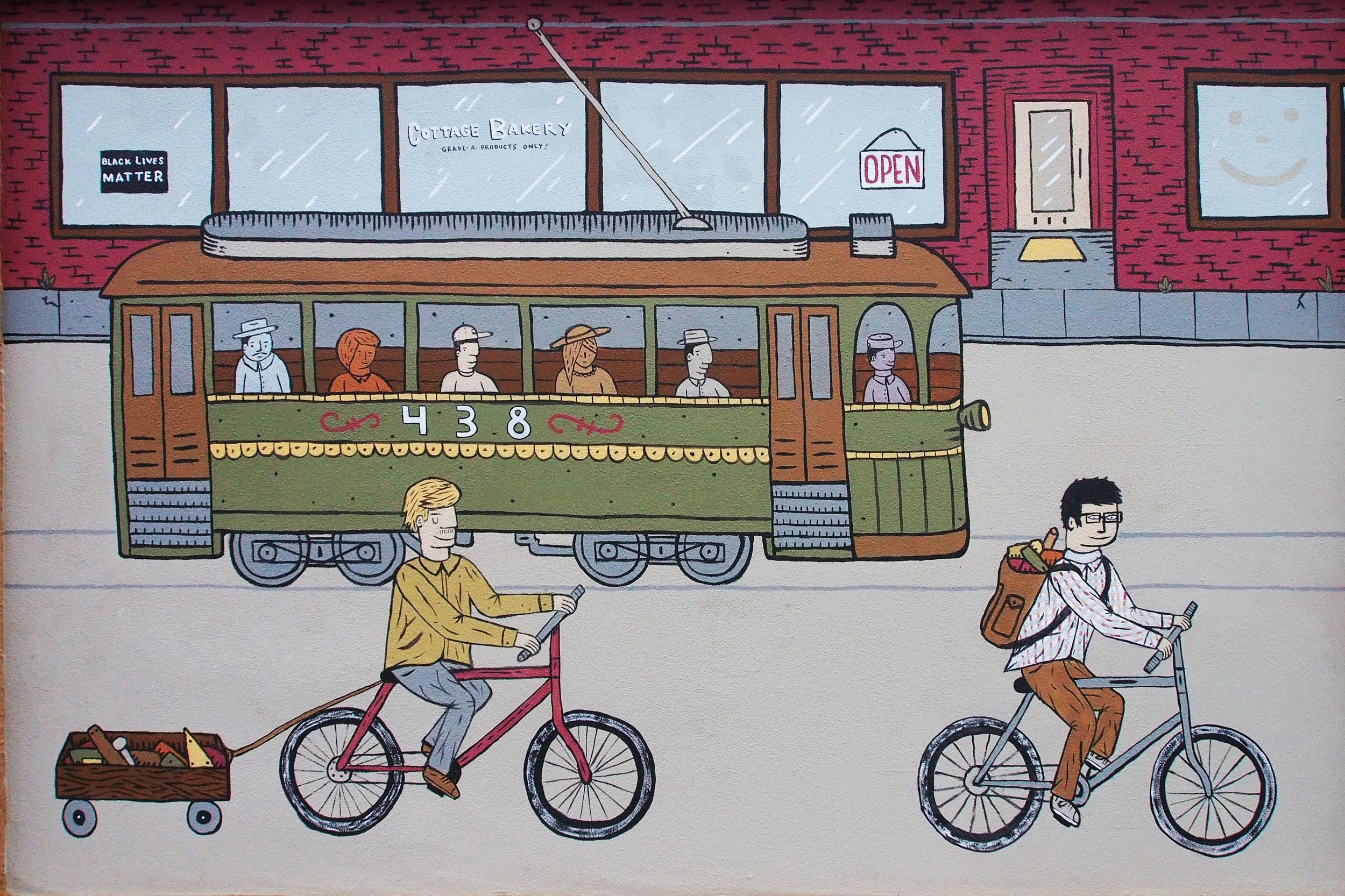
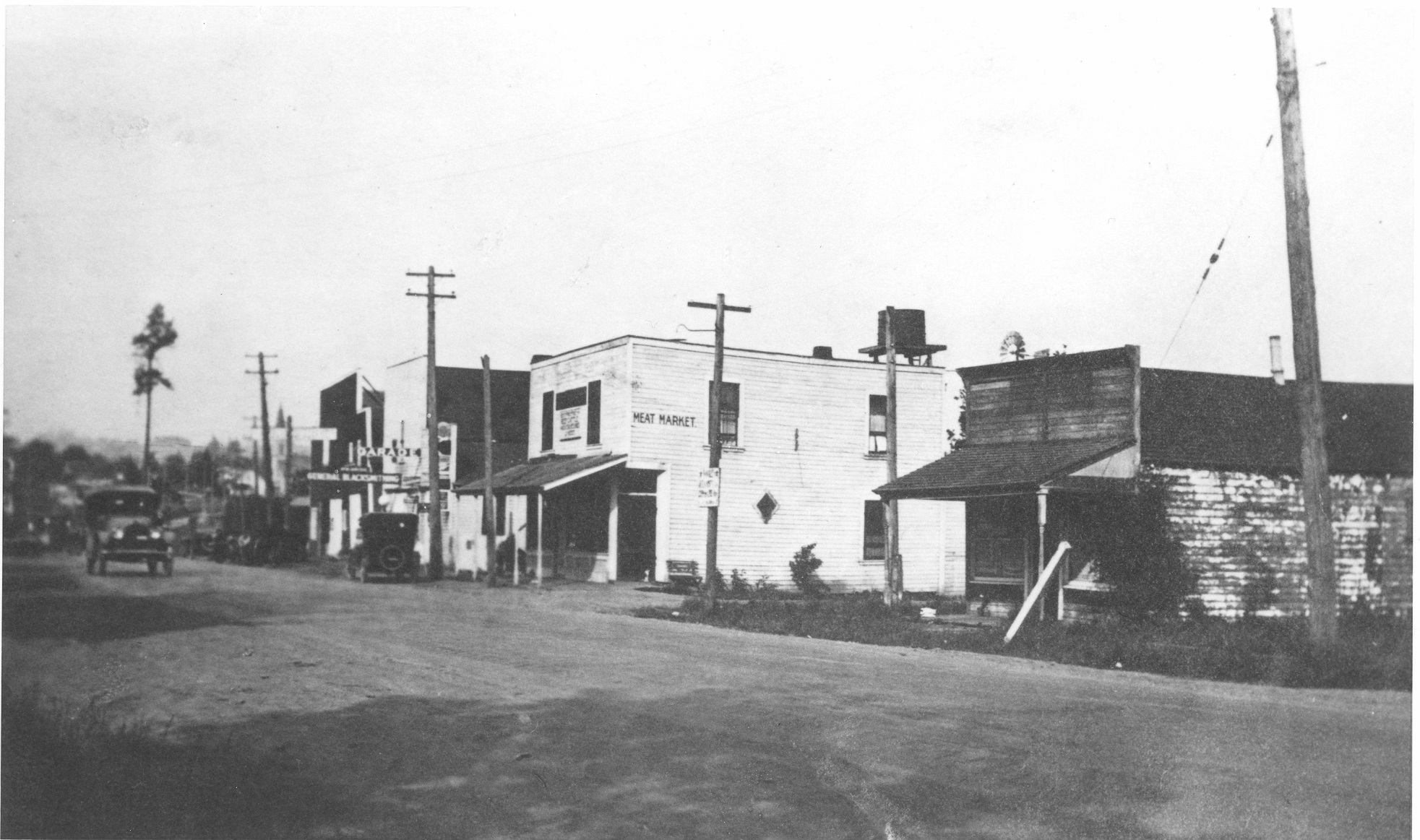
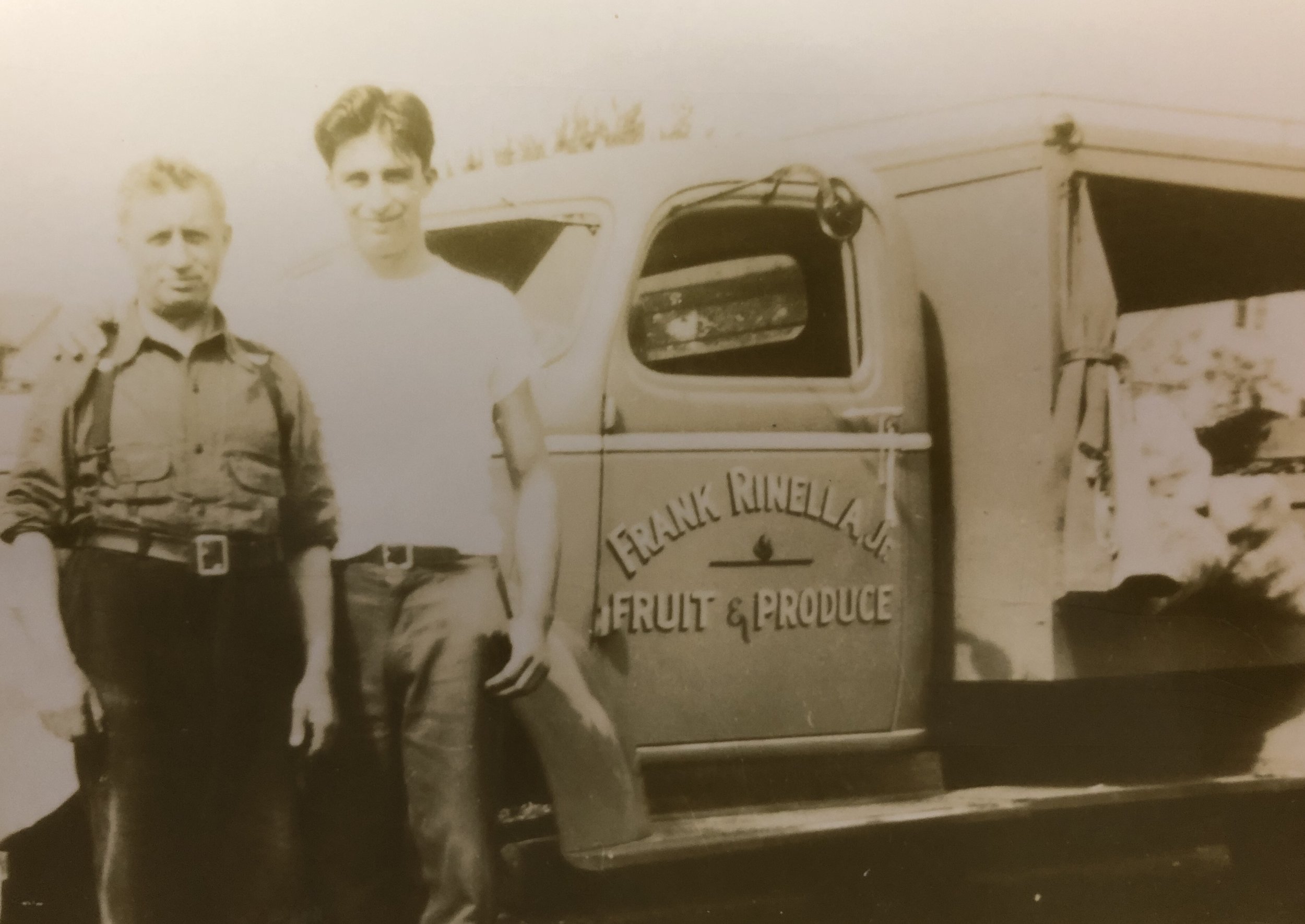
The Fishers were a well-off couple. Thad was a sea merchant during a time when Portland was becoming a key hub for shipping in the west. This house would have surely been a bold statement, a symbol of their class standing. During this time, the production of new inhabitable space on Portland’s Eastside was just beginning. Flight from the discords wrought by the industrial machine age was an achievement mostly possible for those who were wealthy enough to move. The elite were on a quest to escape the grimy city and reconnect to the natural world, enjoy sunlight, fresh air, greenery, and open space. SE Portland would have been a very different type of place to live in the late 1800s. The majority of the roads were still dirt and gravel, which turned to mud during the rainy months (Portland Paving Map). Horses and kerosene lamps were everyday objects, as electricity and automobiles were bourgeoning ideas. The Fishers, and their neighbors, were urban pioneers settling in and taming this new environment. There would have been an enthusiasm brewing in the Sunnyside neighborhood, because the very same year the Fishers built their home, the Mt. Tabor streetcar line began, extending from the river to 34th and Belmont.
The Fishers did not have any children. Thad passed away in 1904 and was buried down the avenue at Lone Fir Cemetery. His wake was held at his home. A few years after Thad passed away Pheobe remarried a man that was boarding in the house for many years, Edgar Allen. The house remained in the Fisher family until 1935 when Phoebe sold it. Interestingly, Edgar is buried right next to Thaddeus in Lone Fir Cemetery, along with his son, but Phoebe lies in an unmarked grave in-between her two husbands.
In the 1930s the home was temporarily converted to eight units during World War II (National Register). Portland’s mushrooming defense industries led to a housing crisis. This epic migration consisted of factory workers, soldiers and their families. Measures were taken to build worker housing, but the demand could not be met, so thousands of single-family houses were converted to accommodate multiple families. Even though the Fisher house is large, it would have been tight quarters. Residents would have shared bathrooms and kitchens. Many would have most likely viewed this home as temporary as they hoped the war would be.
After the war, the house was converted back to accommodate a single-family and the in the 1960s, it was rehabilitated and turned into three apartments by local preservation legends, Jerry Bosco and Ben Milligan (founders of the Architectural Heritage Center). In the early 1970s, when I-405 was under construction, they were alarmed by the tragic demolition of historic buildings throughout the region and salvaged countless architectural pieces. Over several decades, they collected a trove of ornate building elements, some of which were used in the restoration of the Fisher House and the neighboring J.C. Havely House. Dedicated to saving pieces of Portland history, Ben and Jerry worked extraordinarily hard restoring the original siding, repairing and replacing the shingle work, windows, doors, and woodwork.
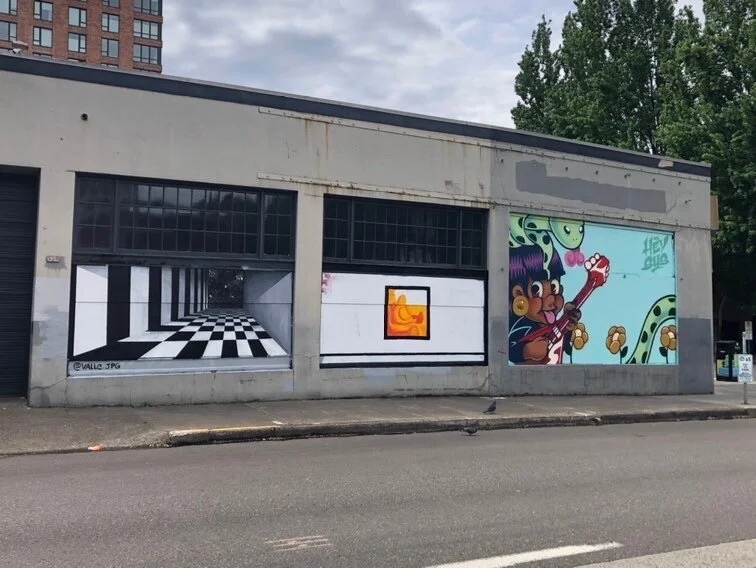
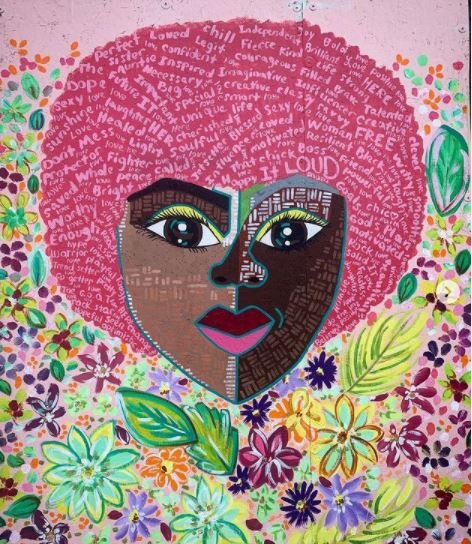
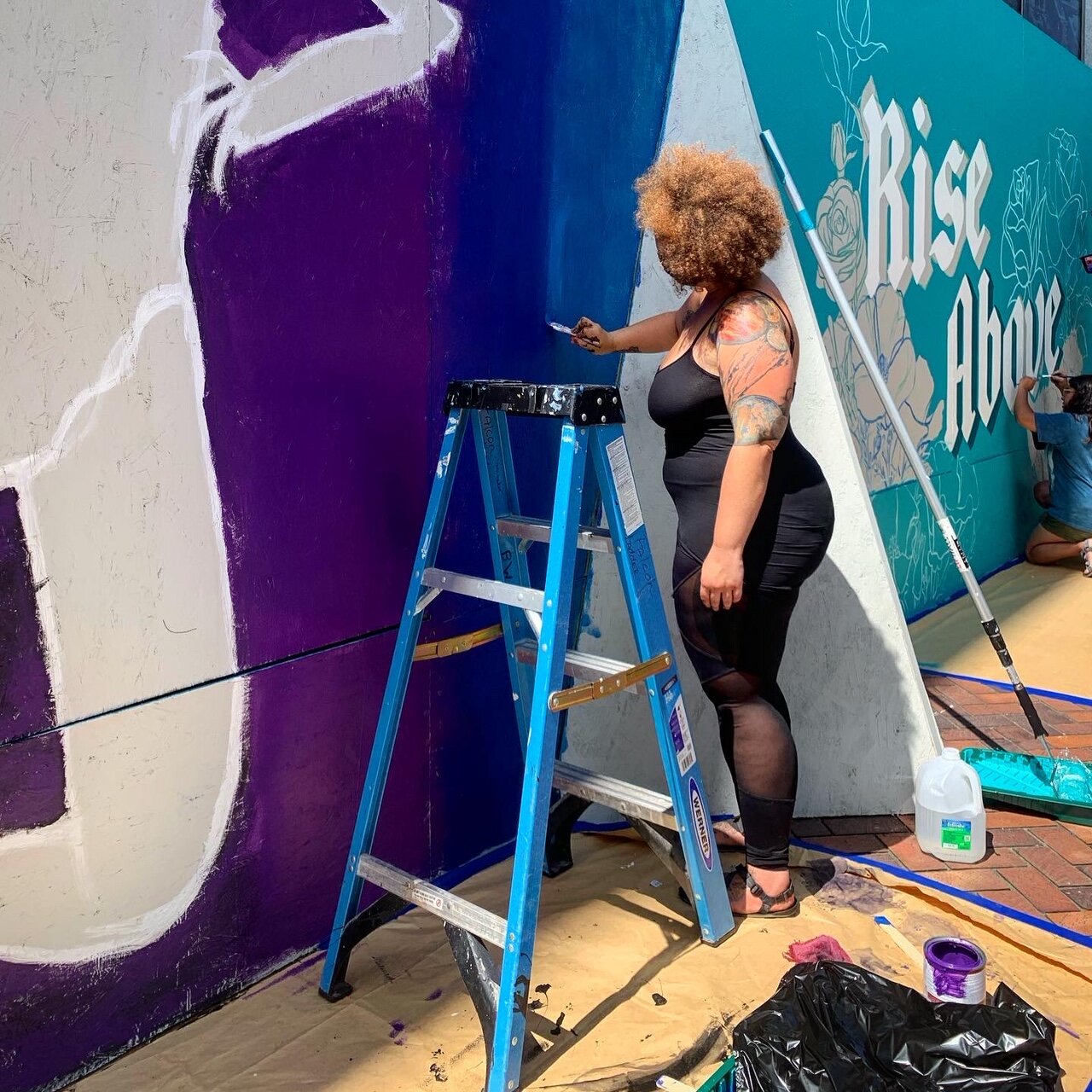
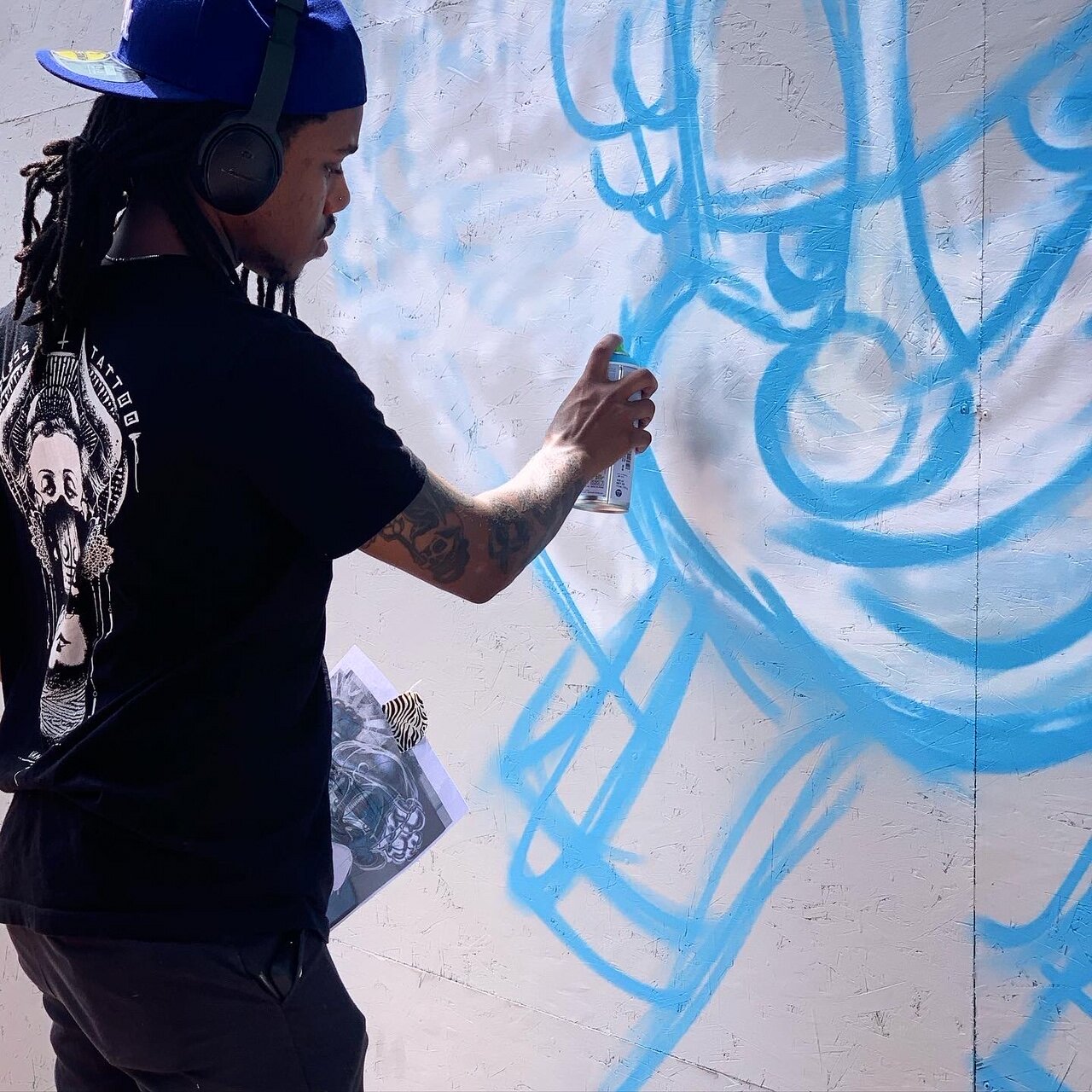
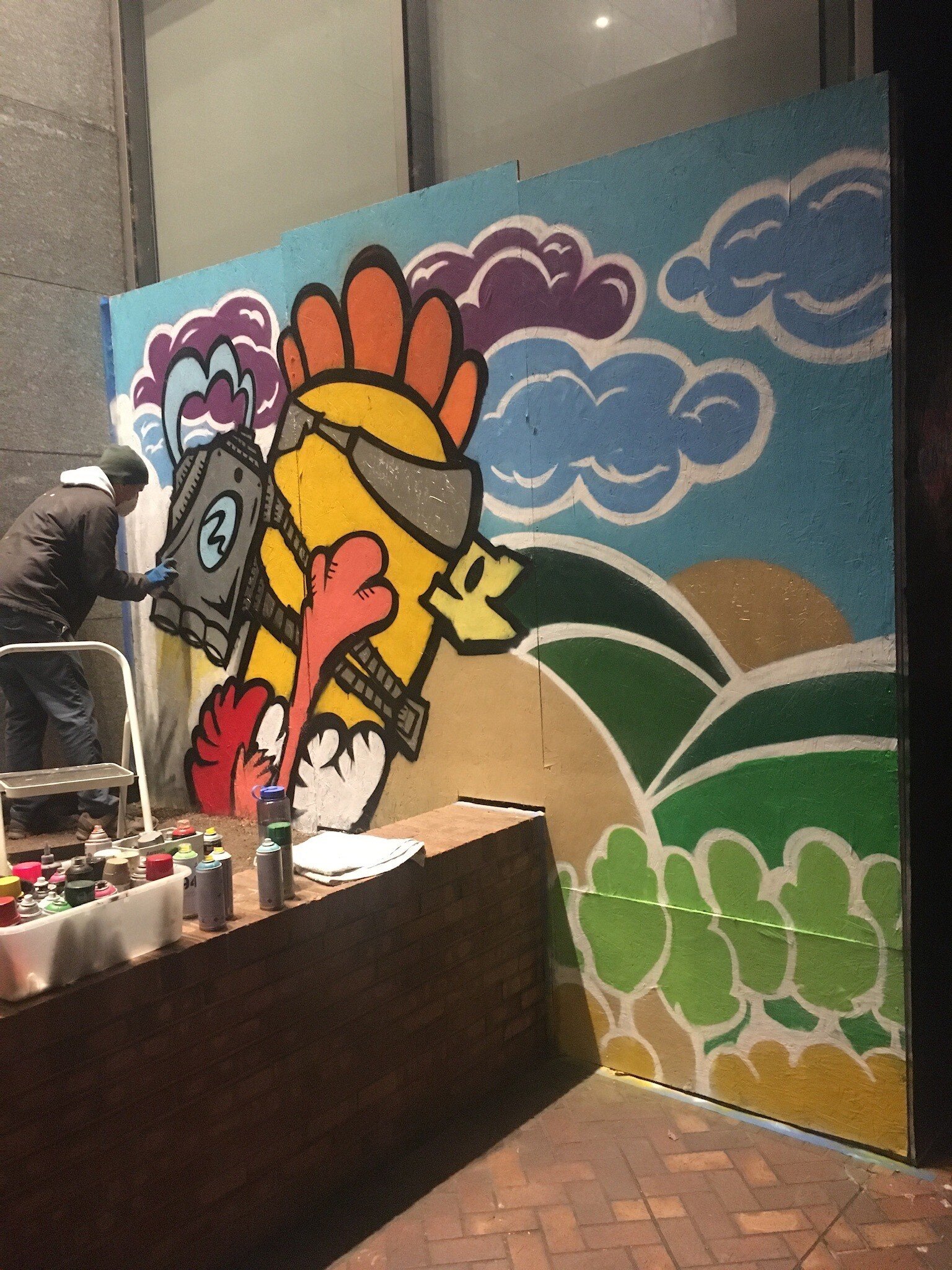
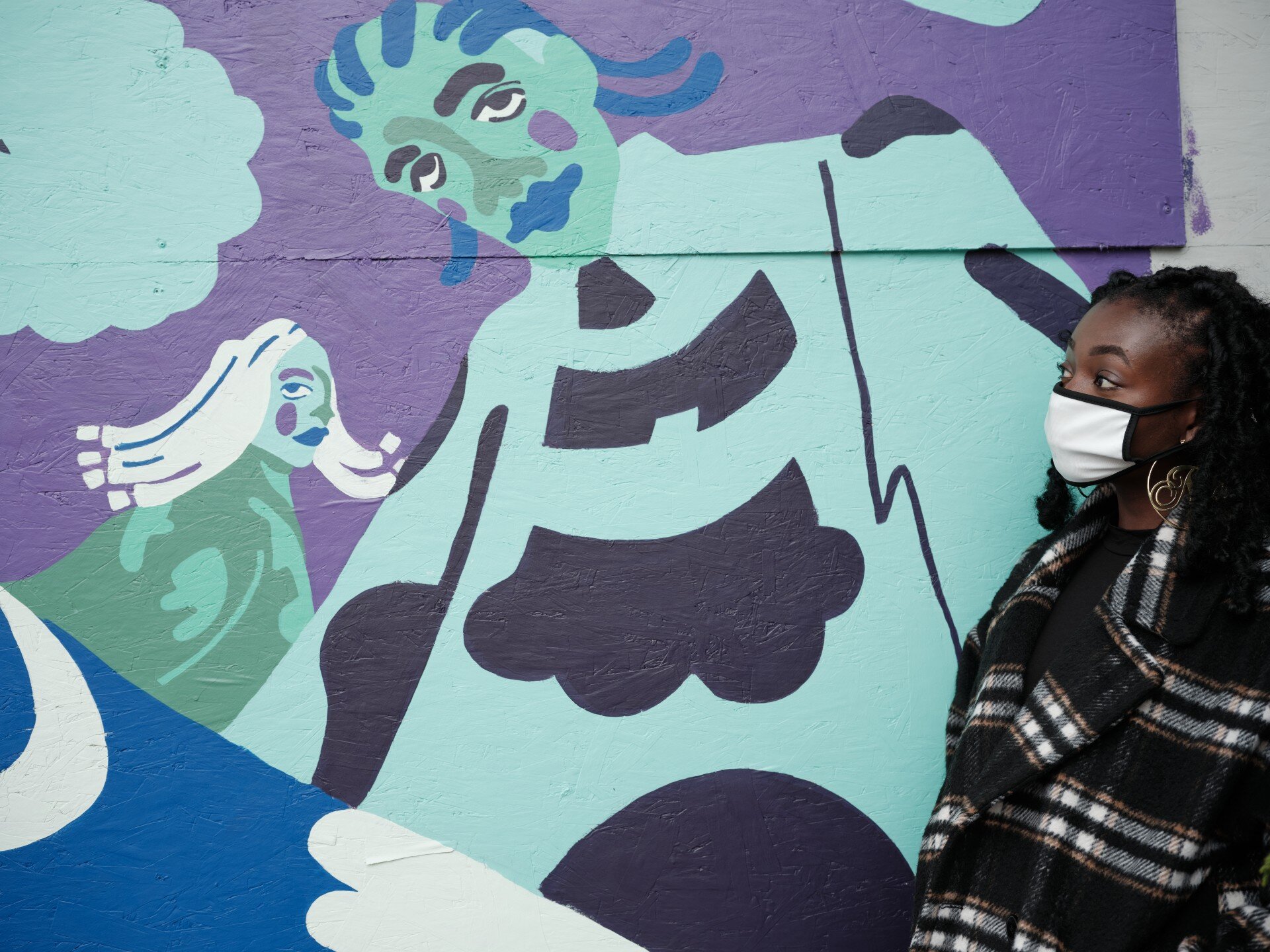
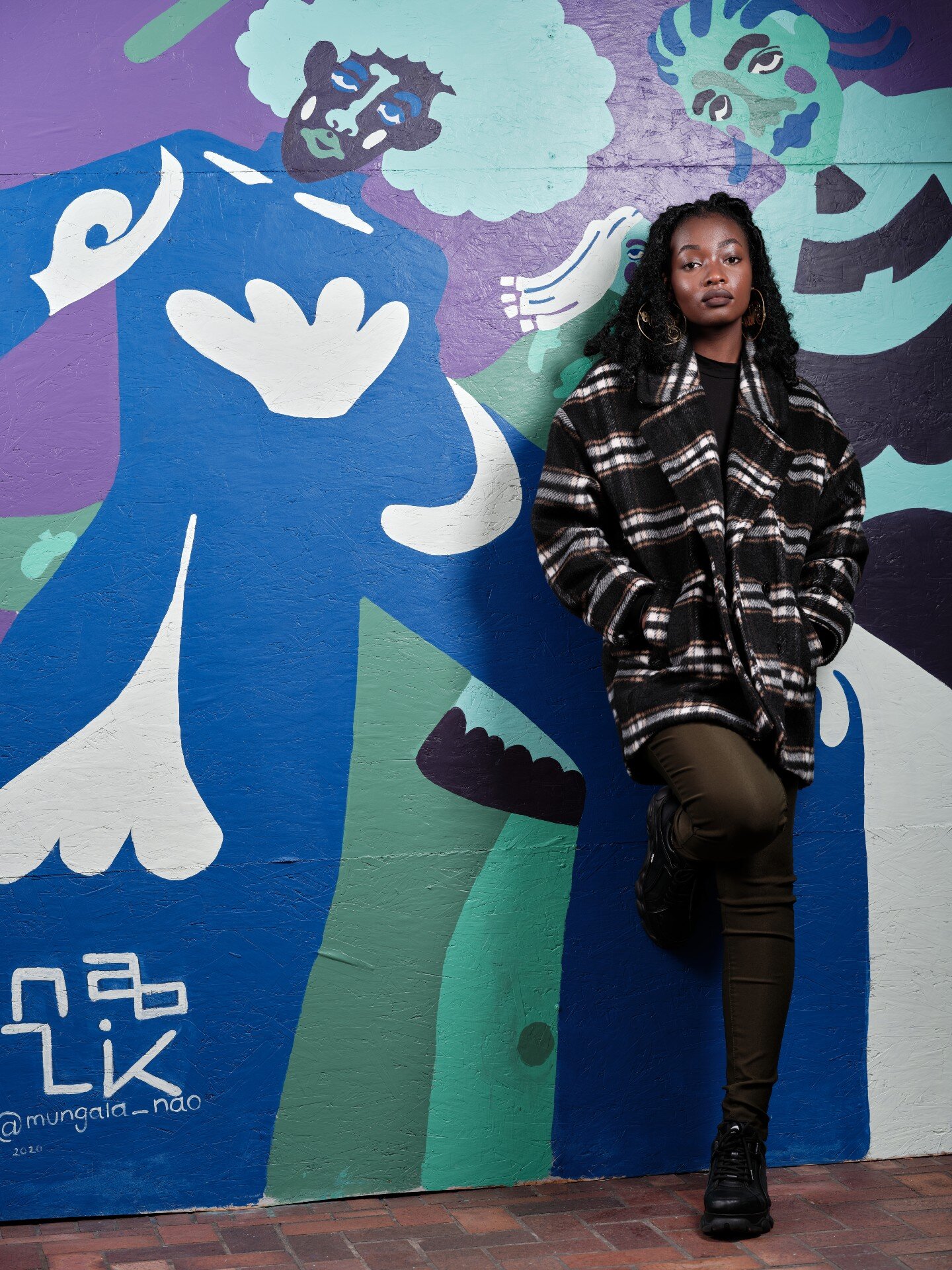
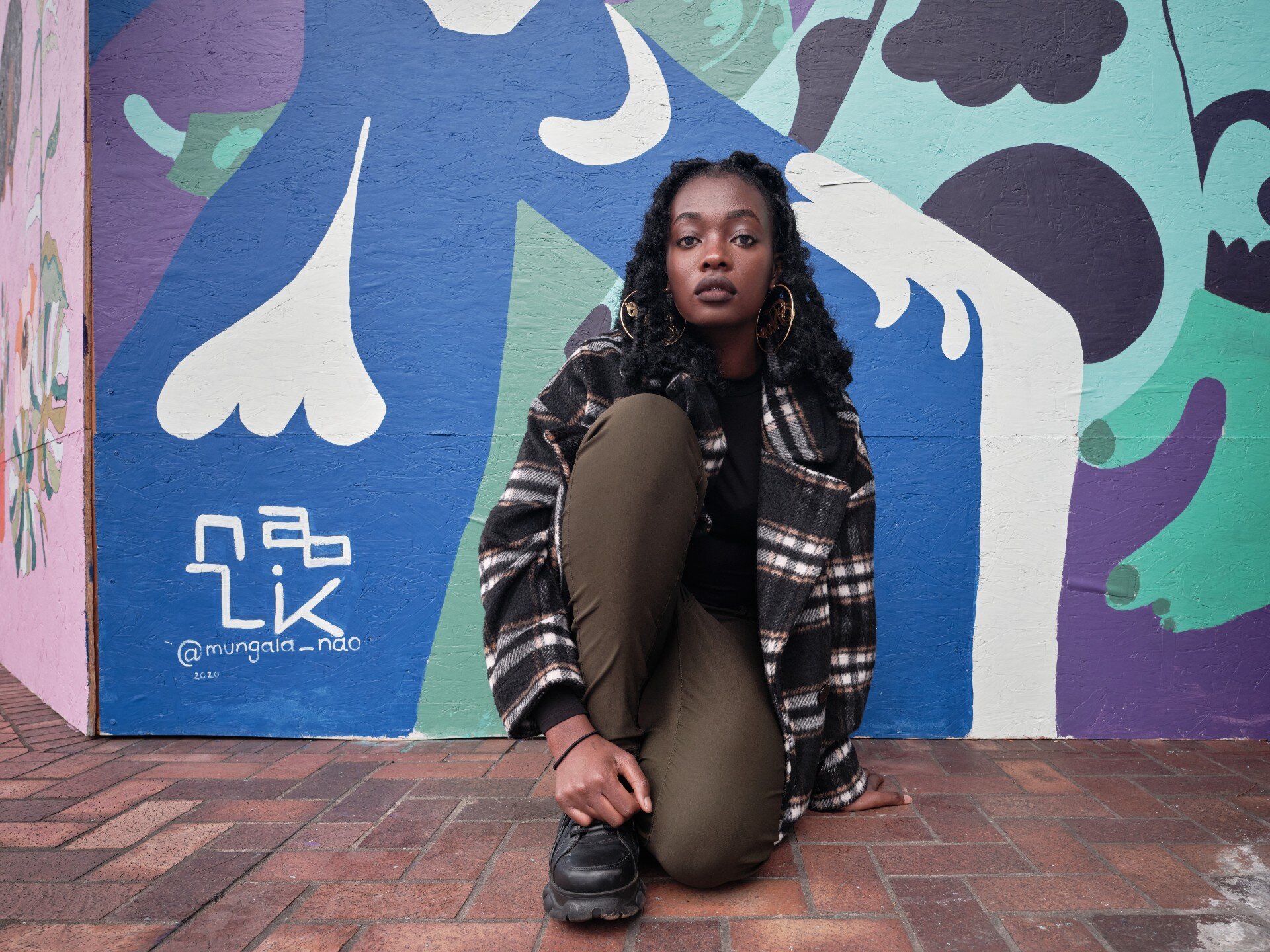
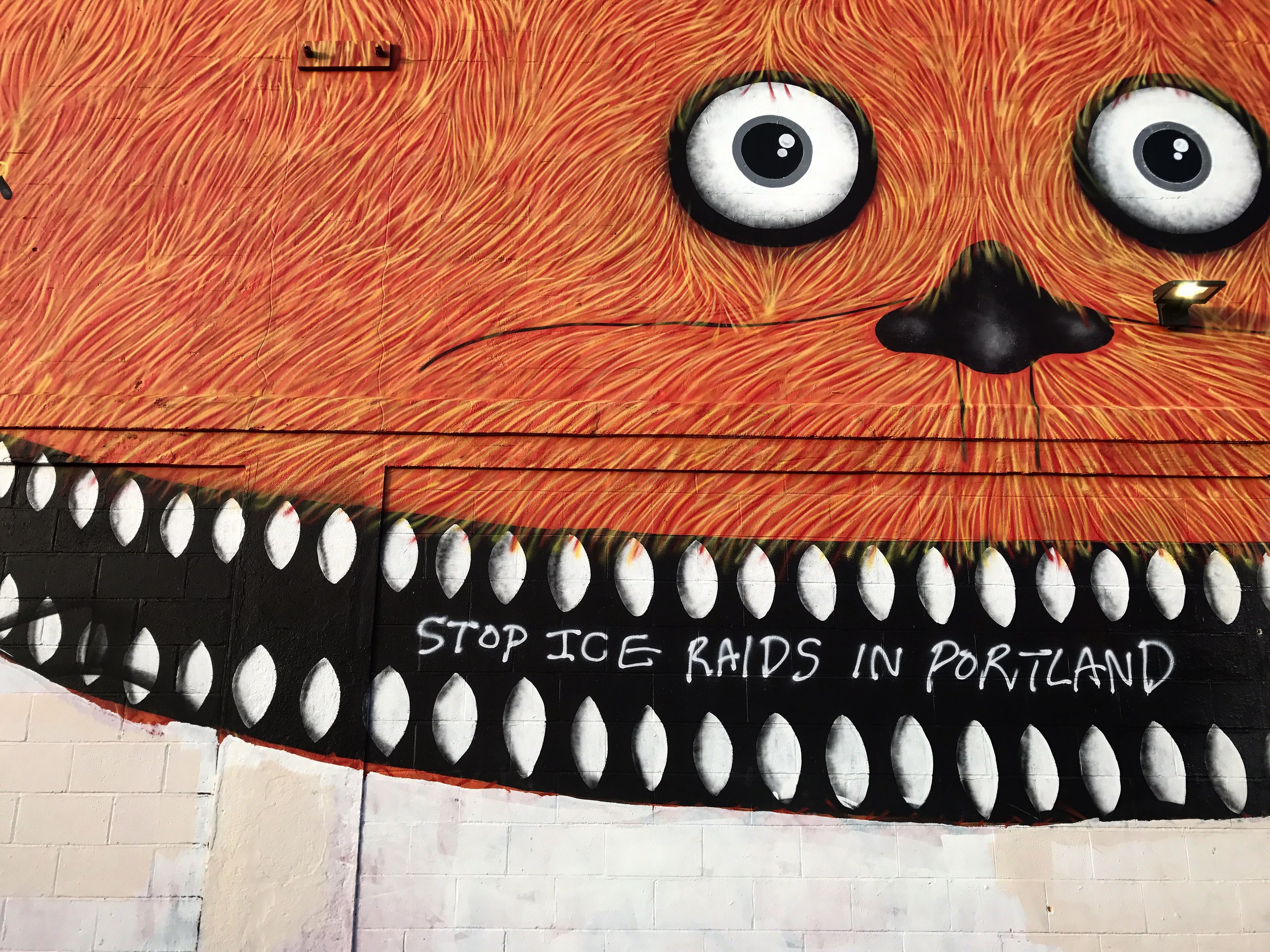
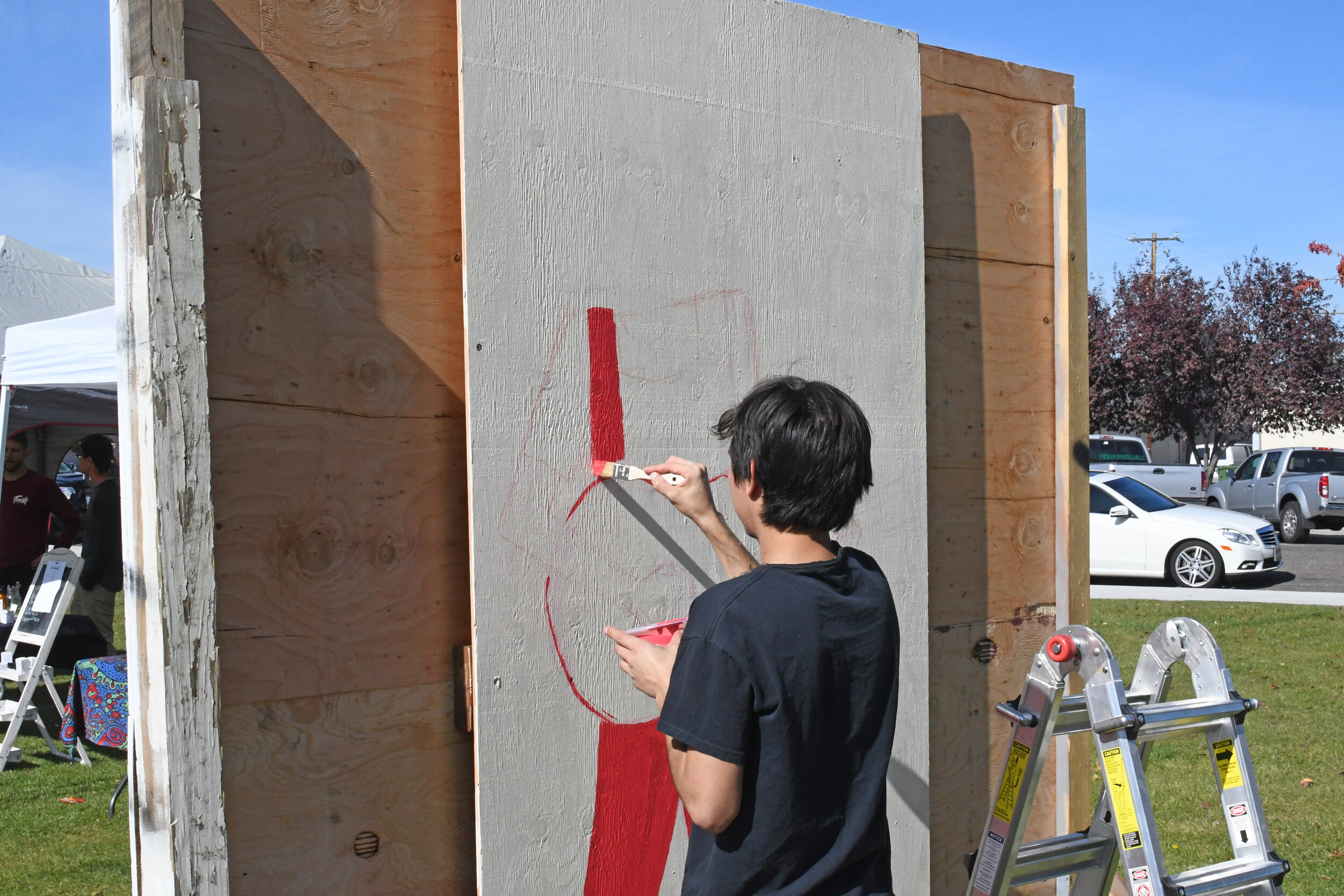
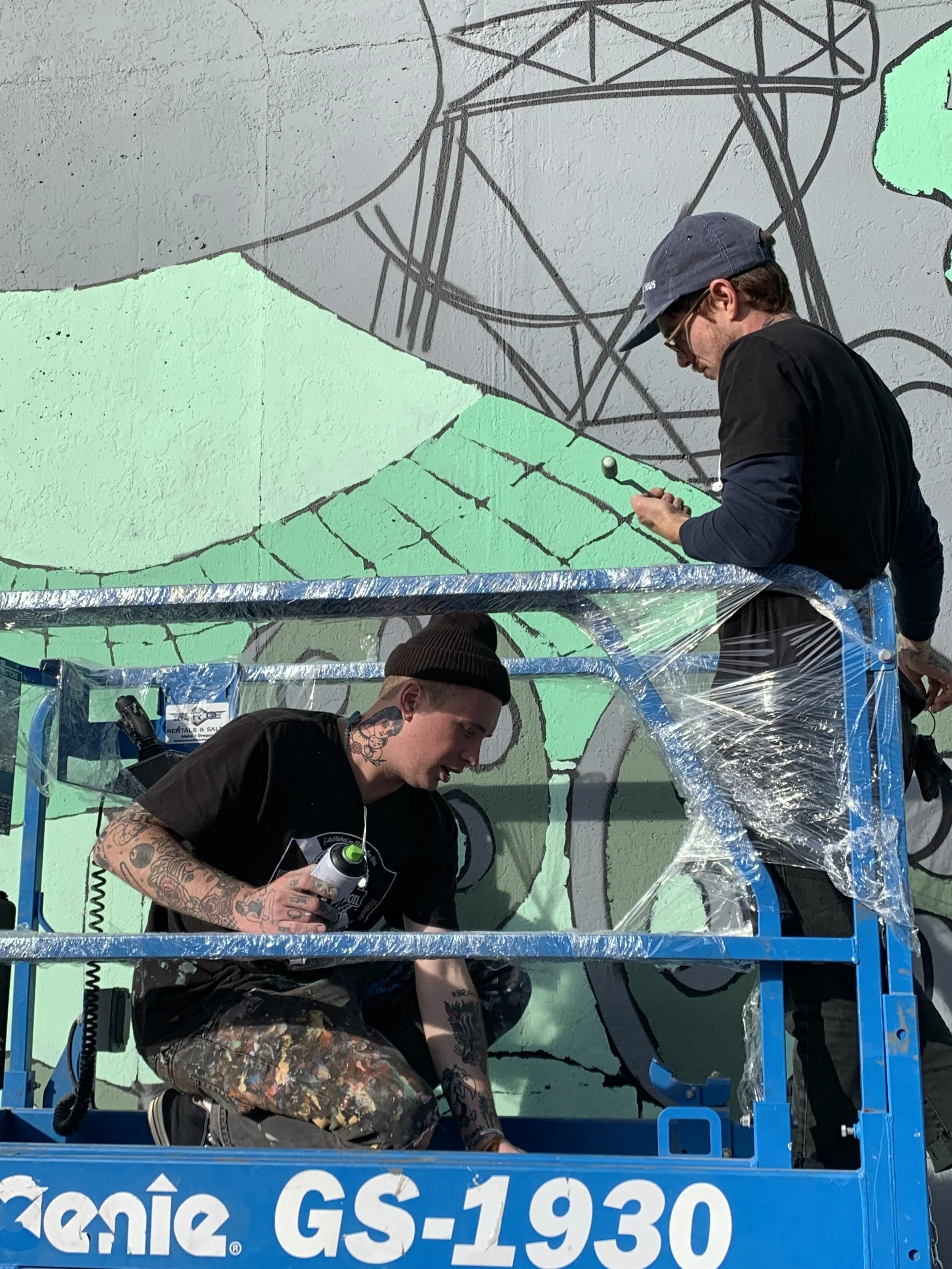
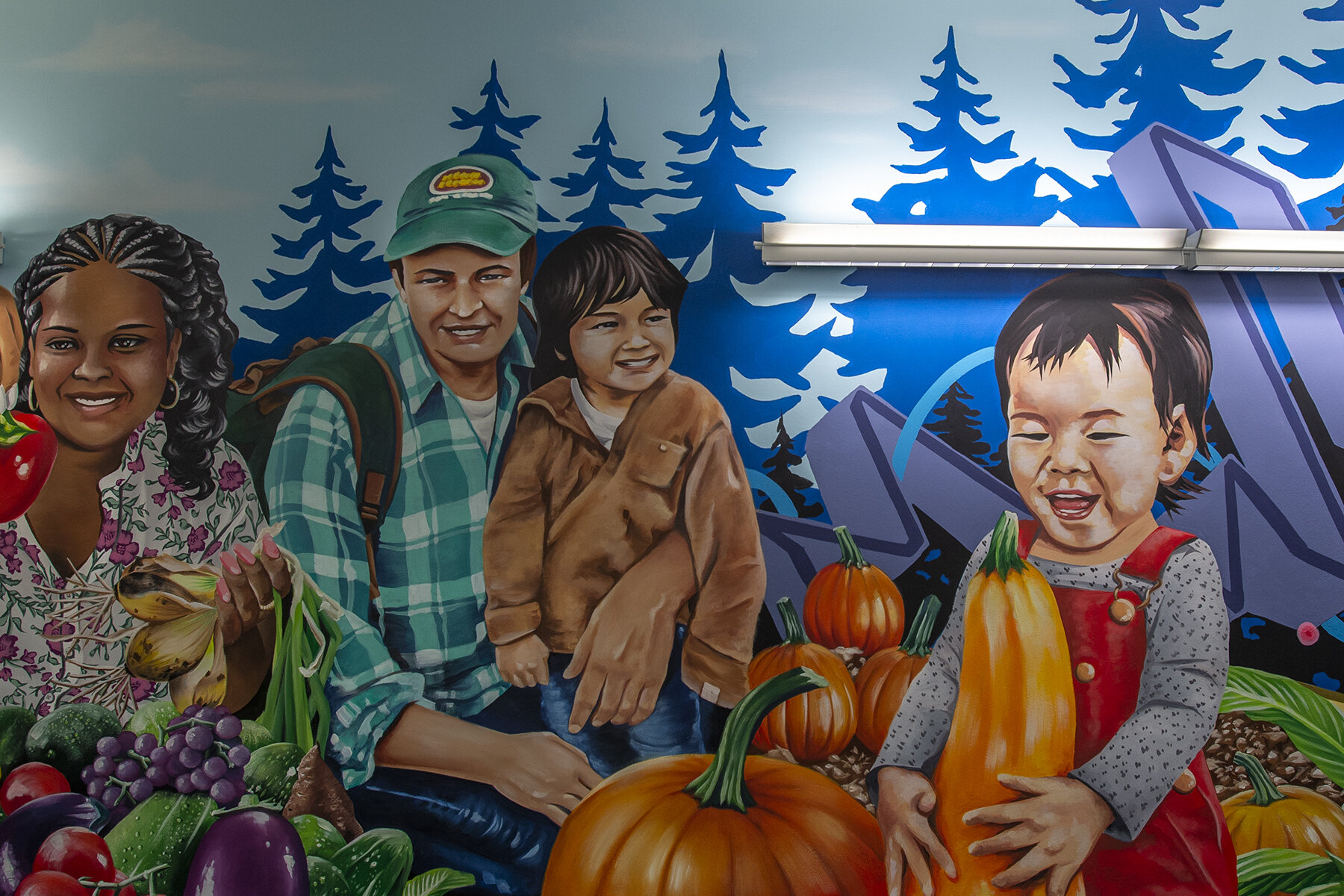
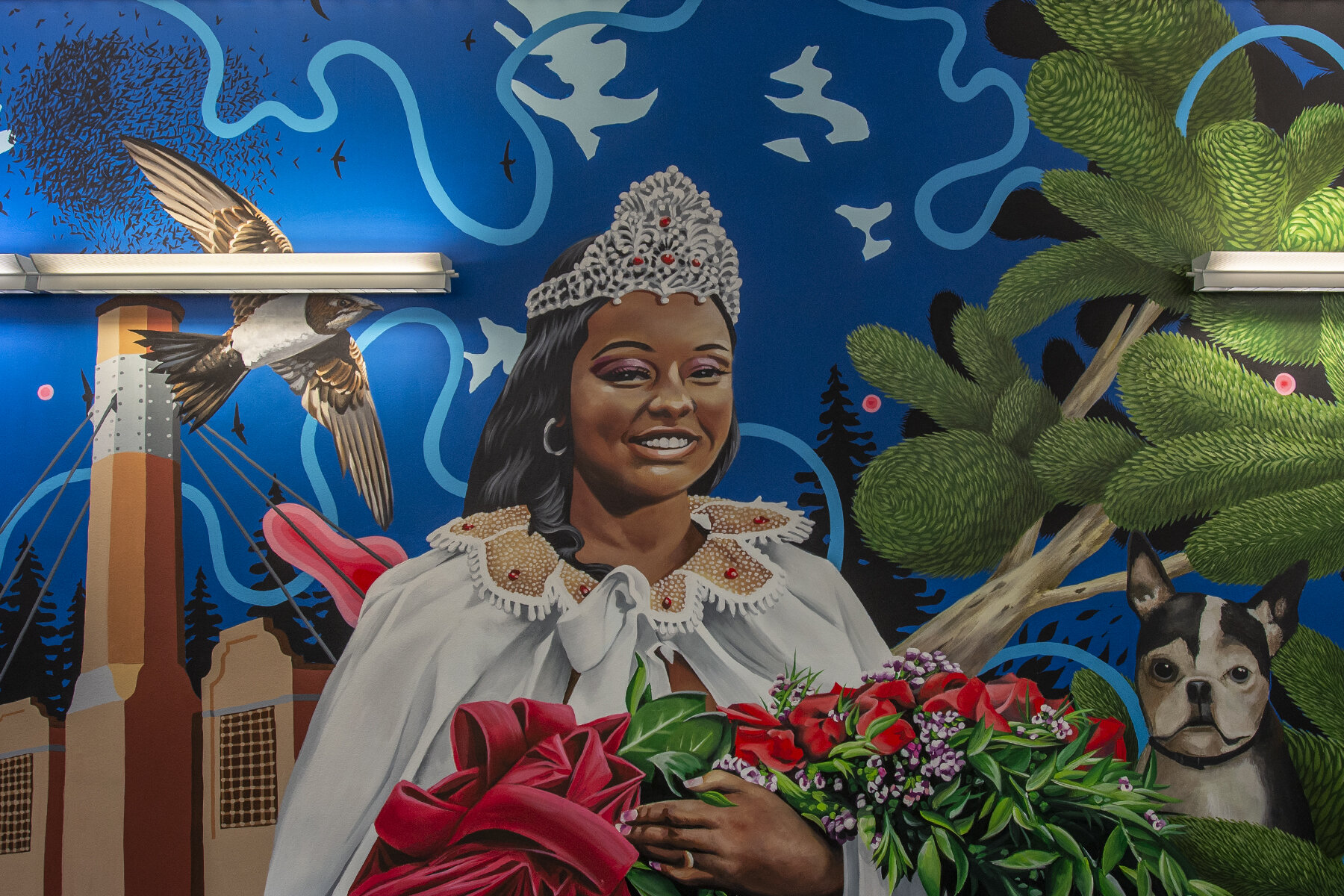
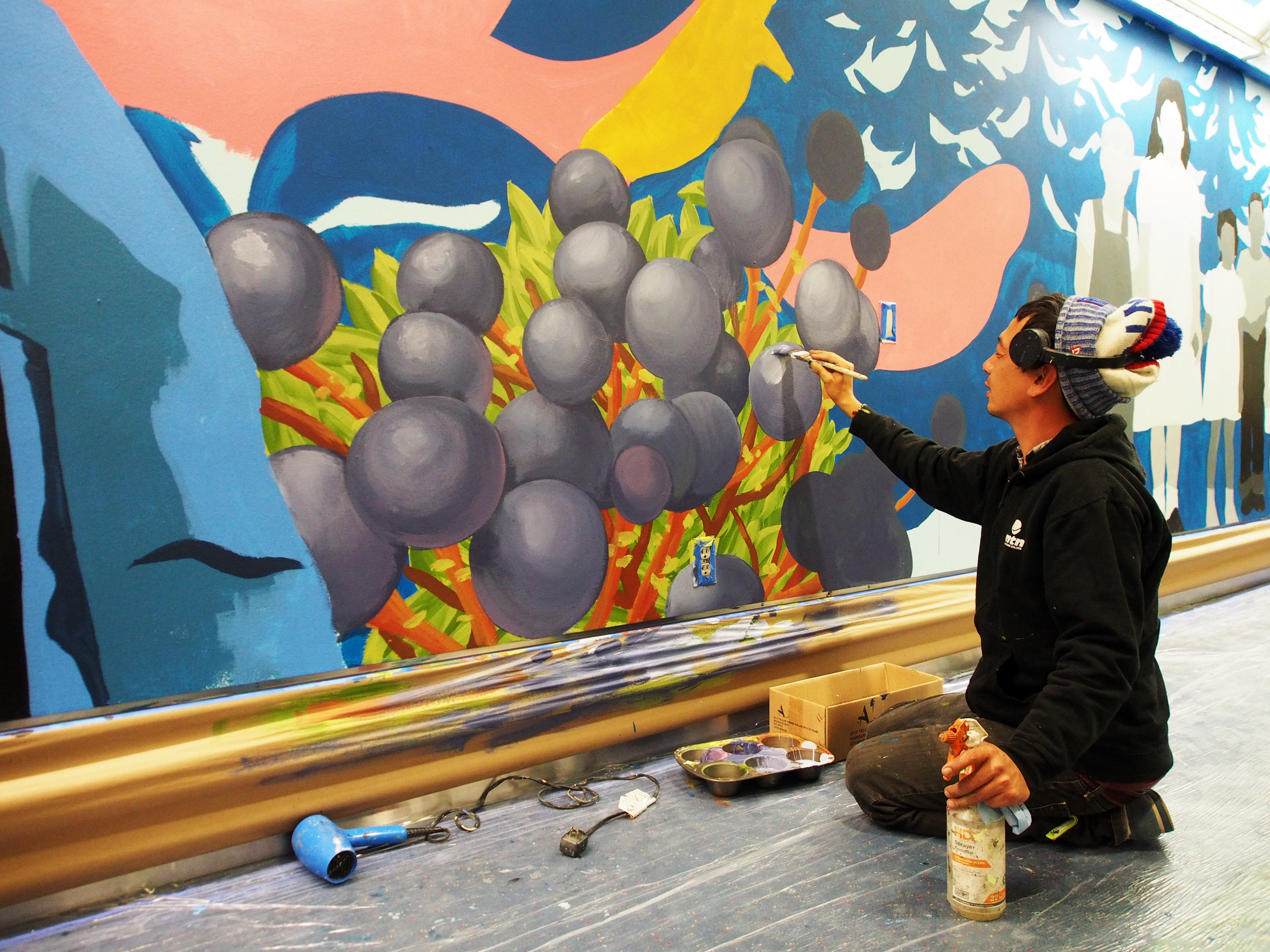
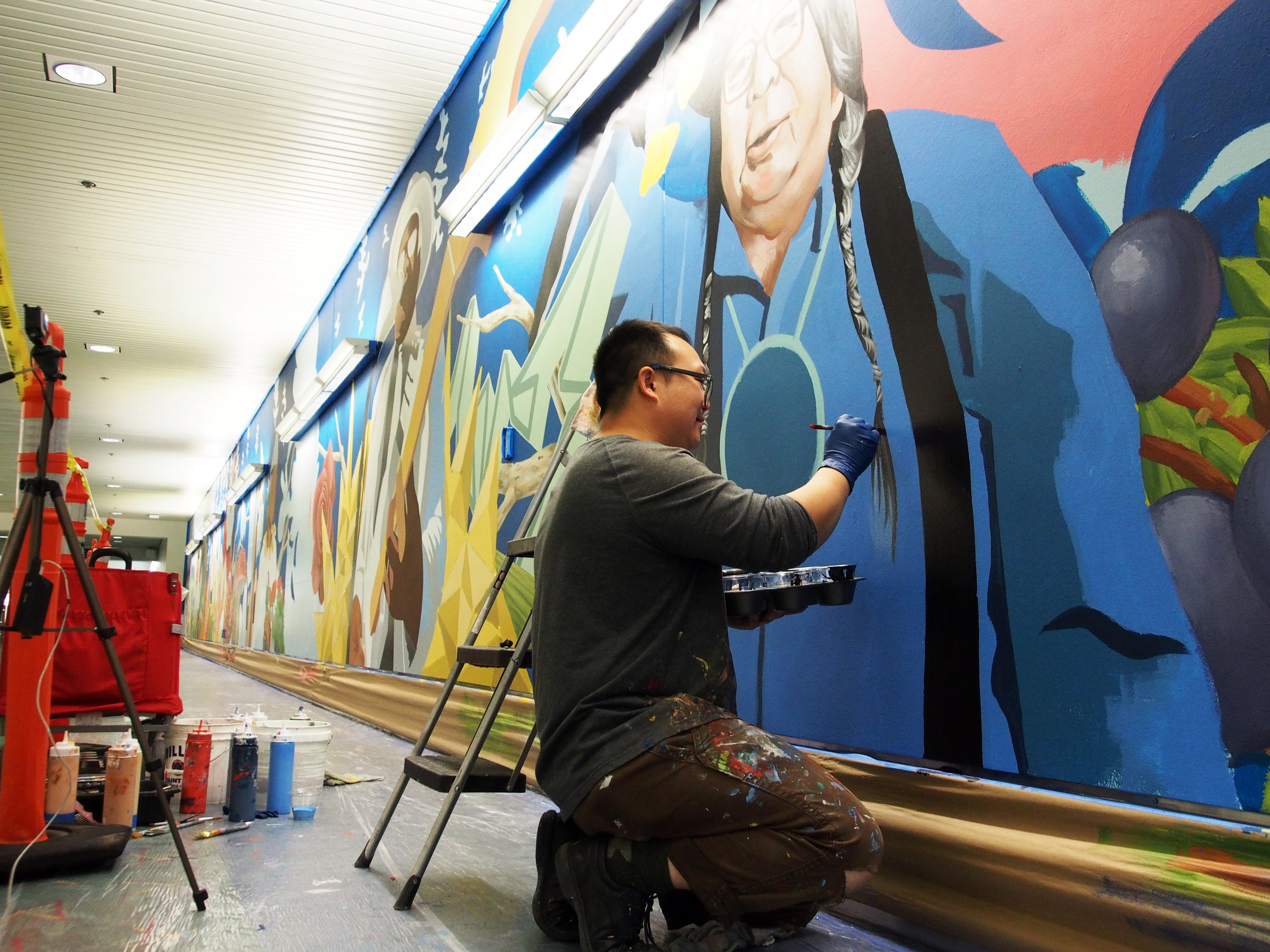
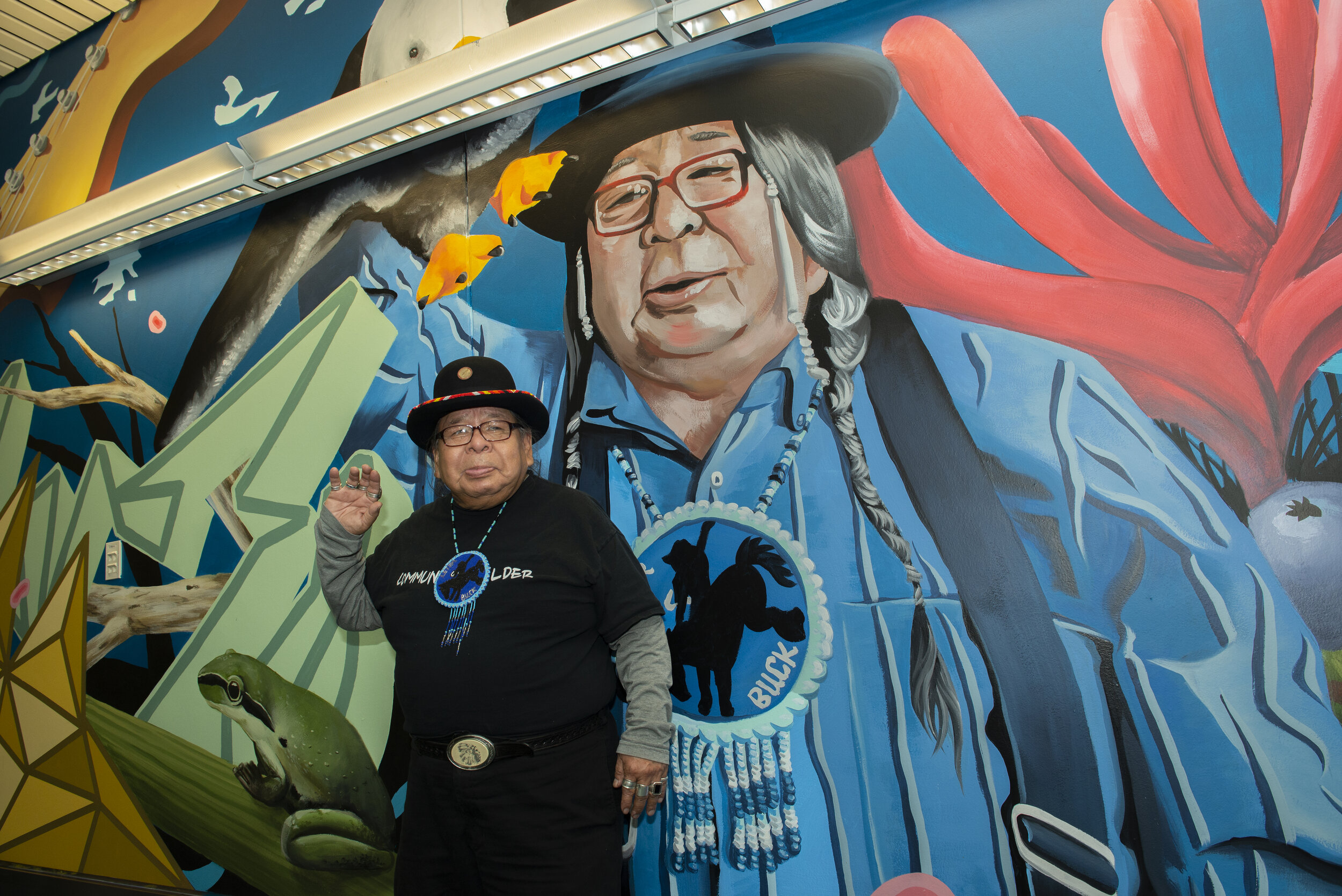
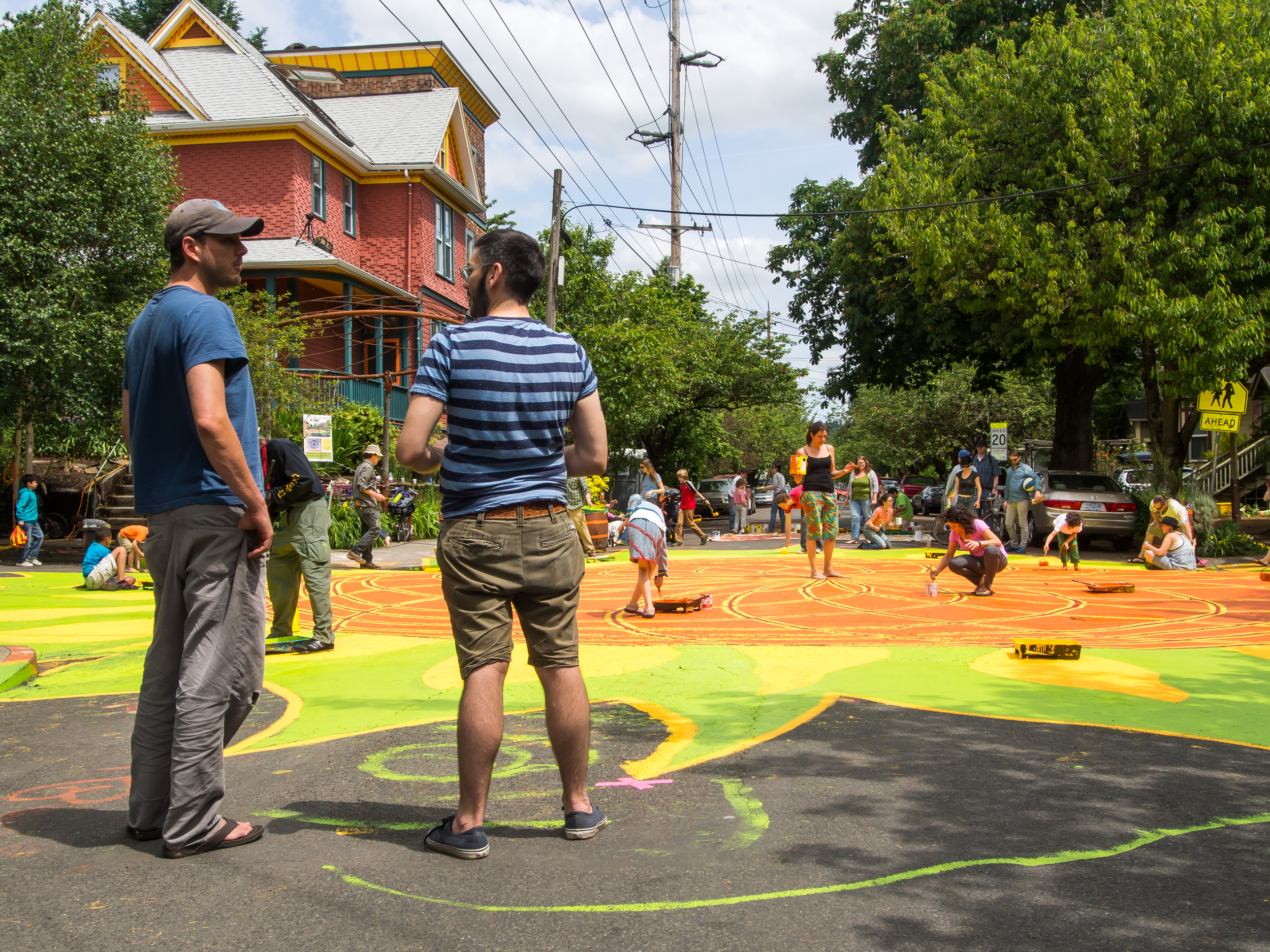
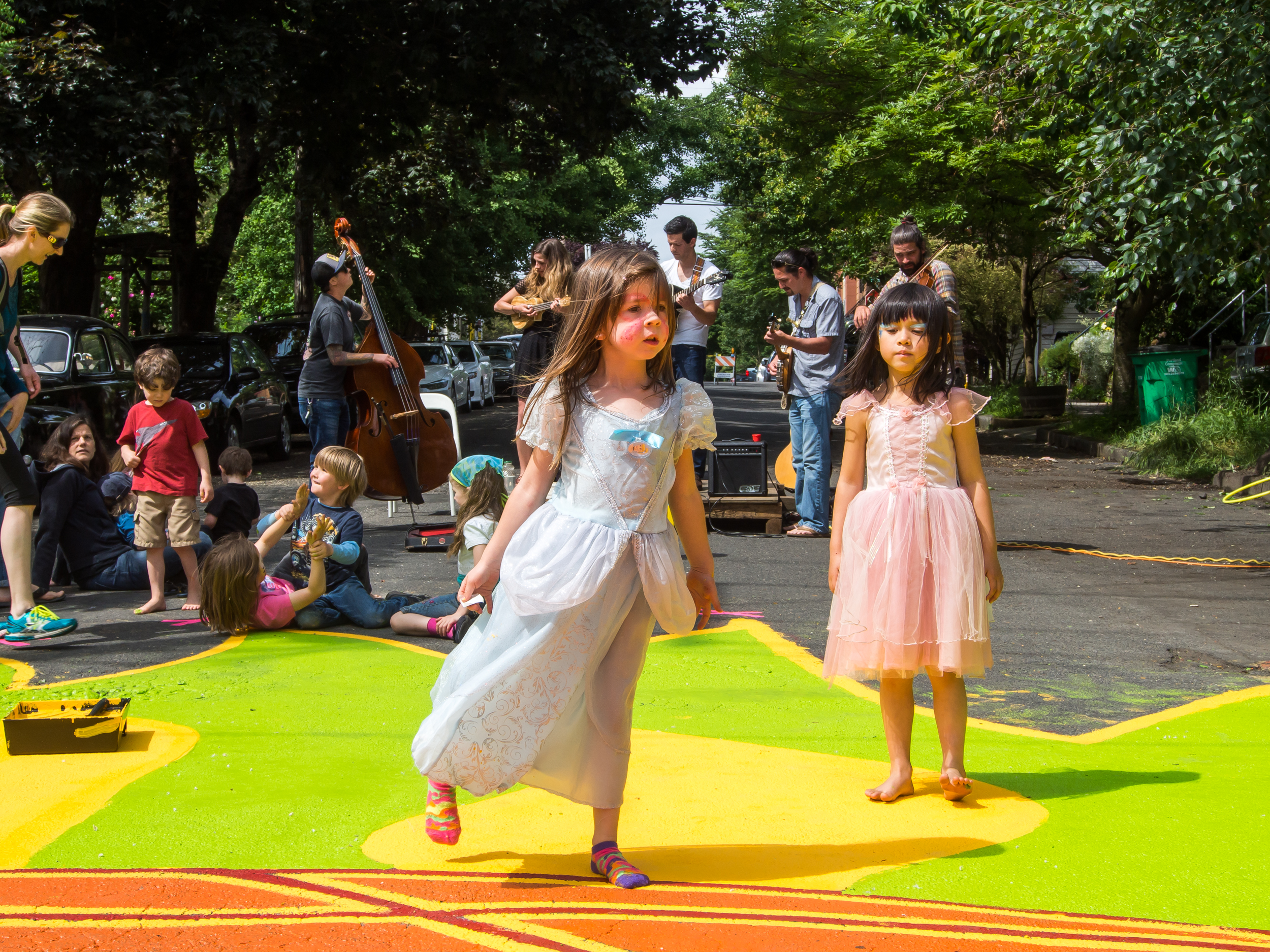
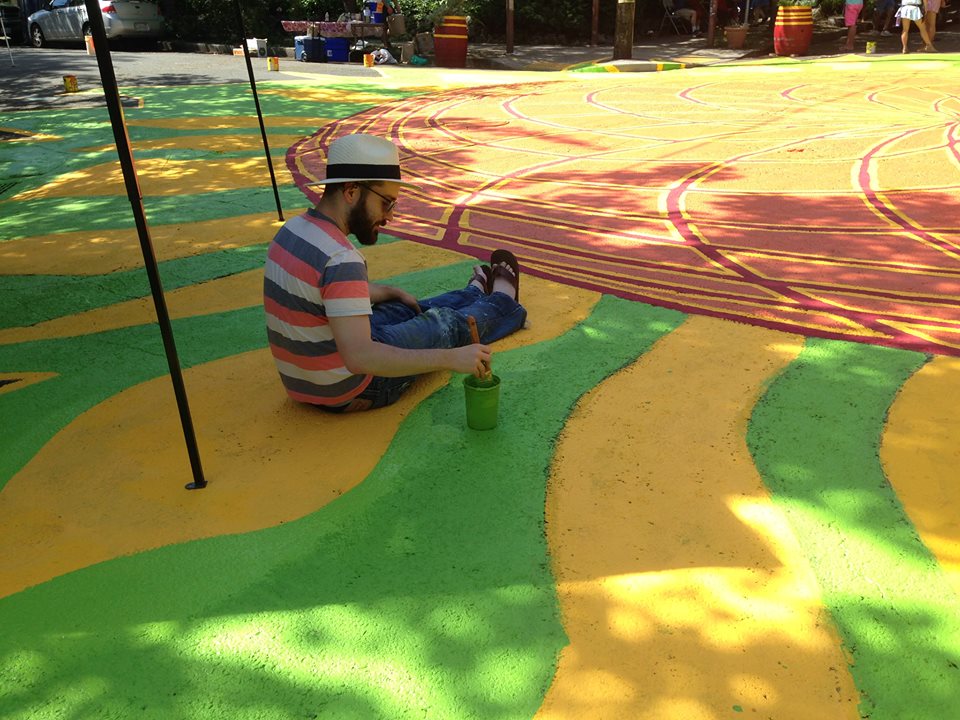
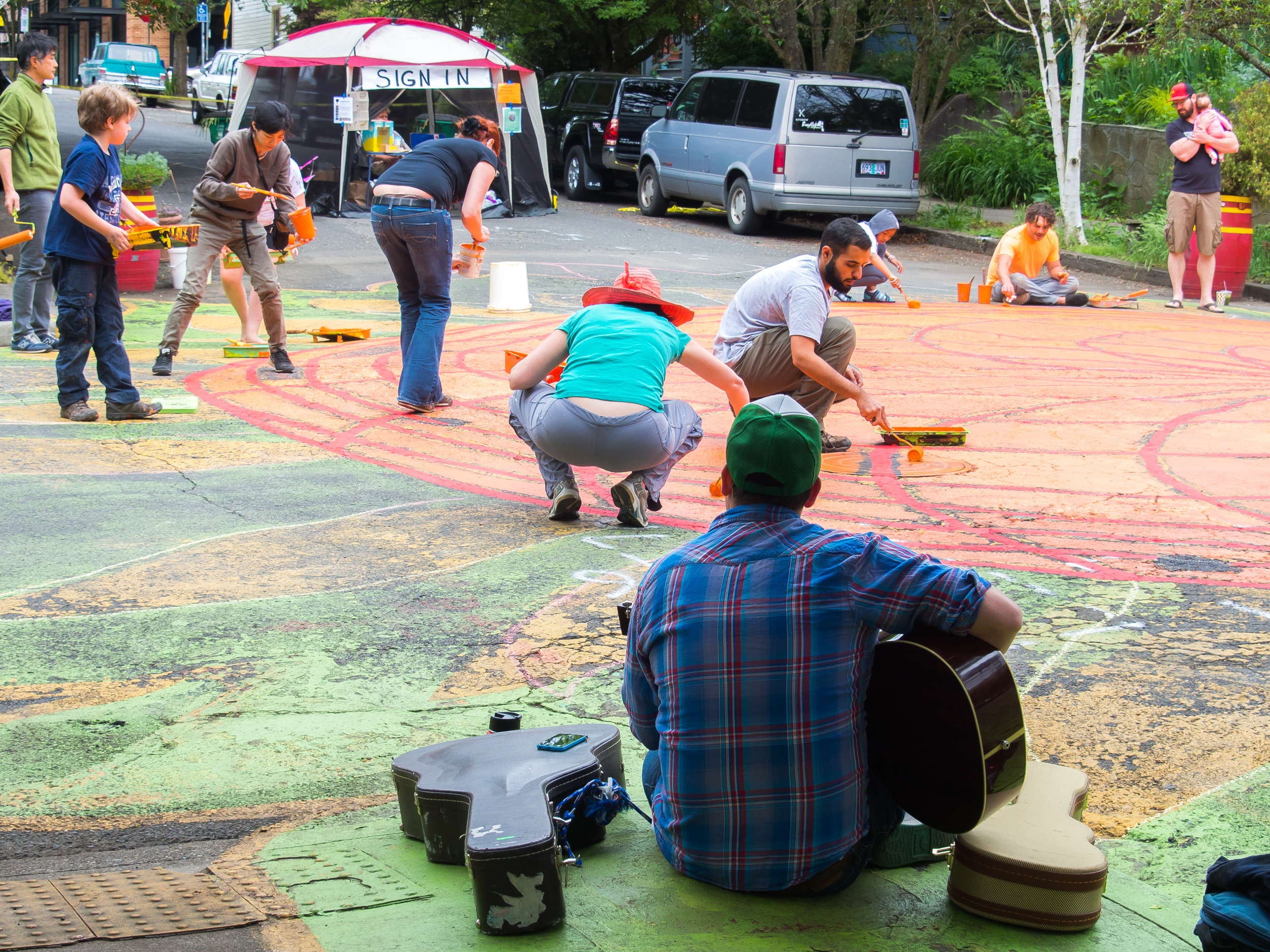
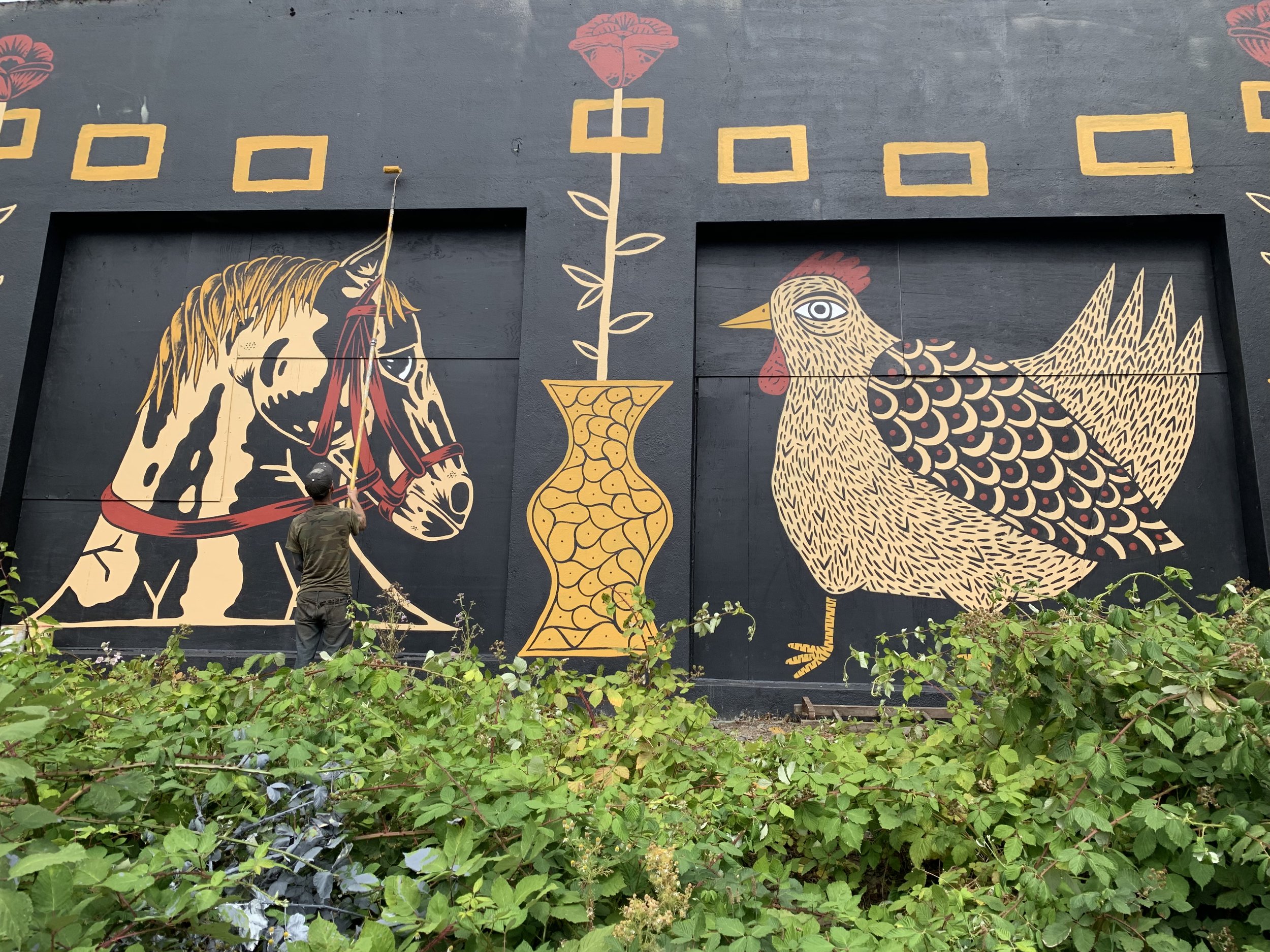
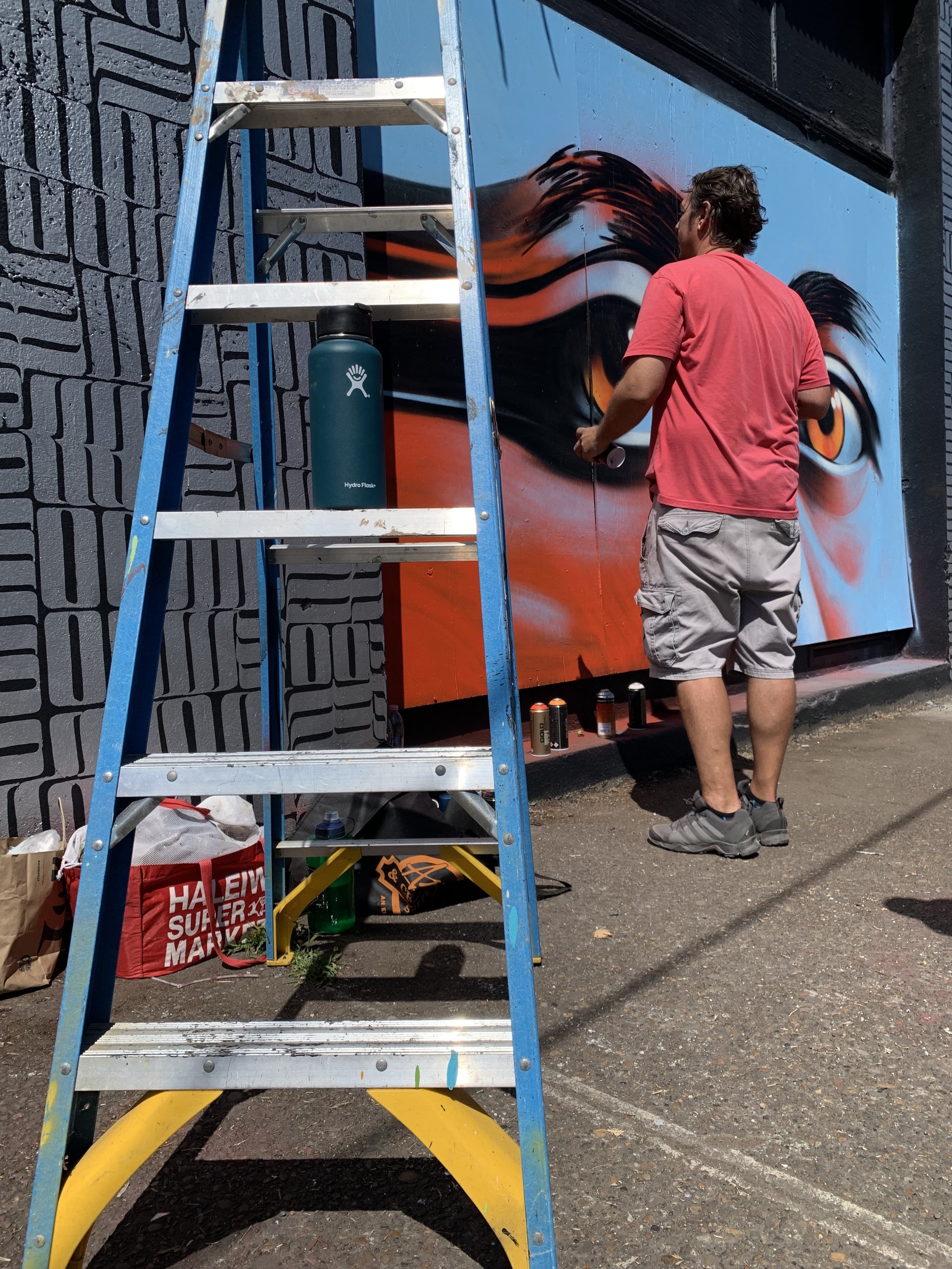
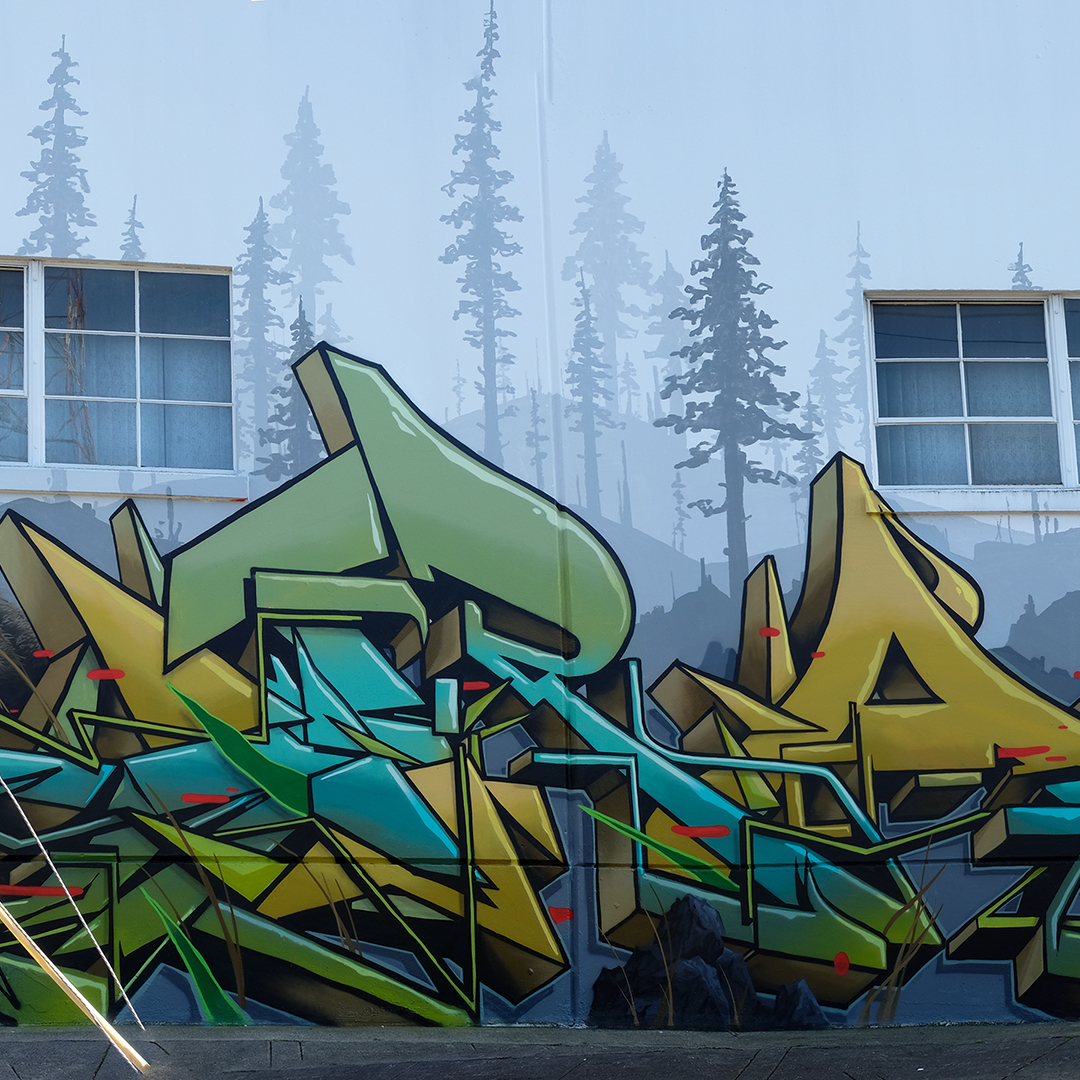
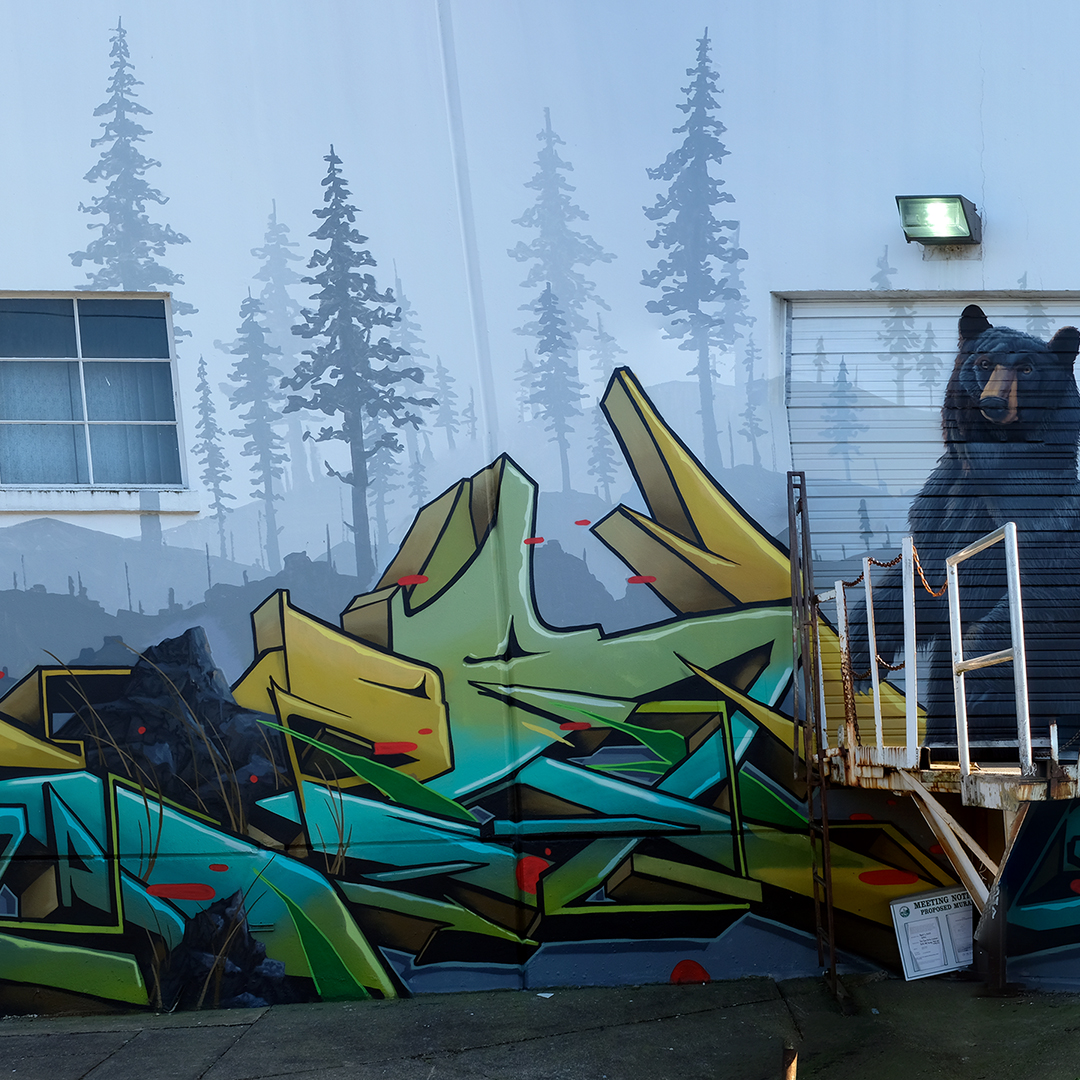
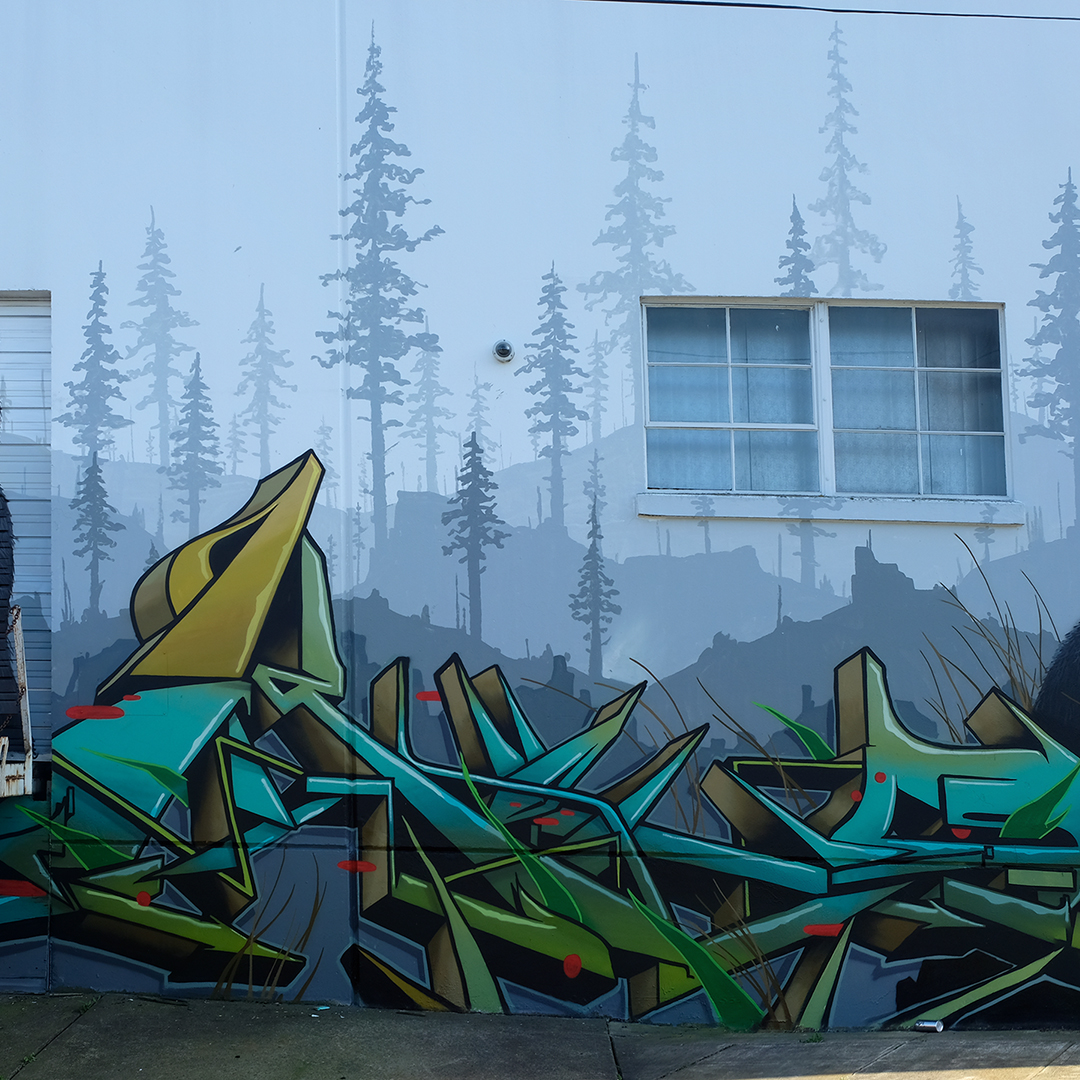
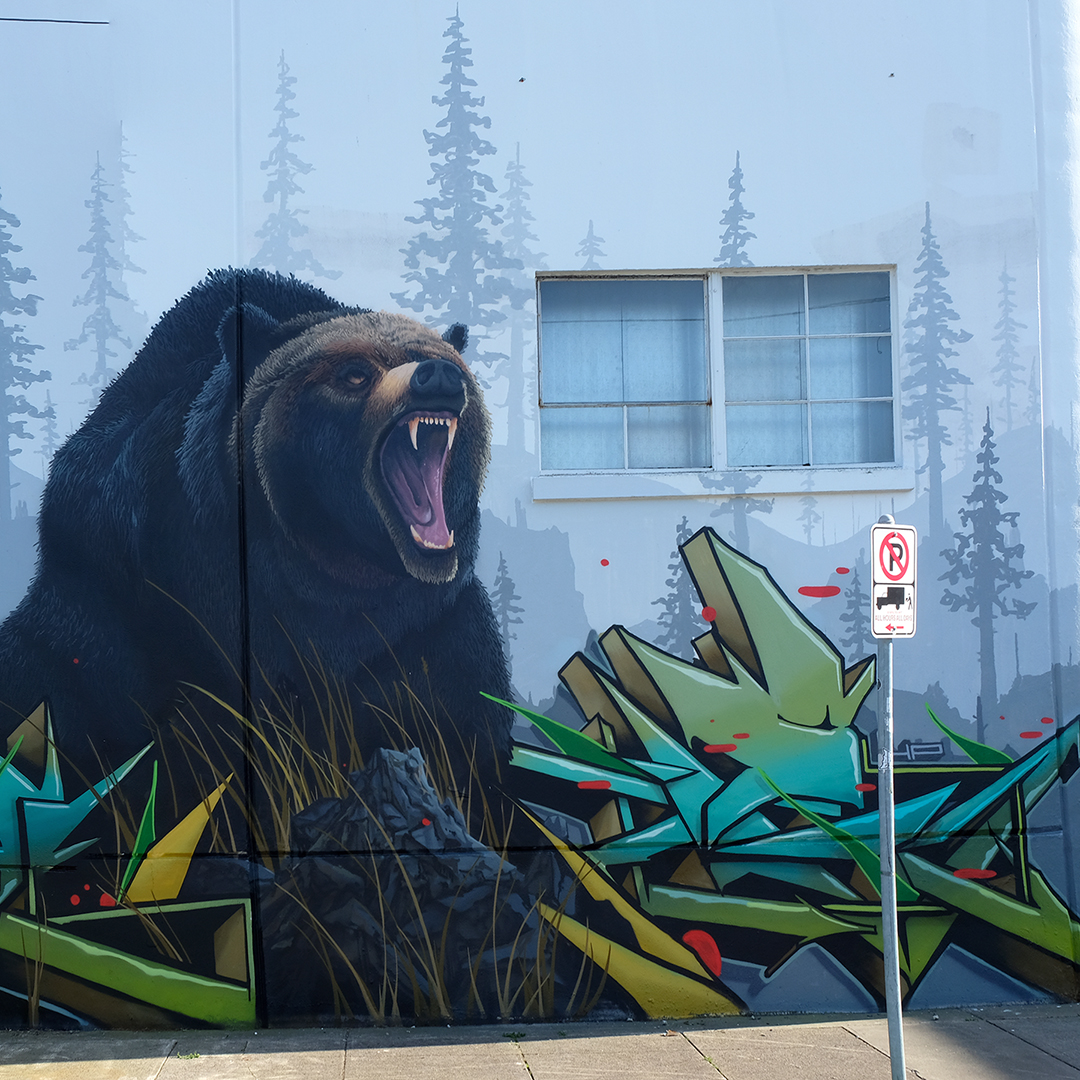
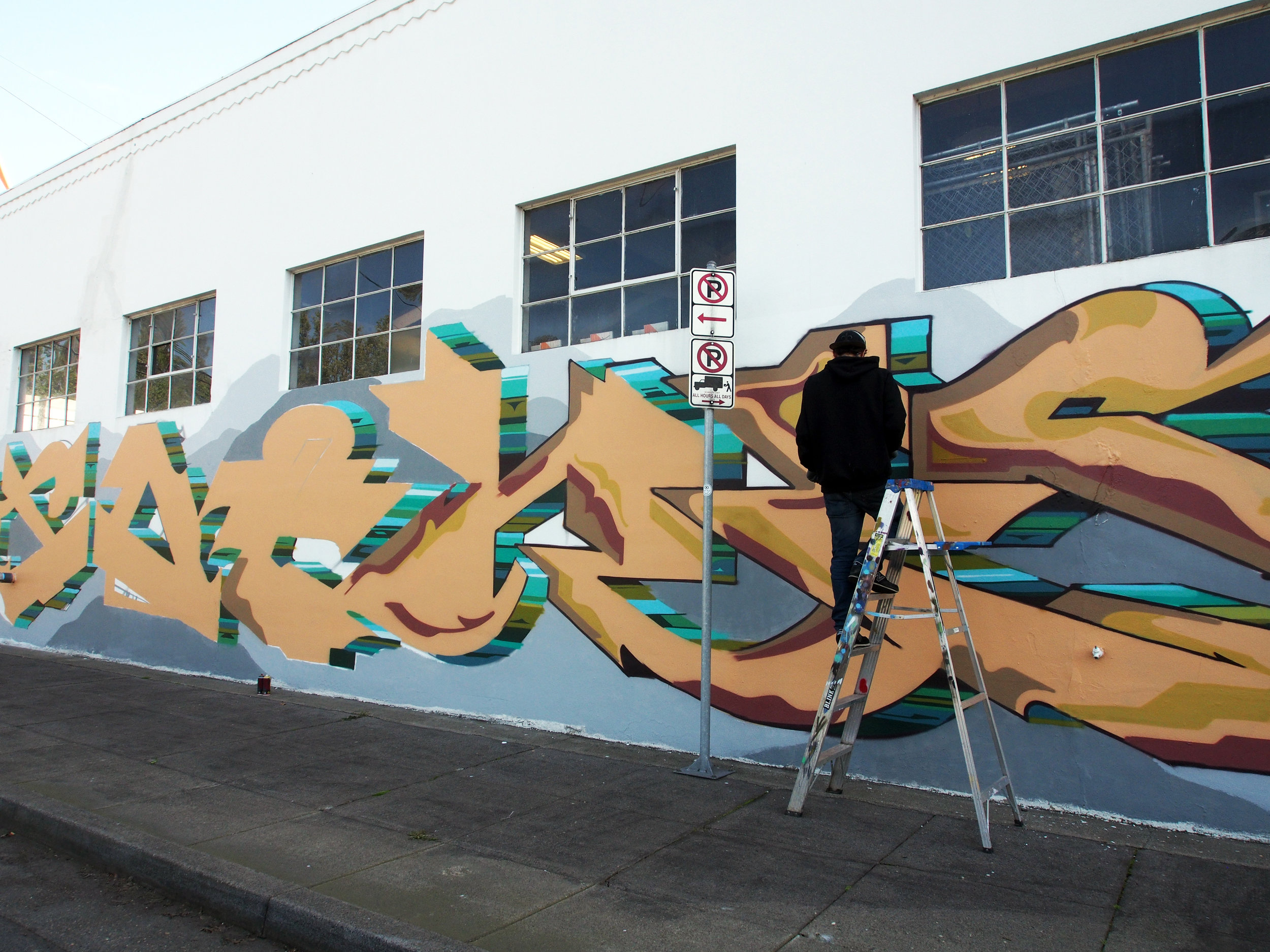
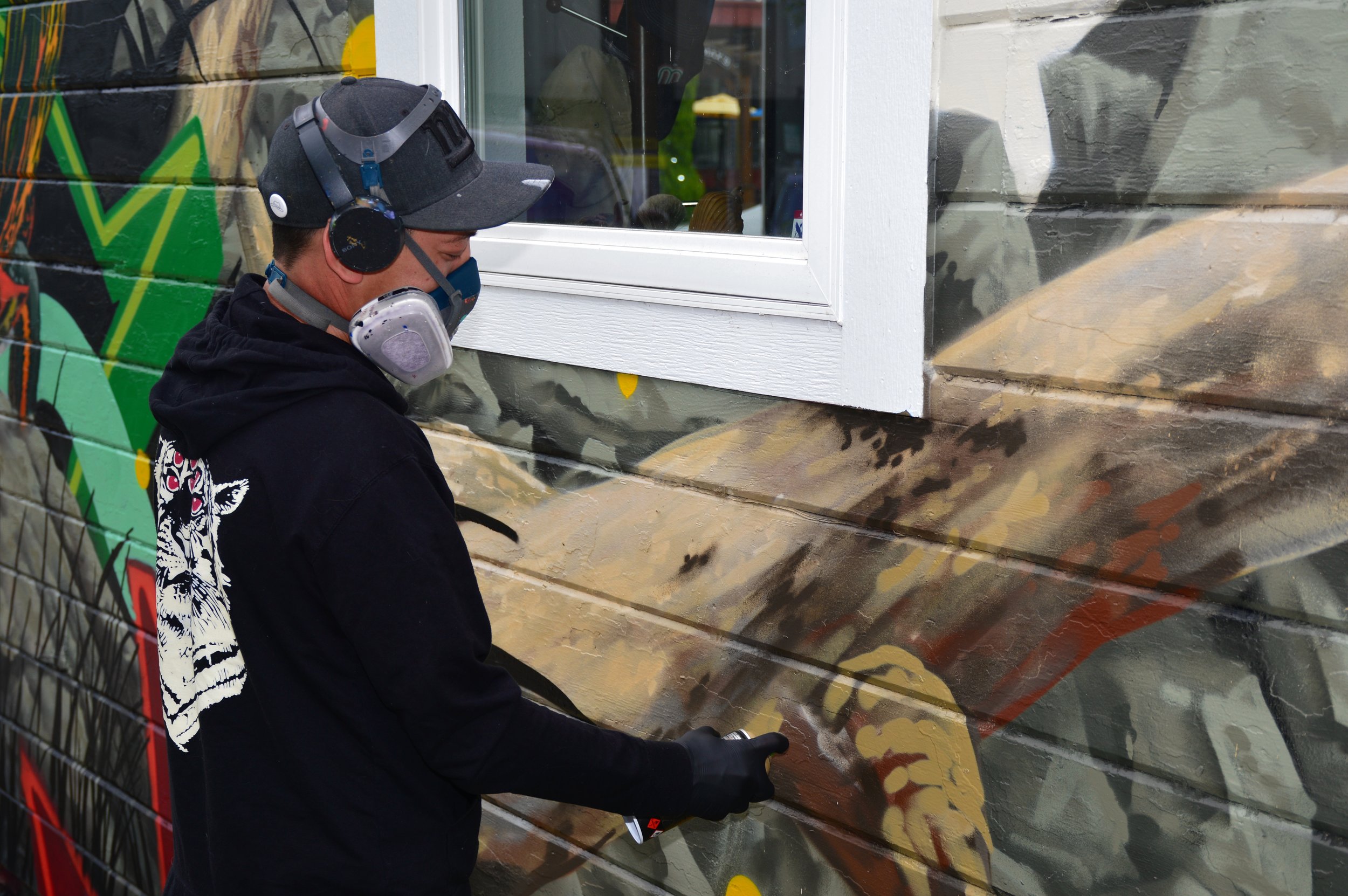
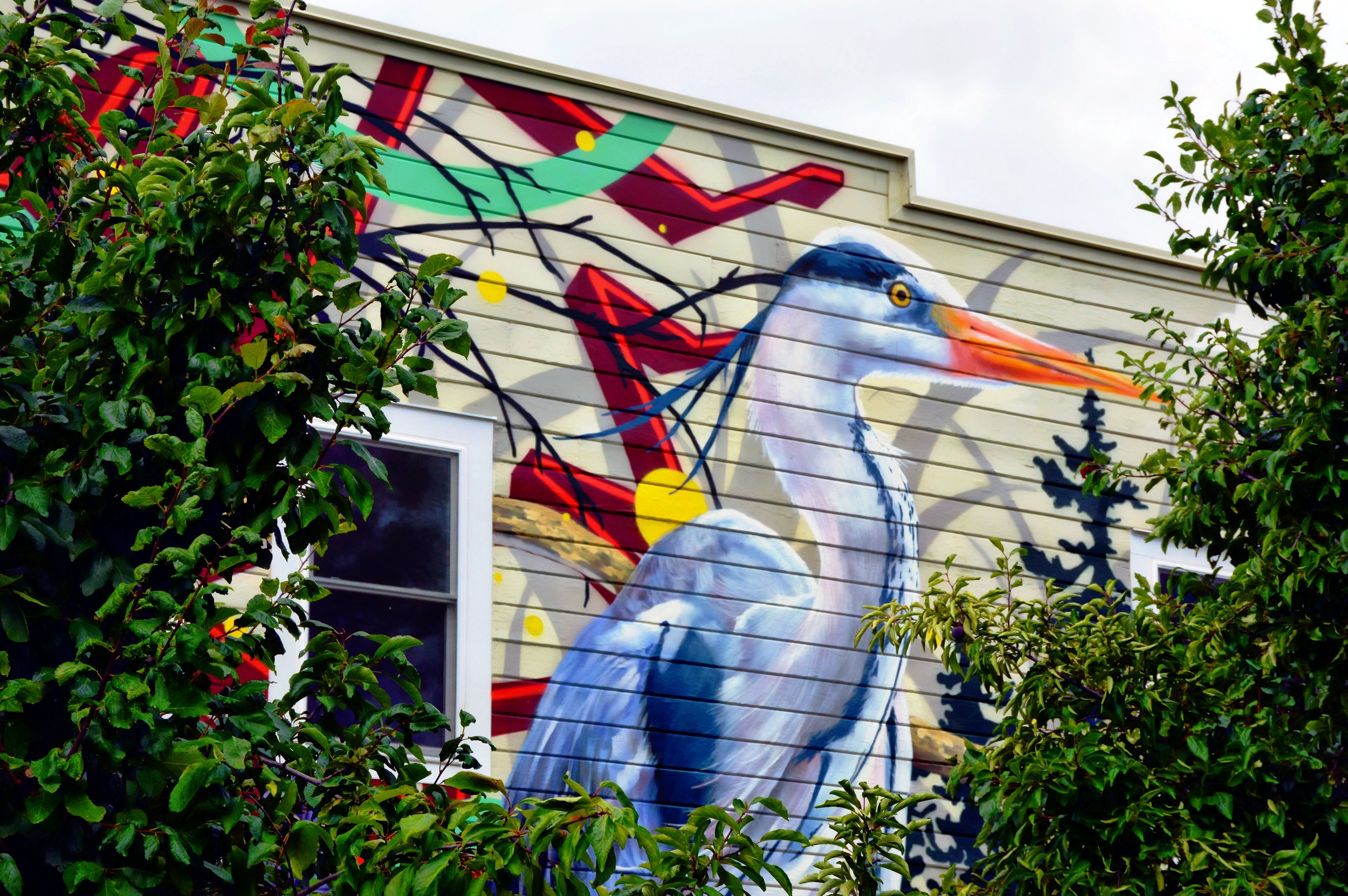
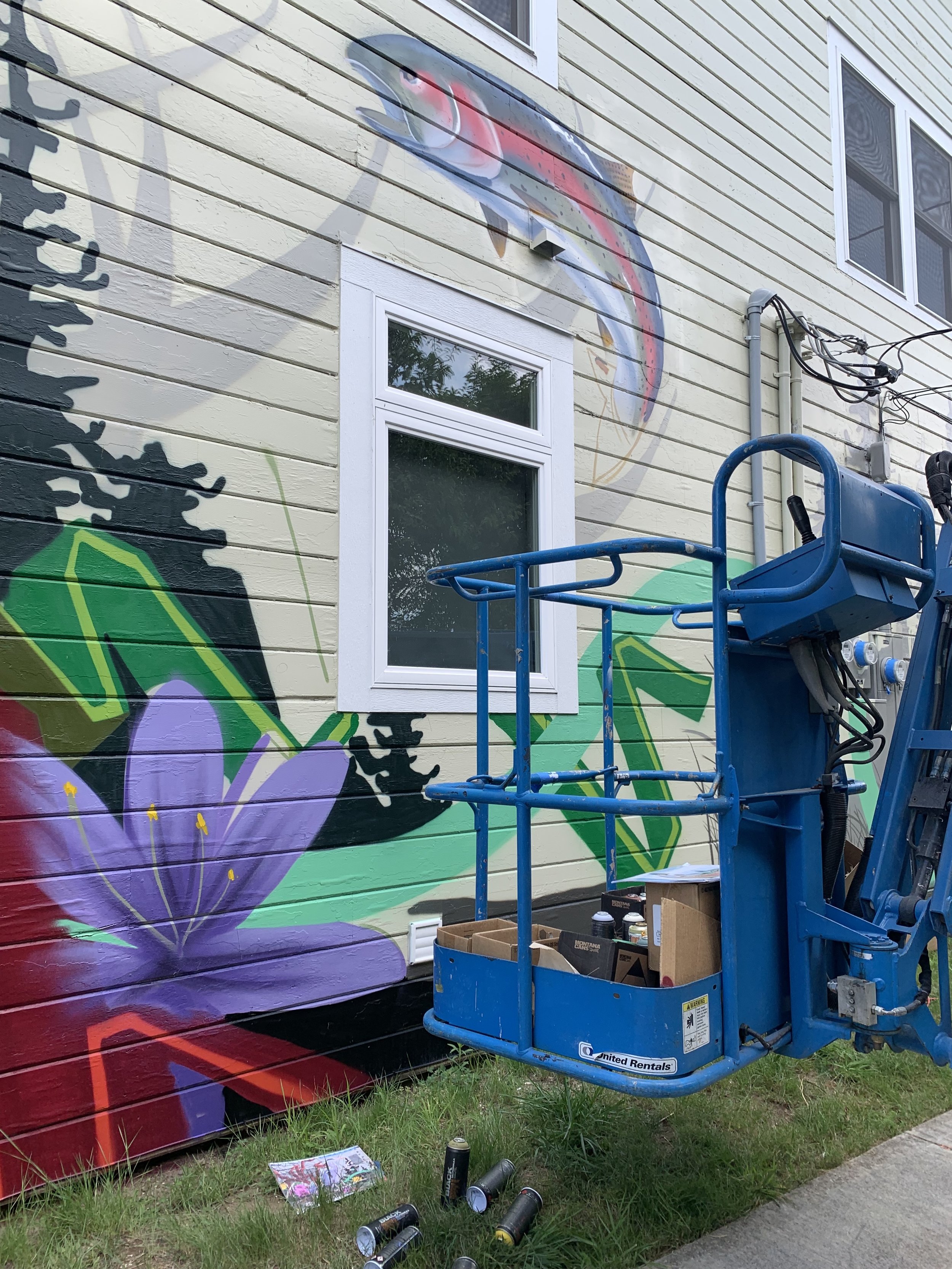
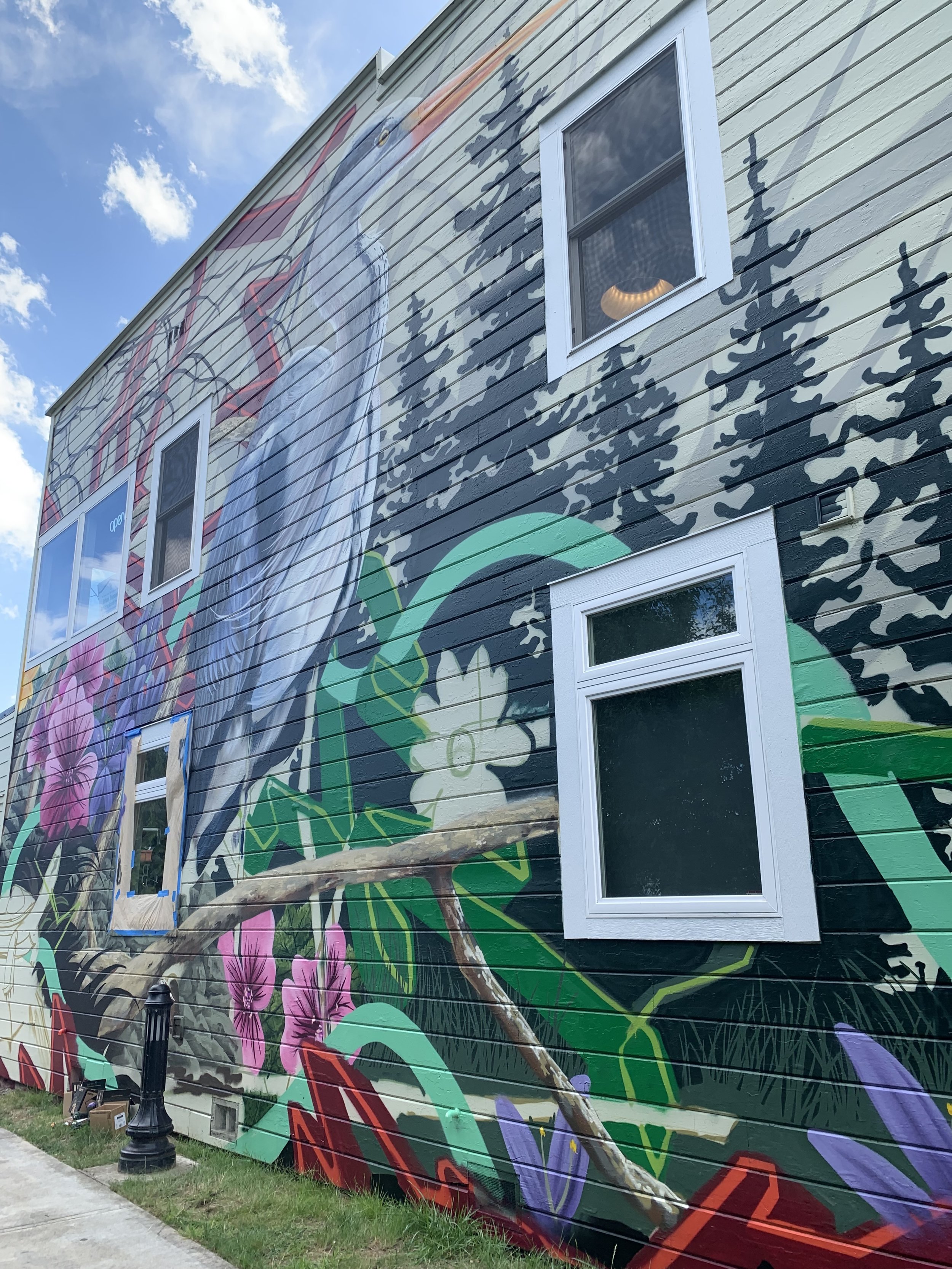
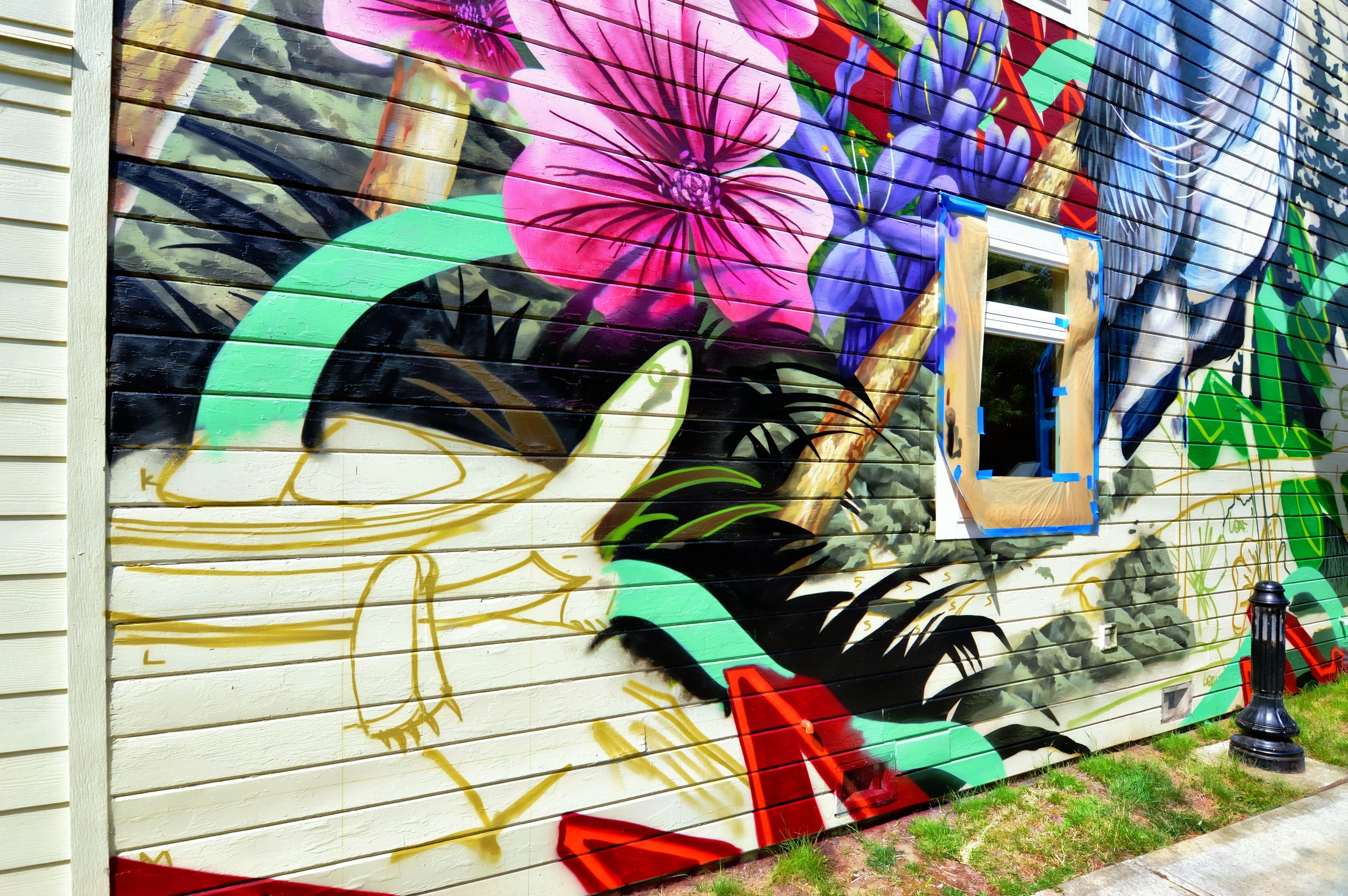
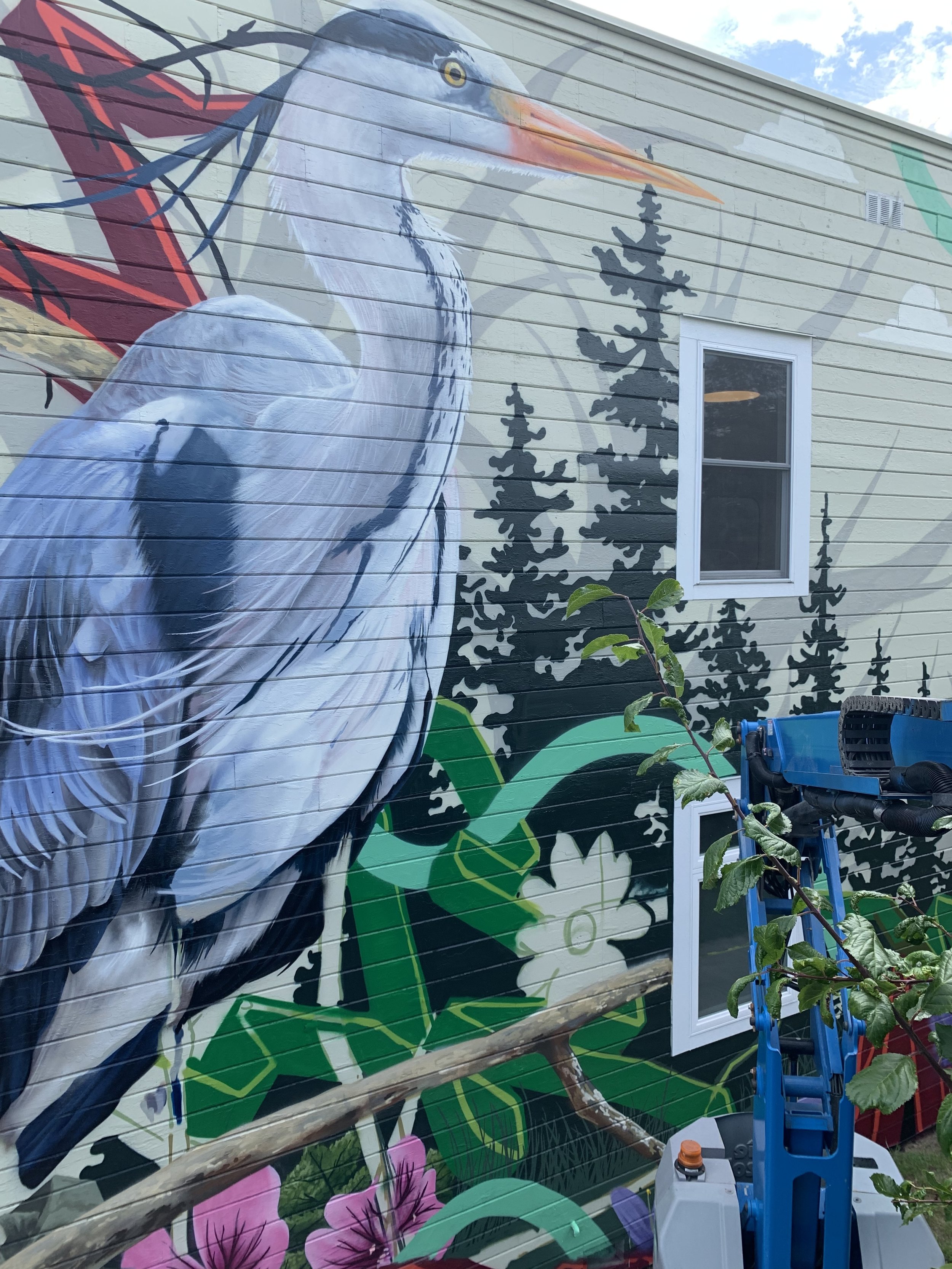
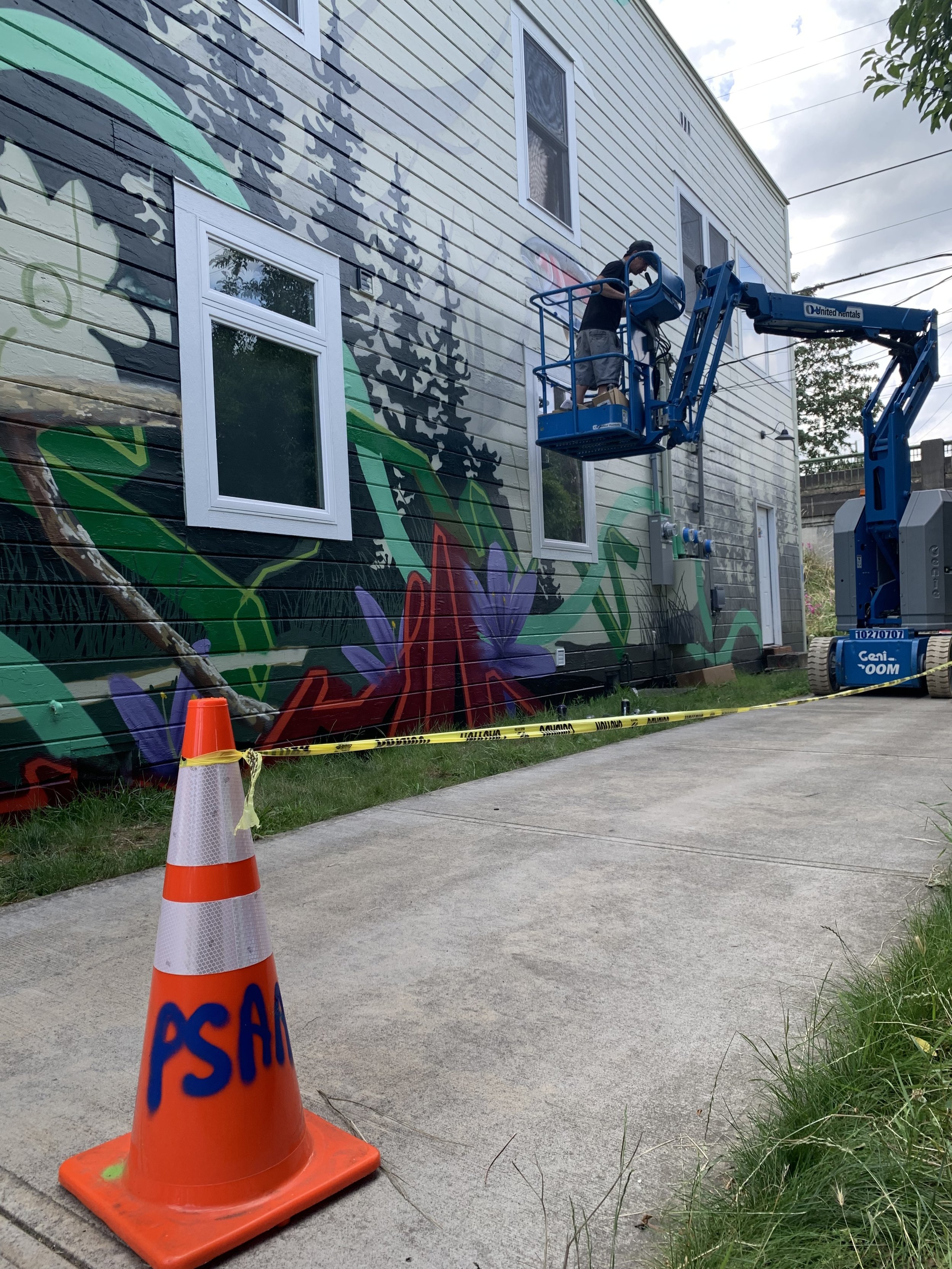
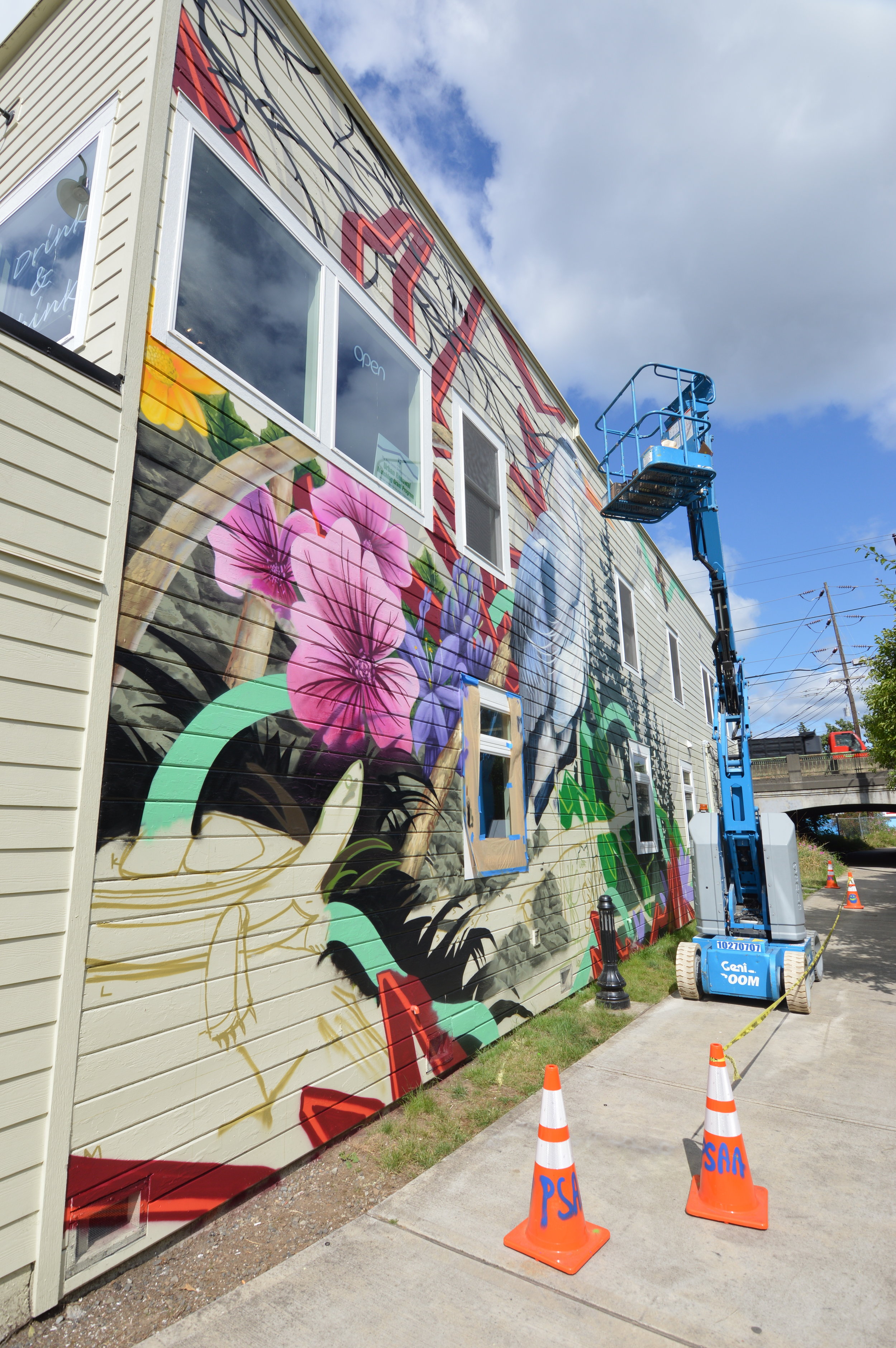
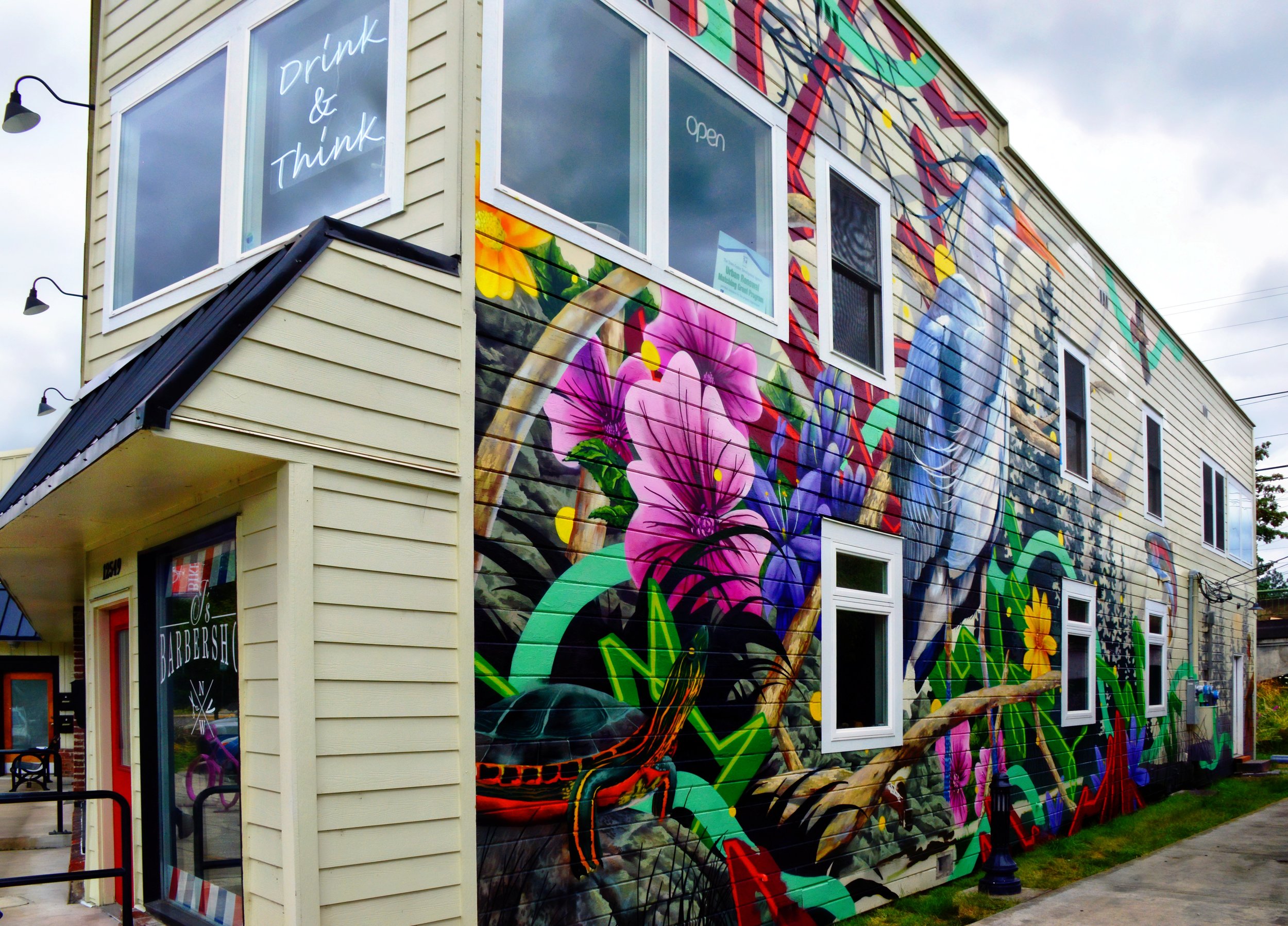
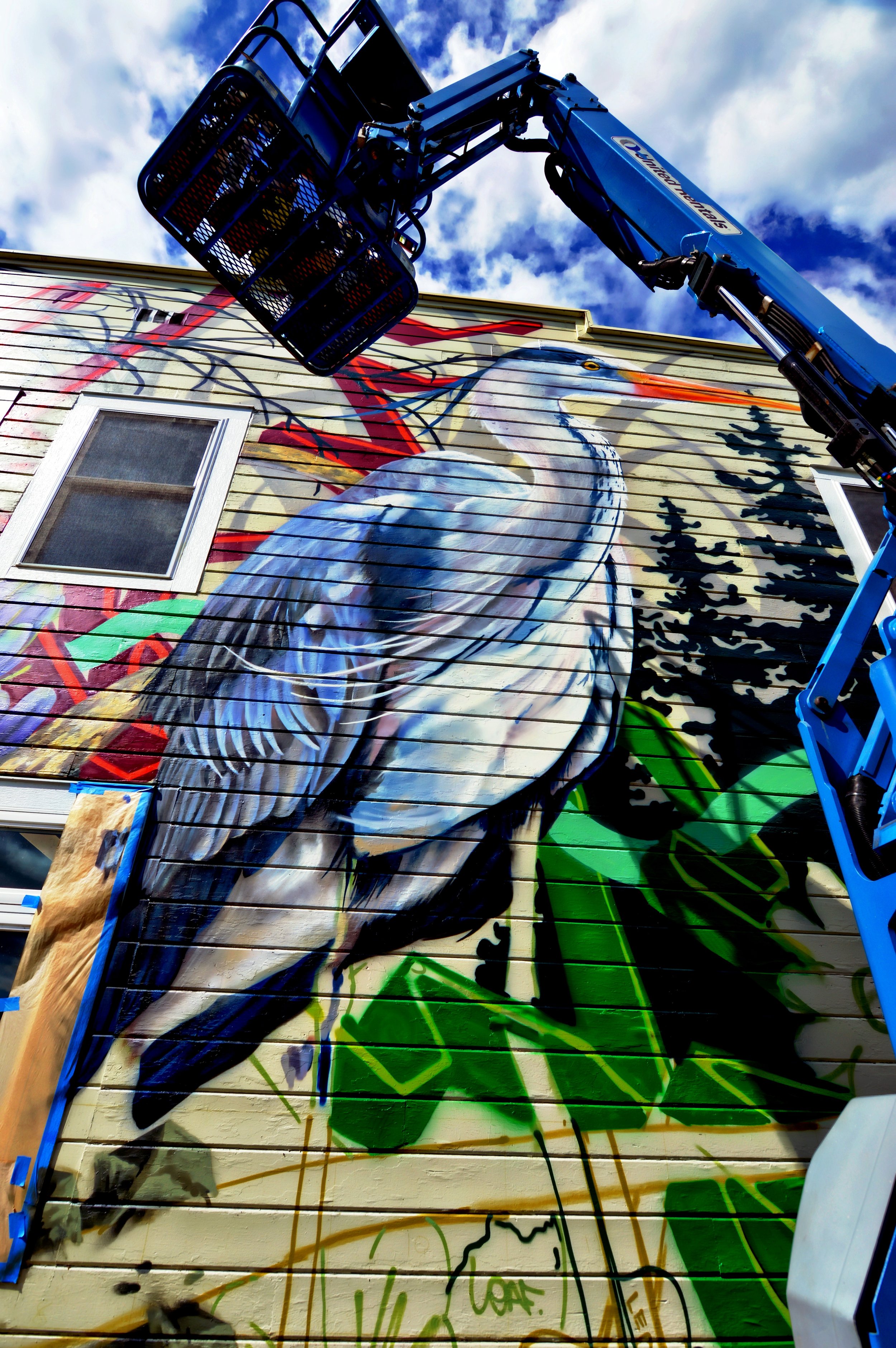
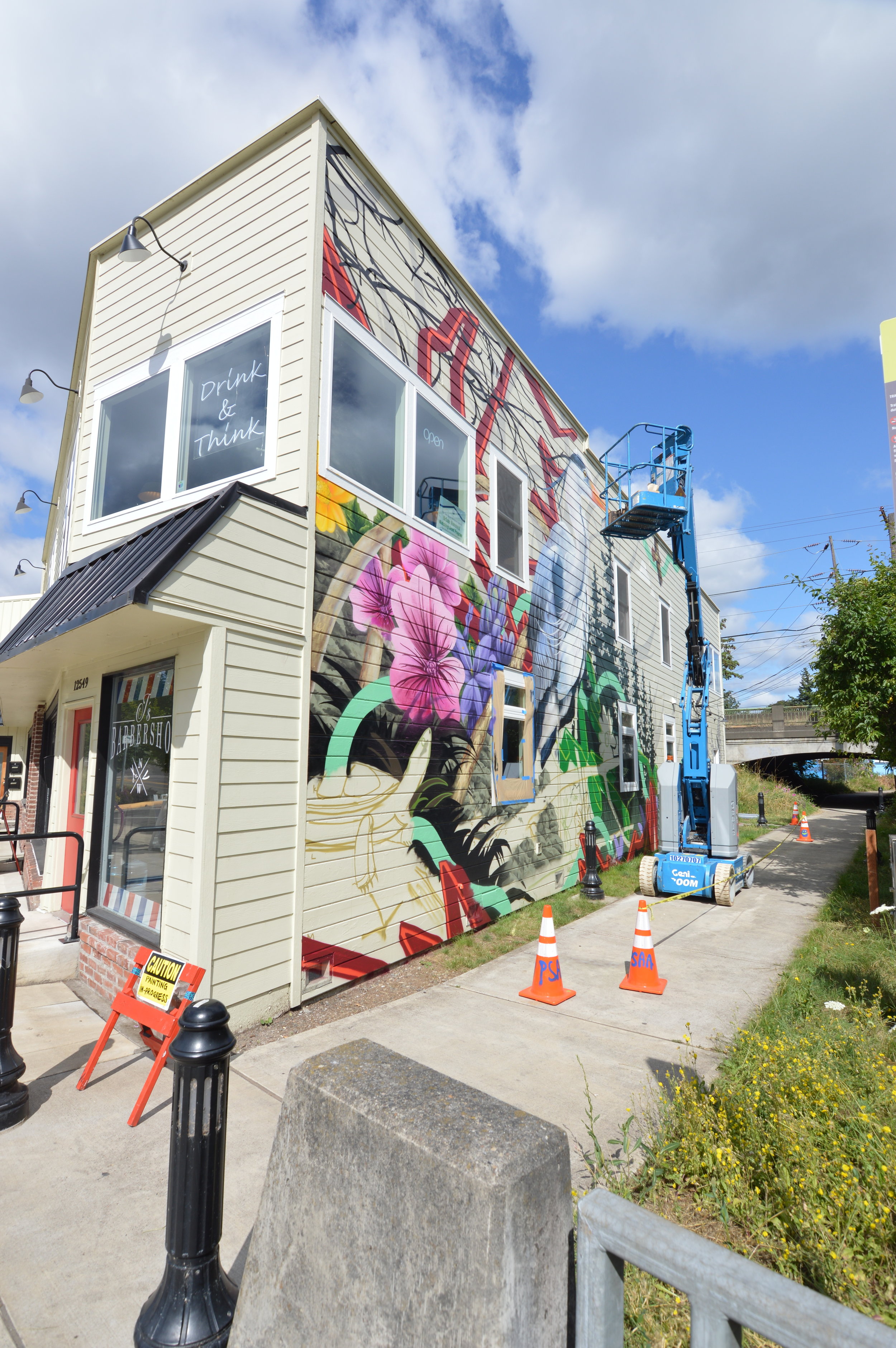
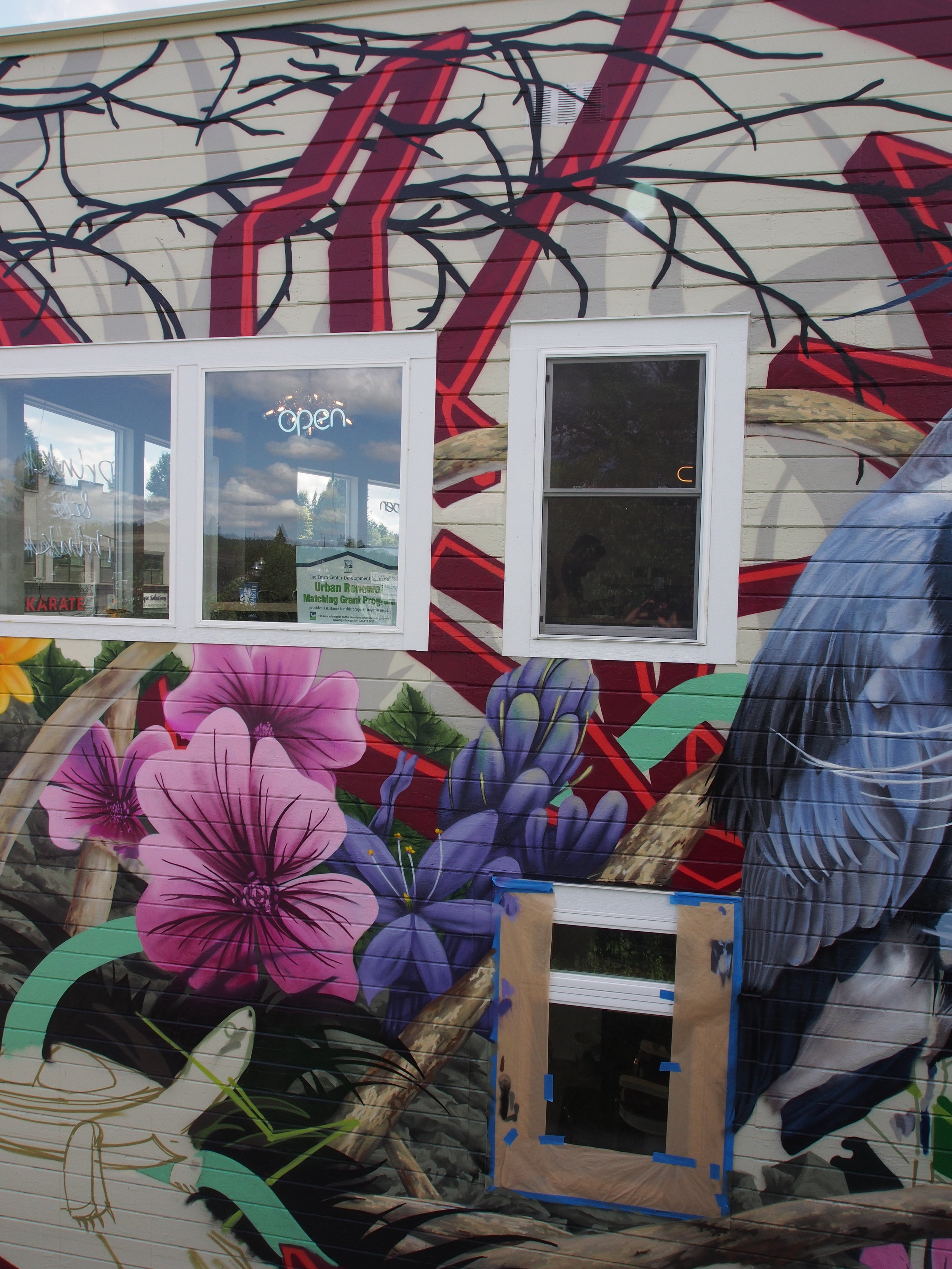
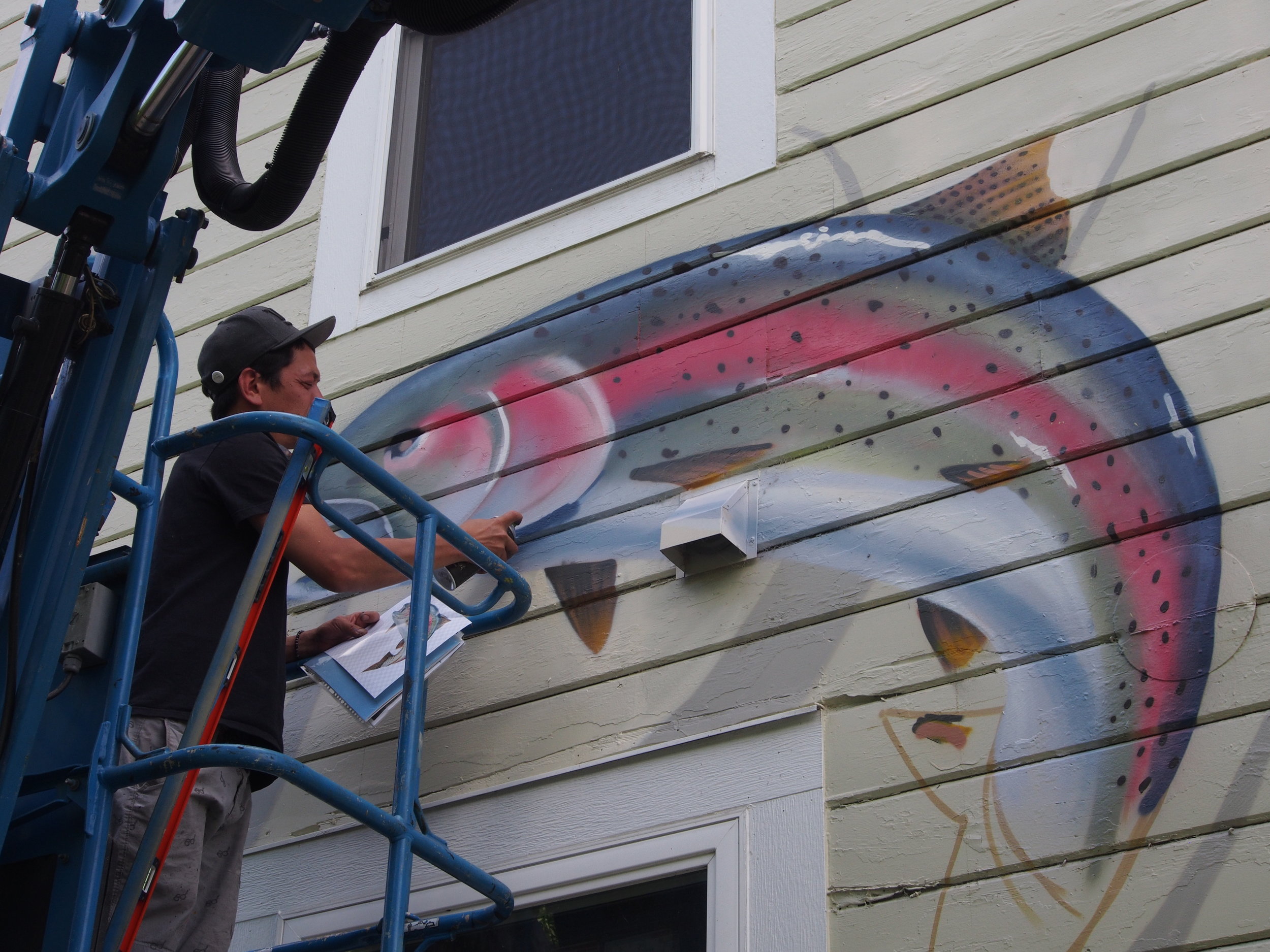
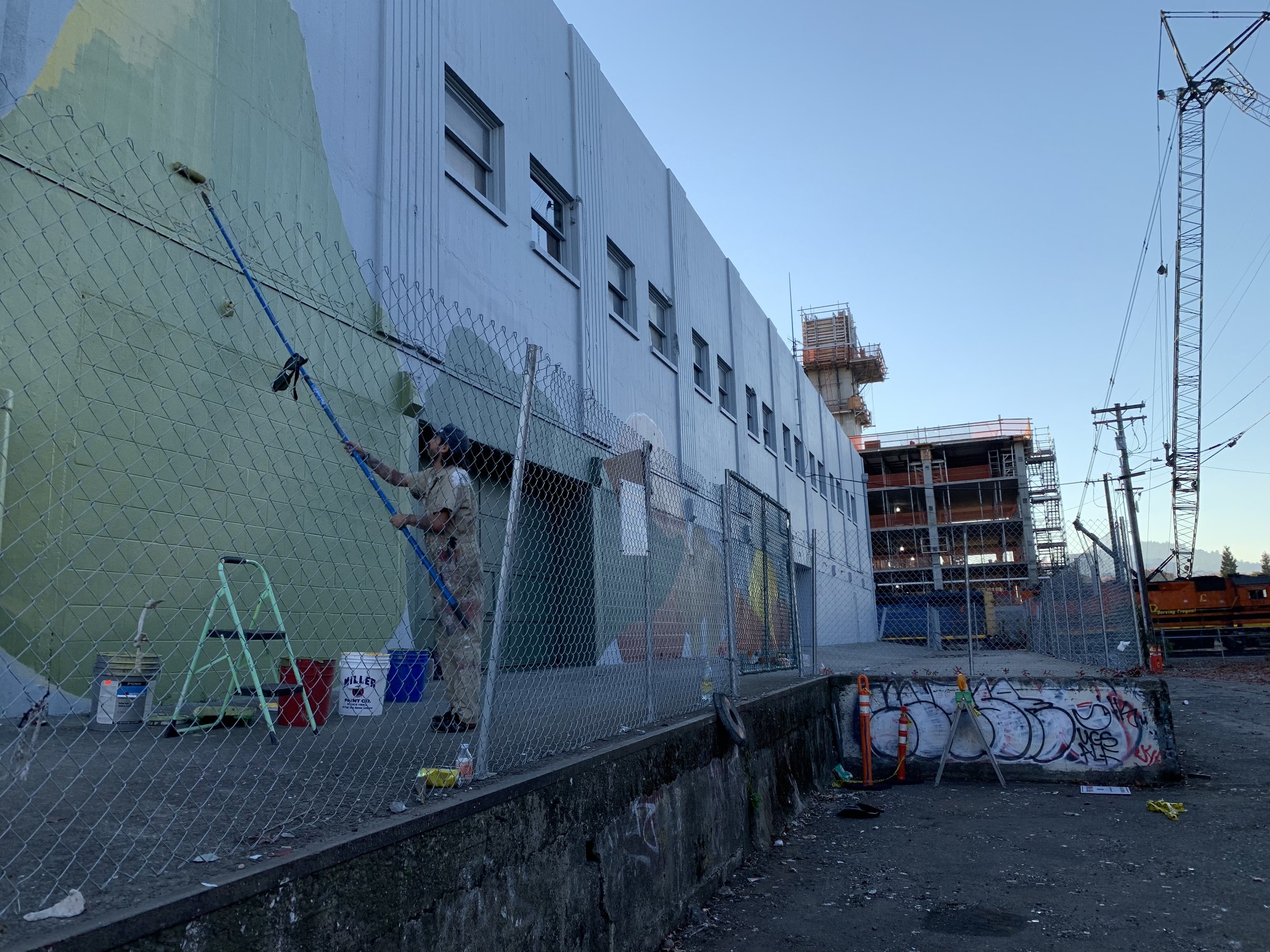
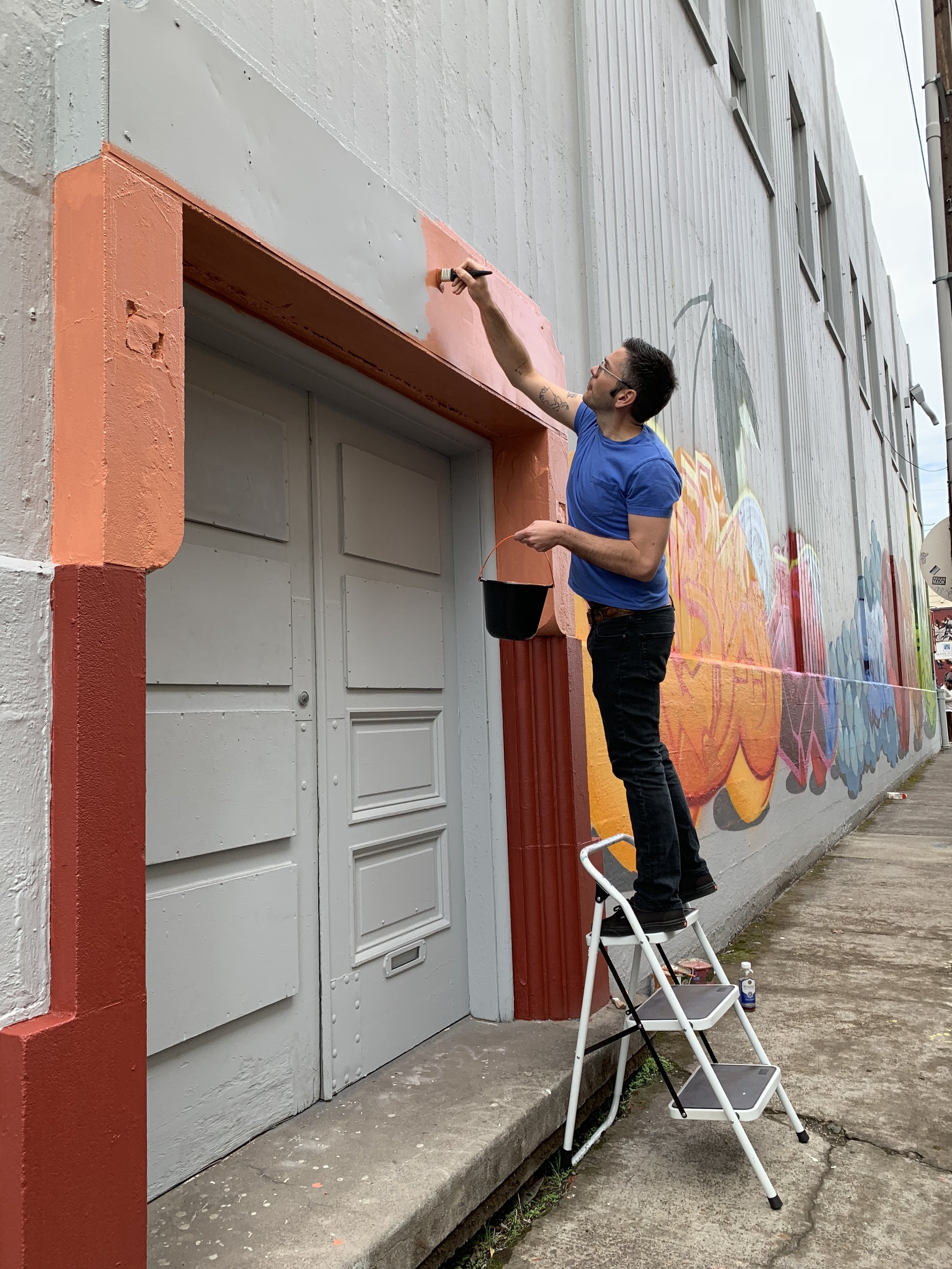
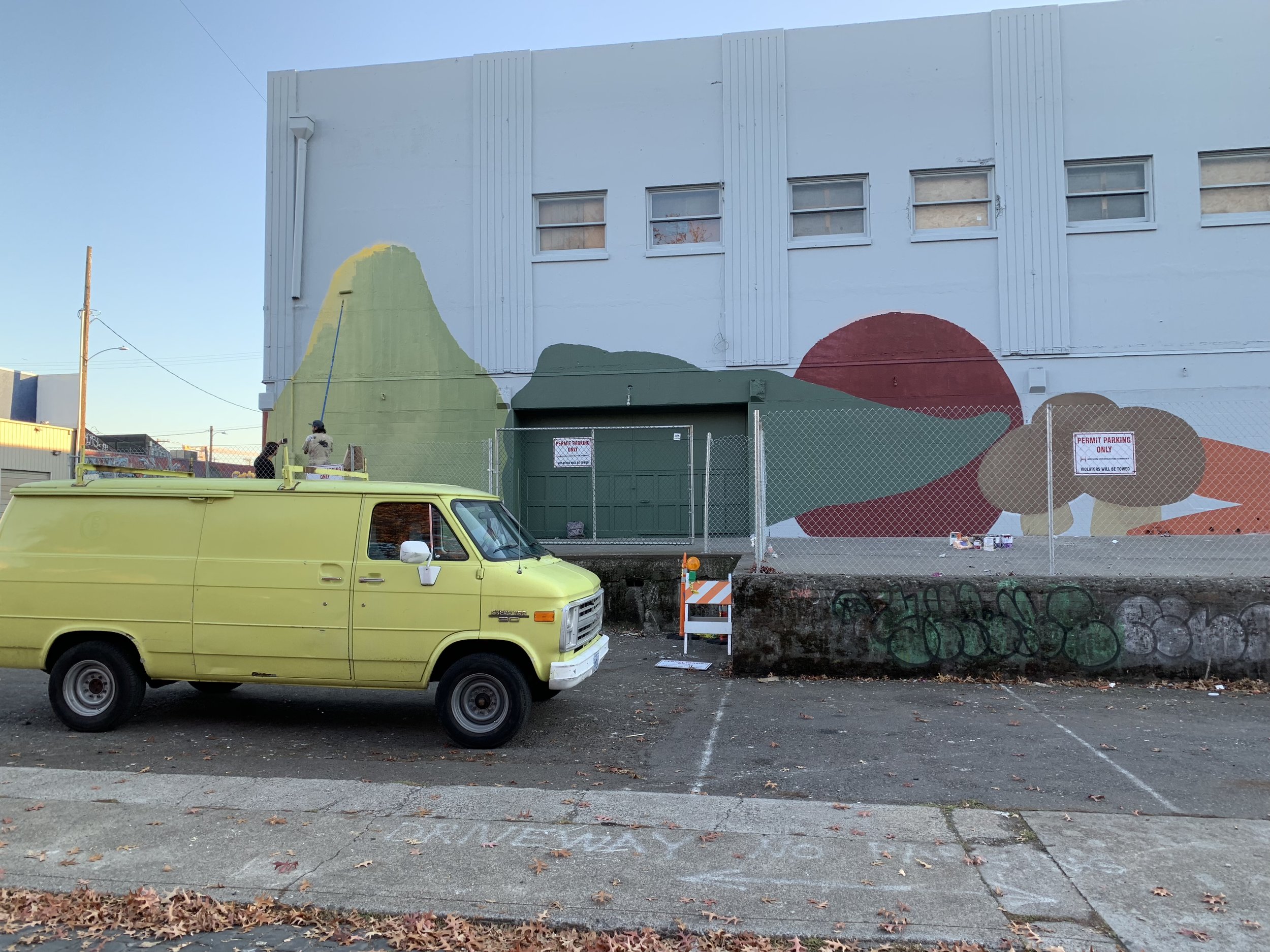
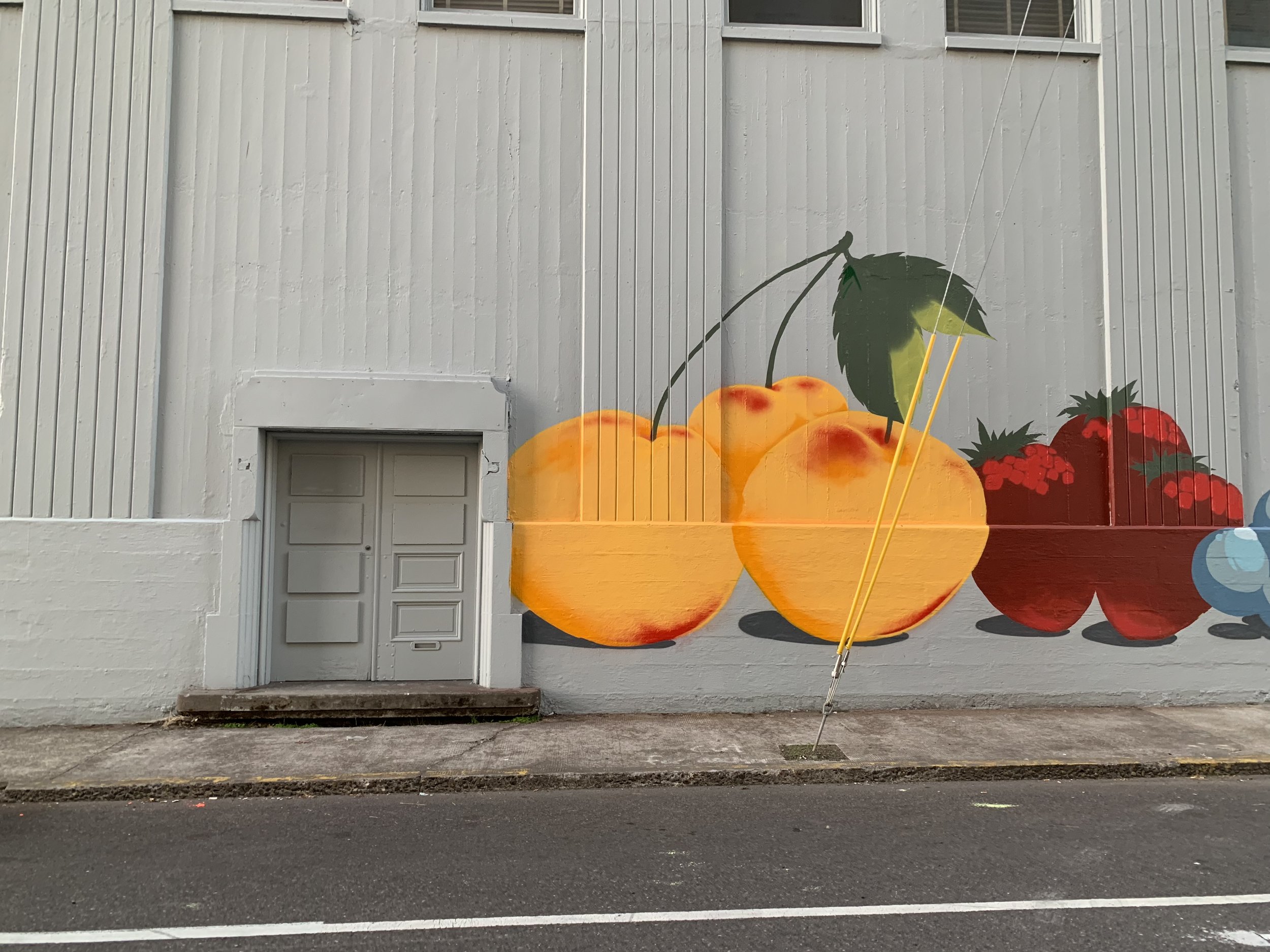
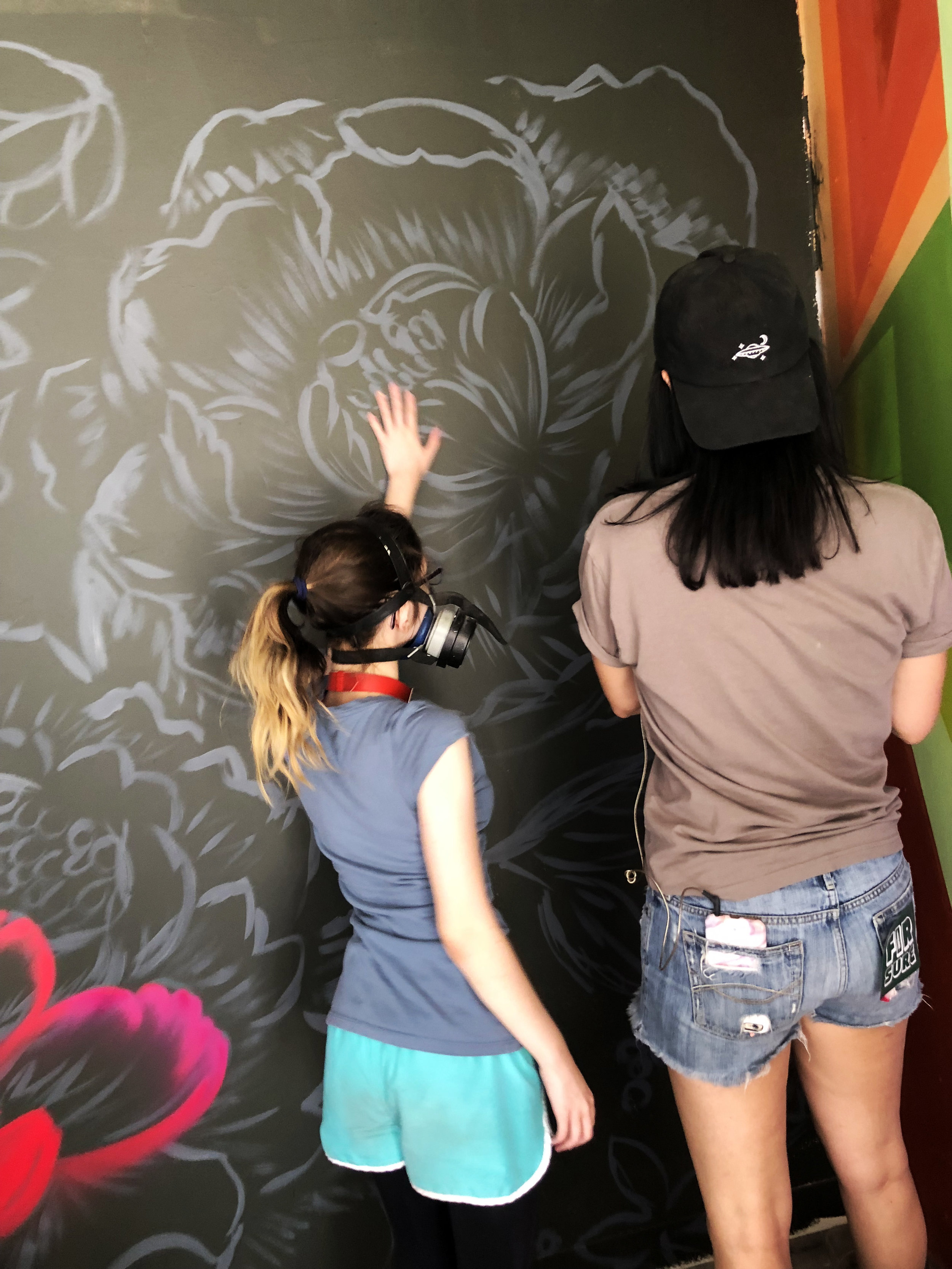
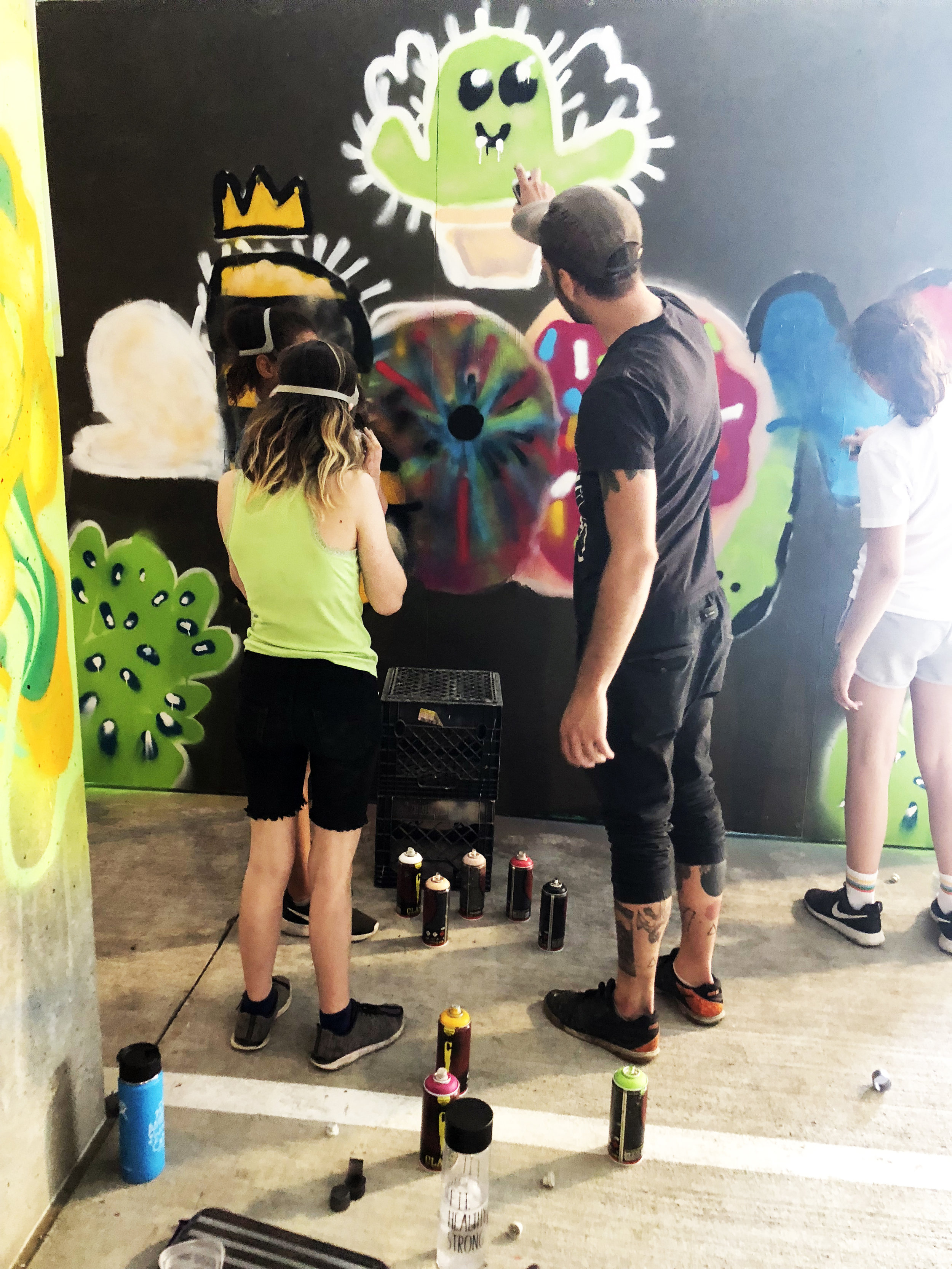
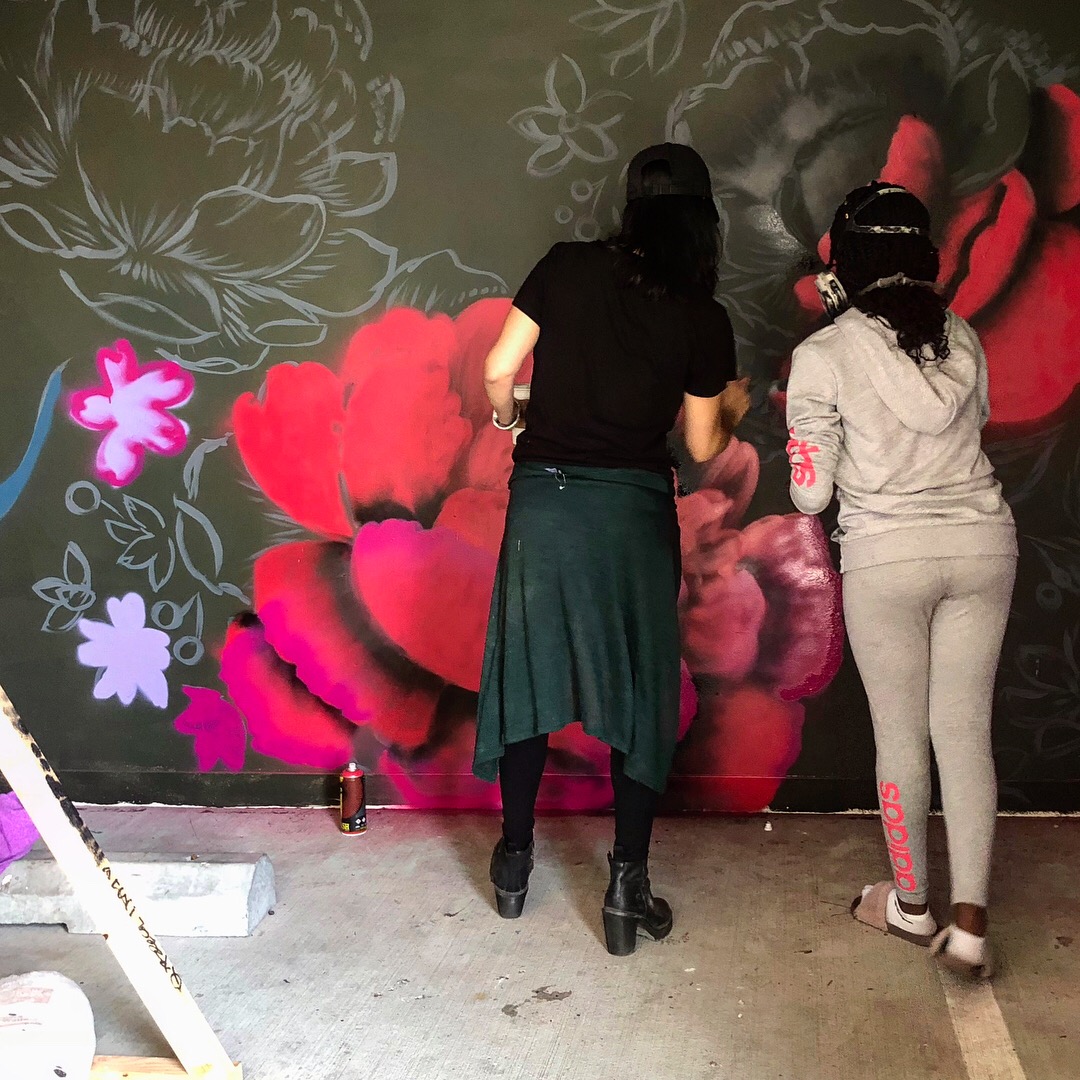
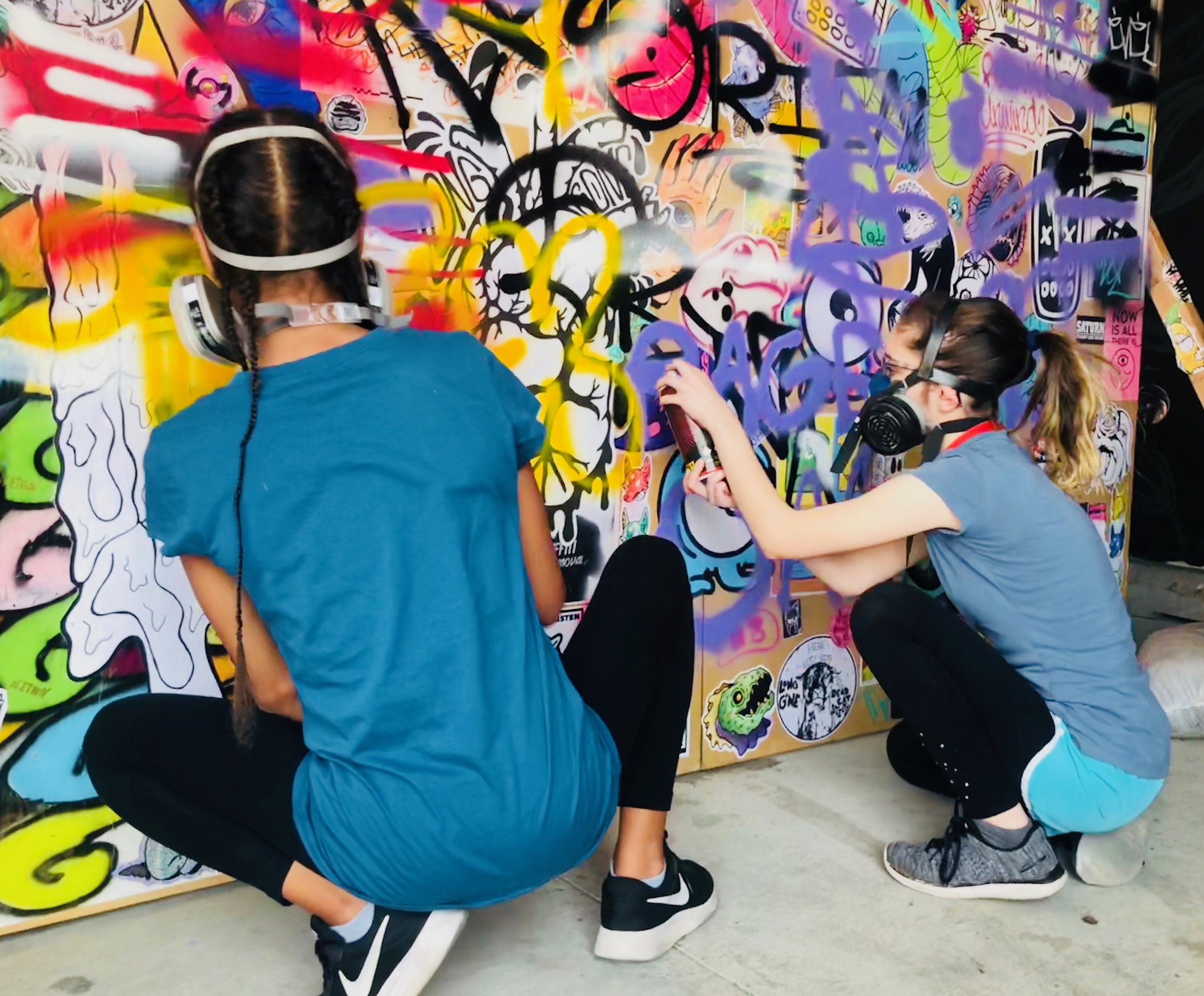
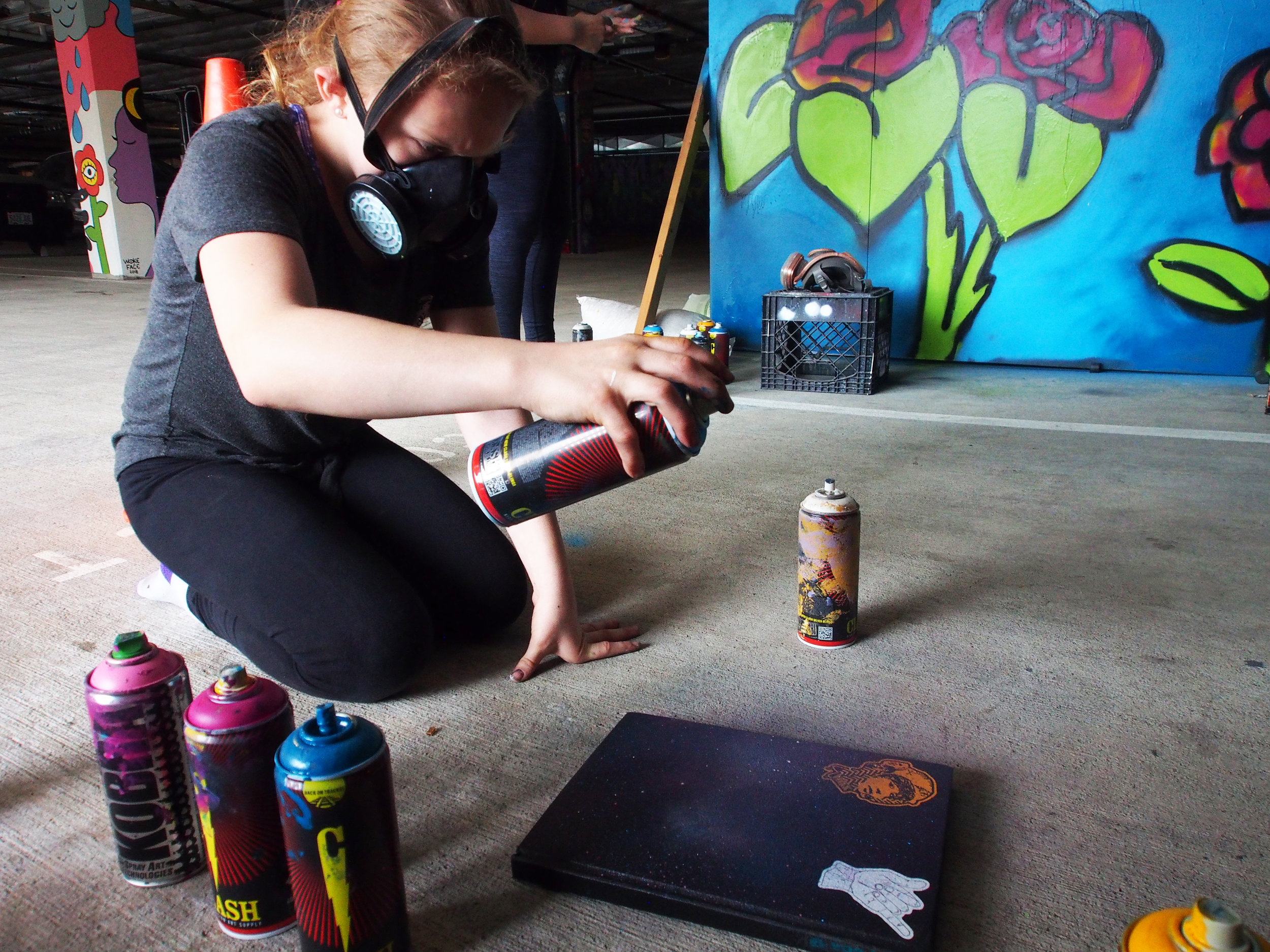
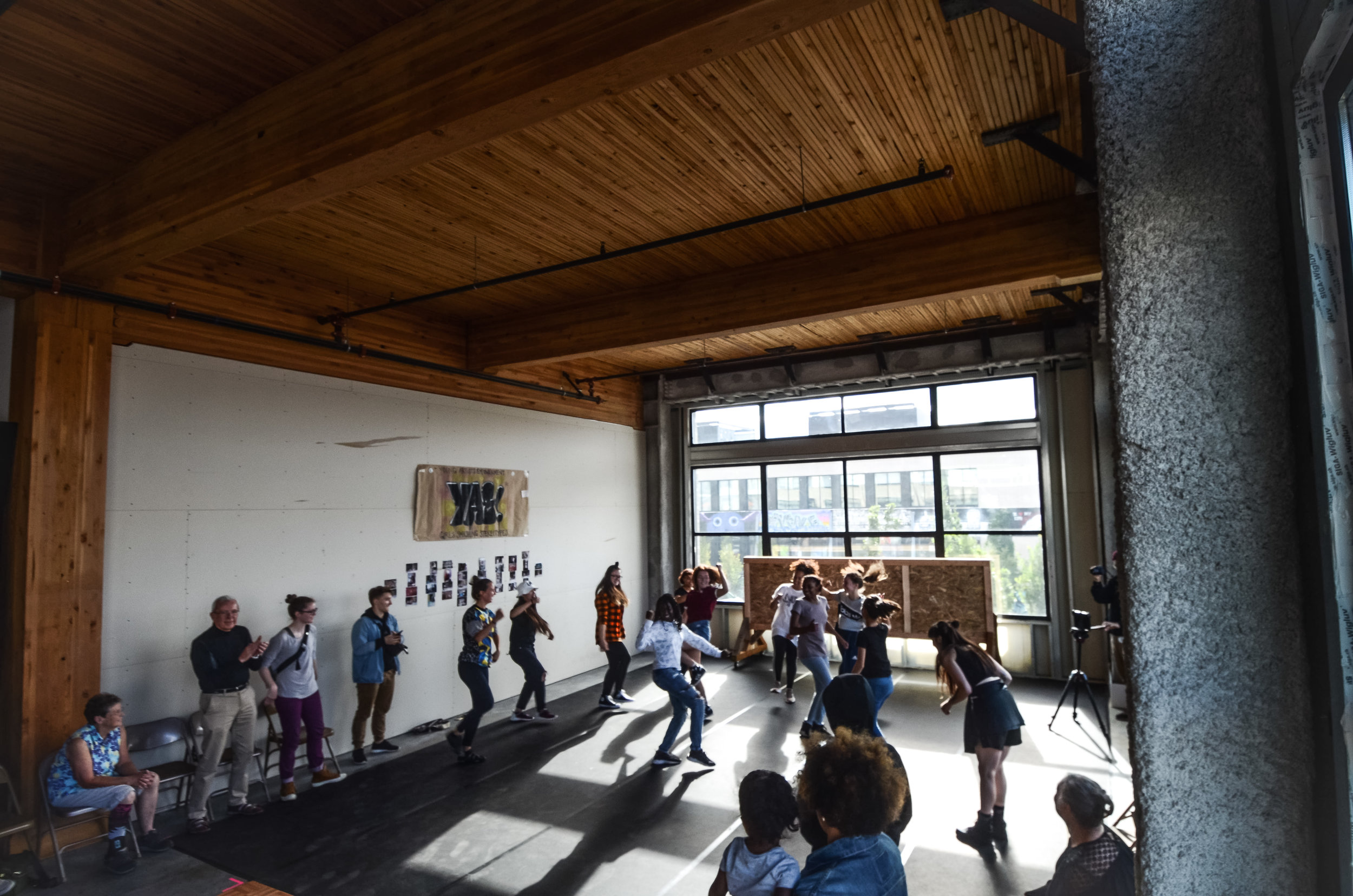
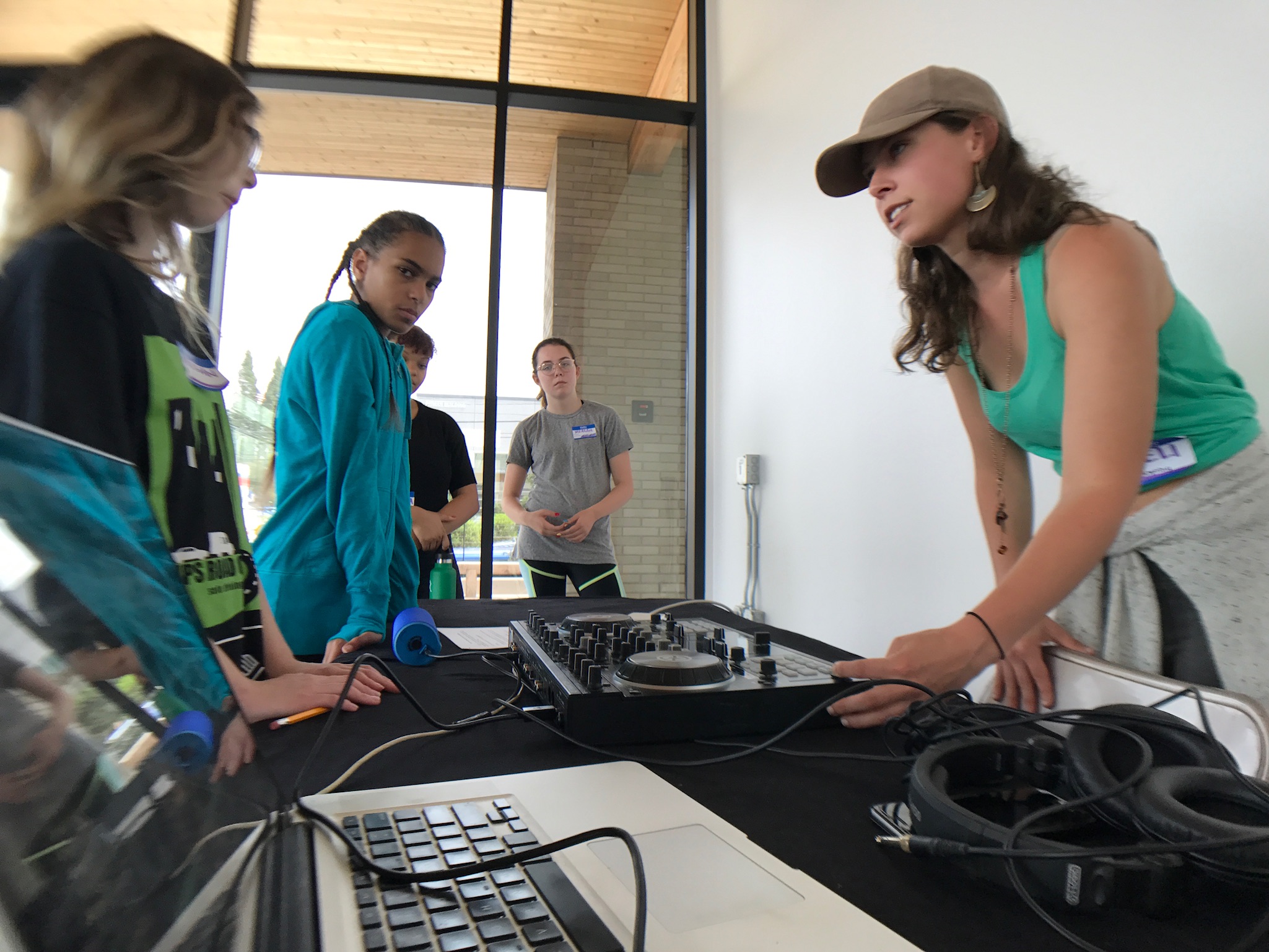
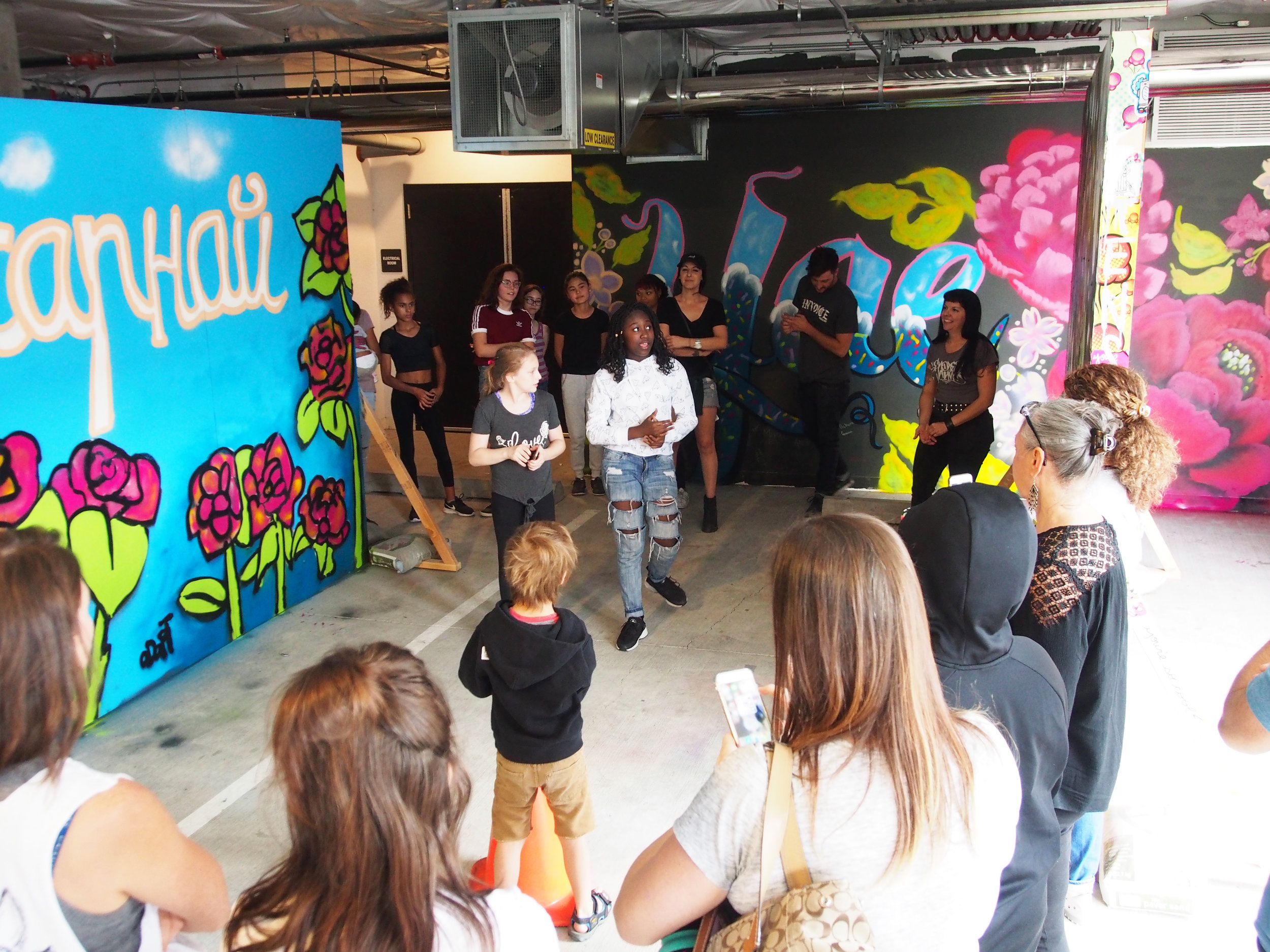
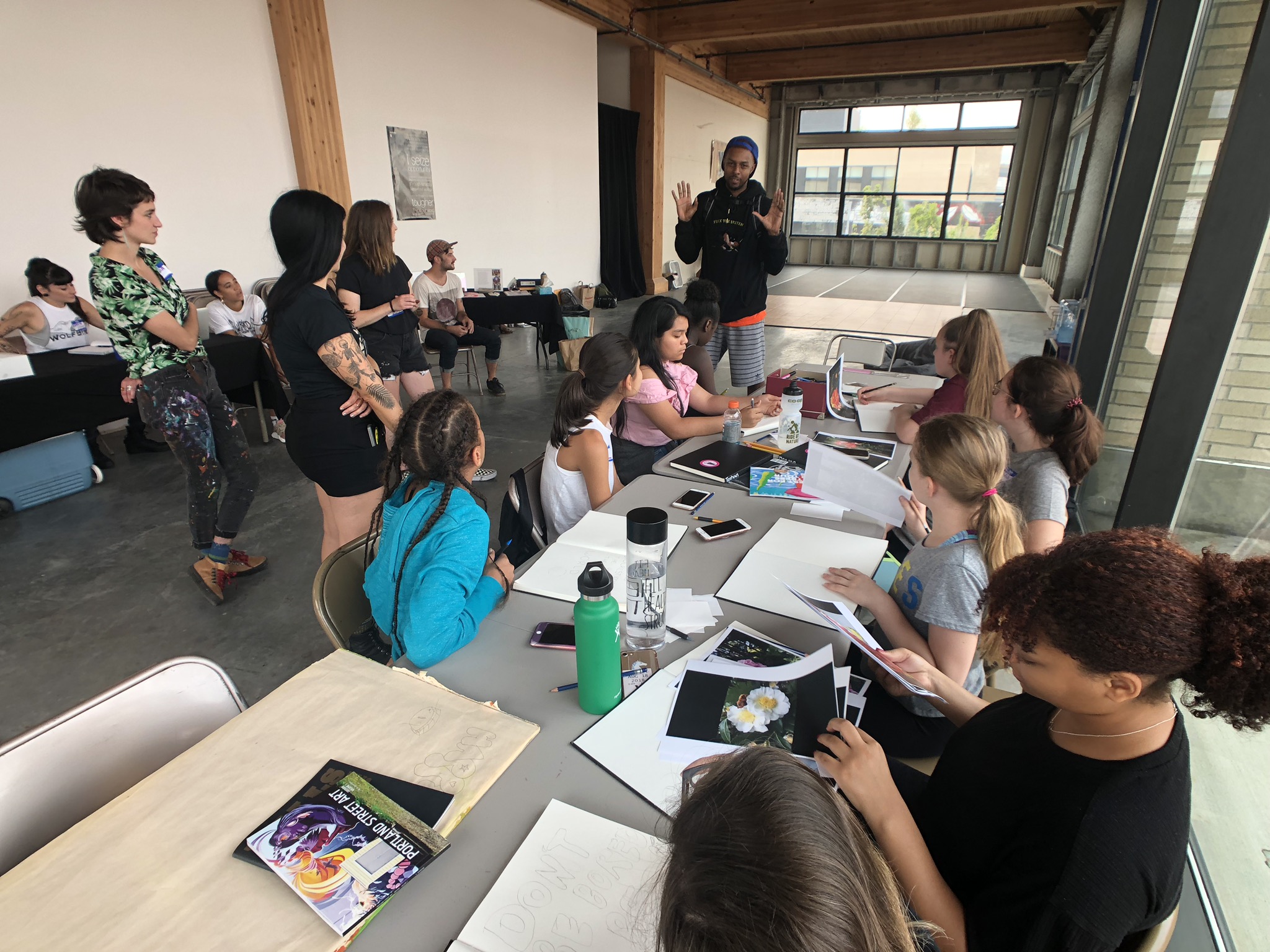
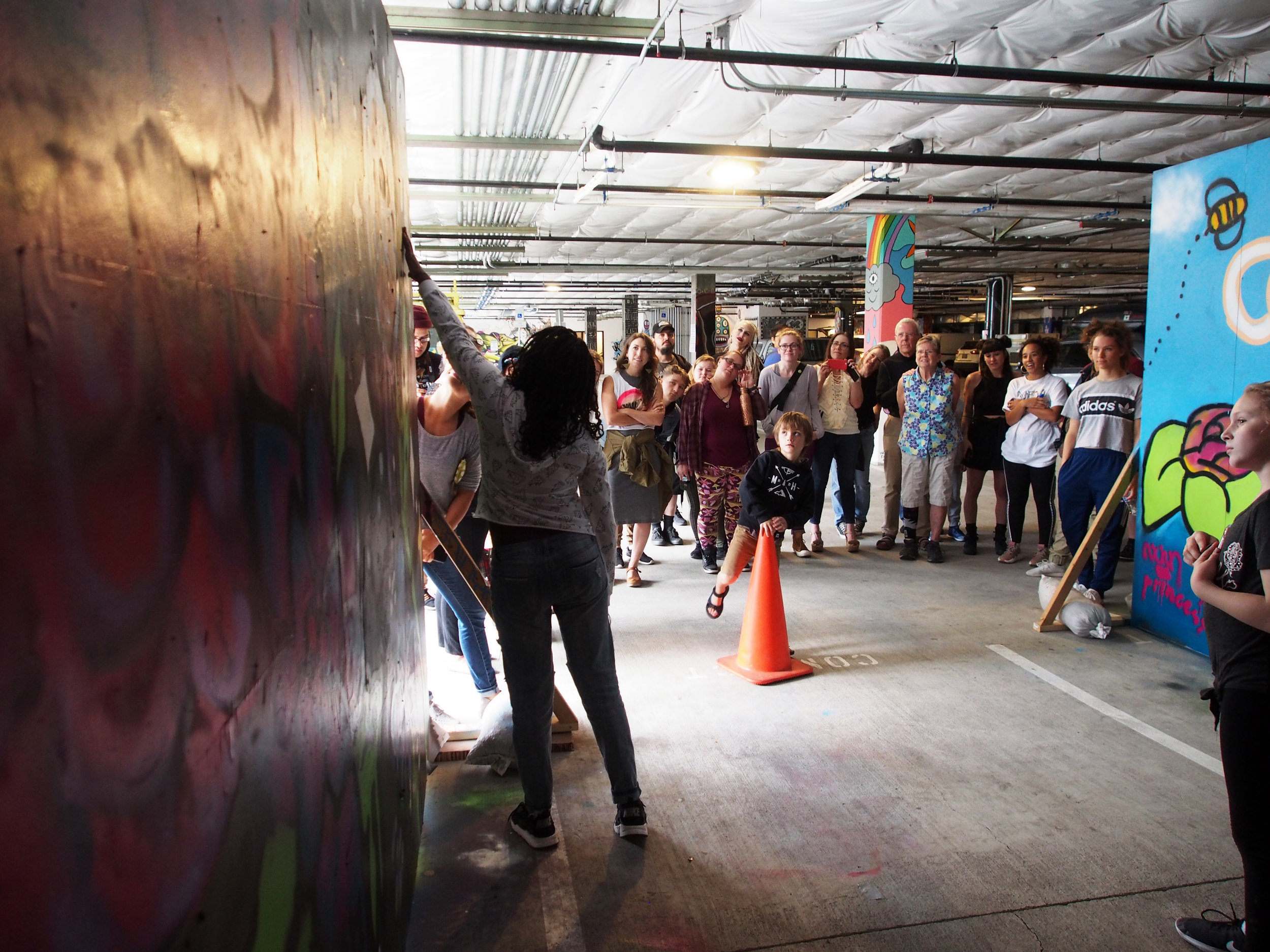
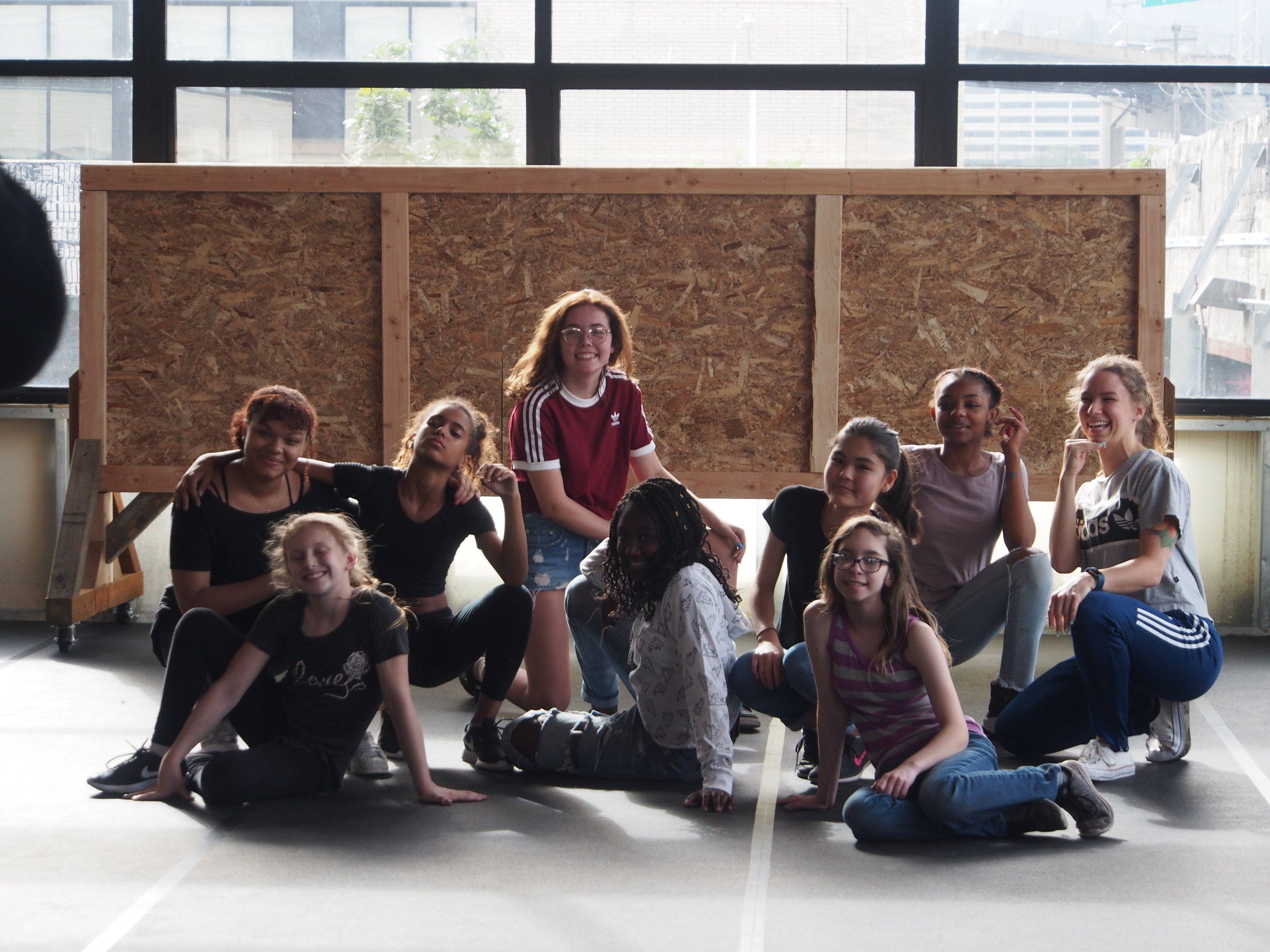
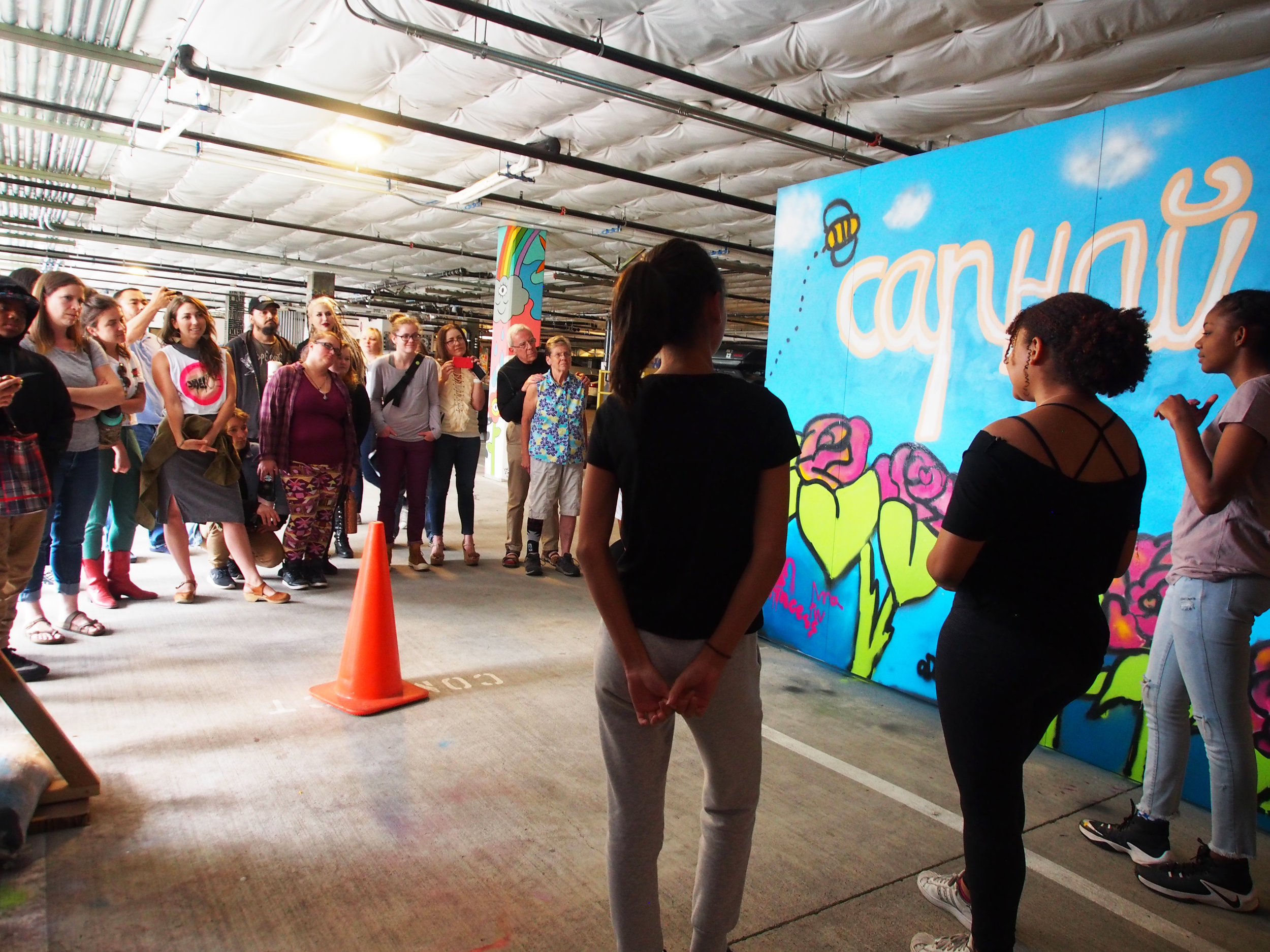
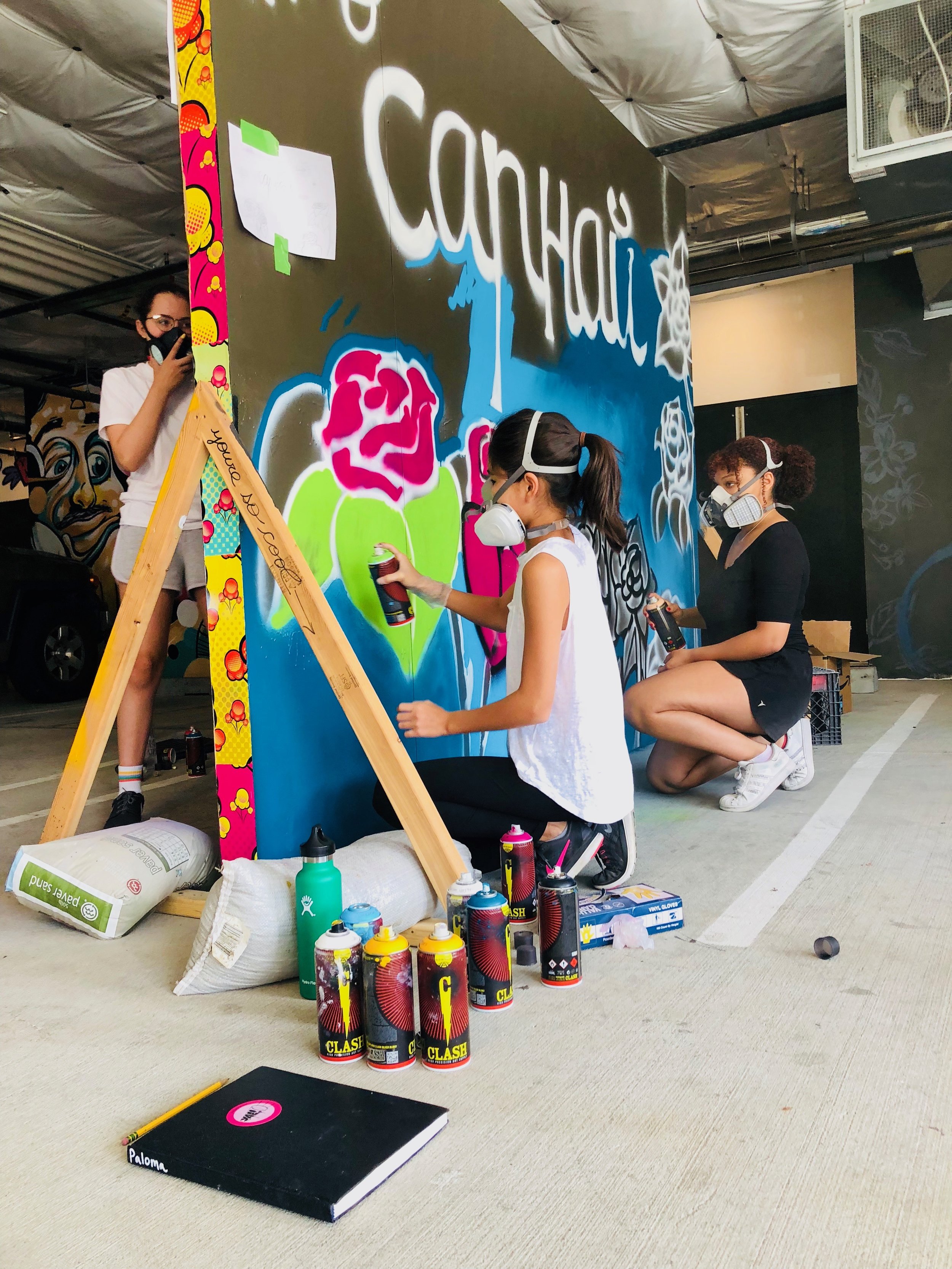
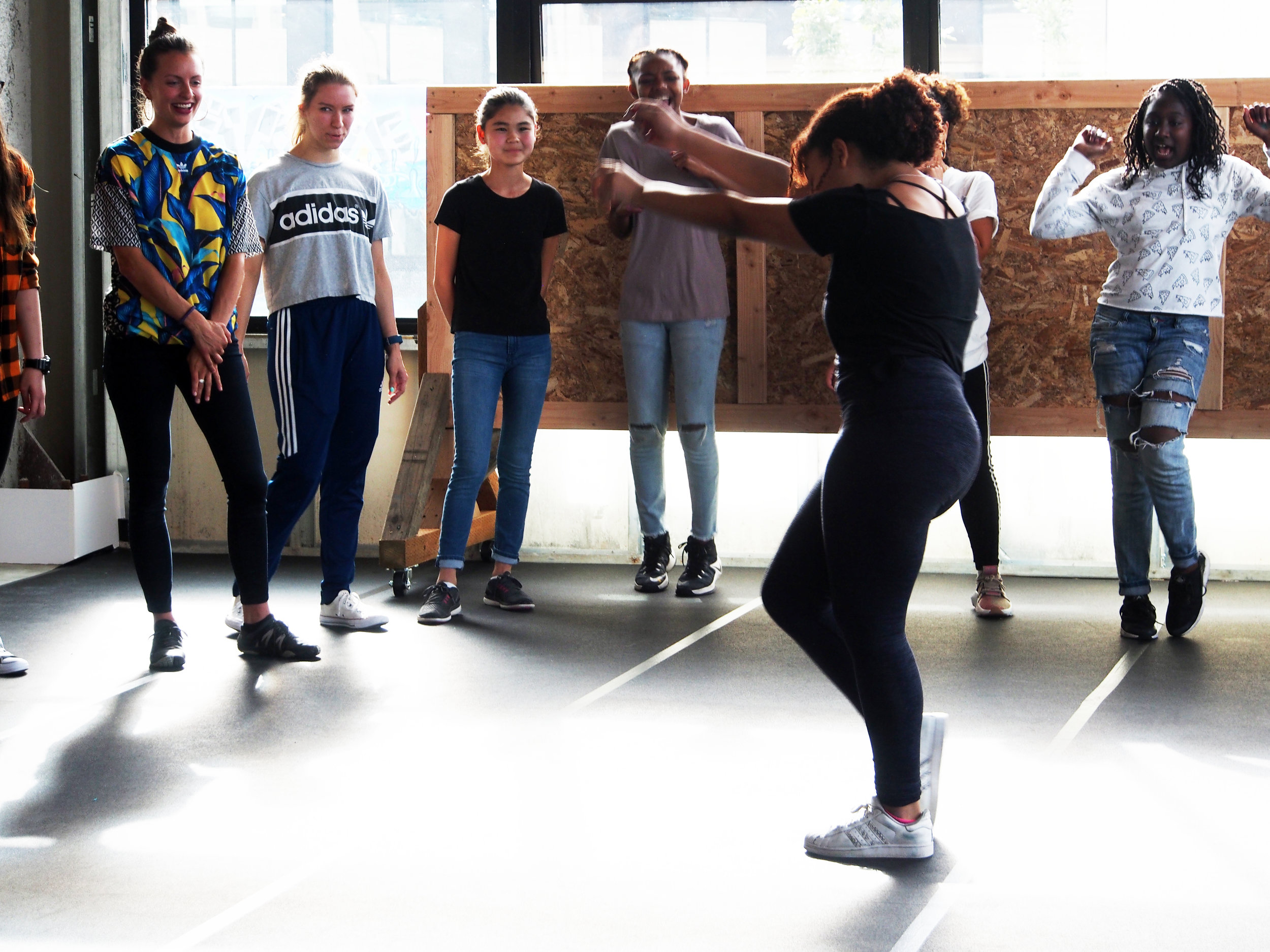
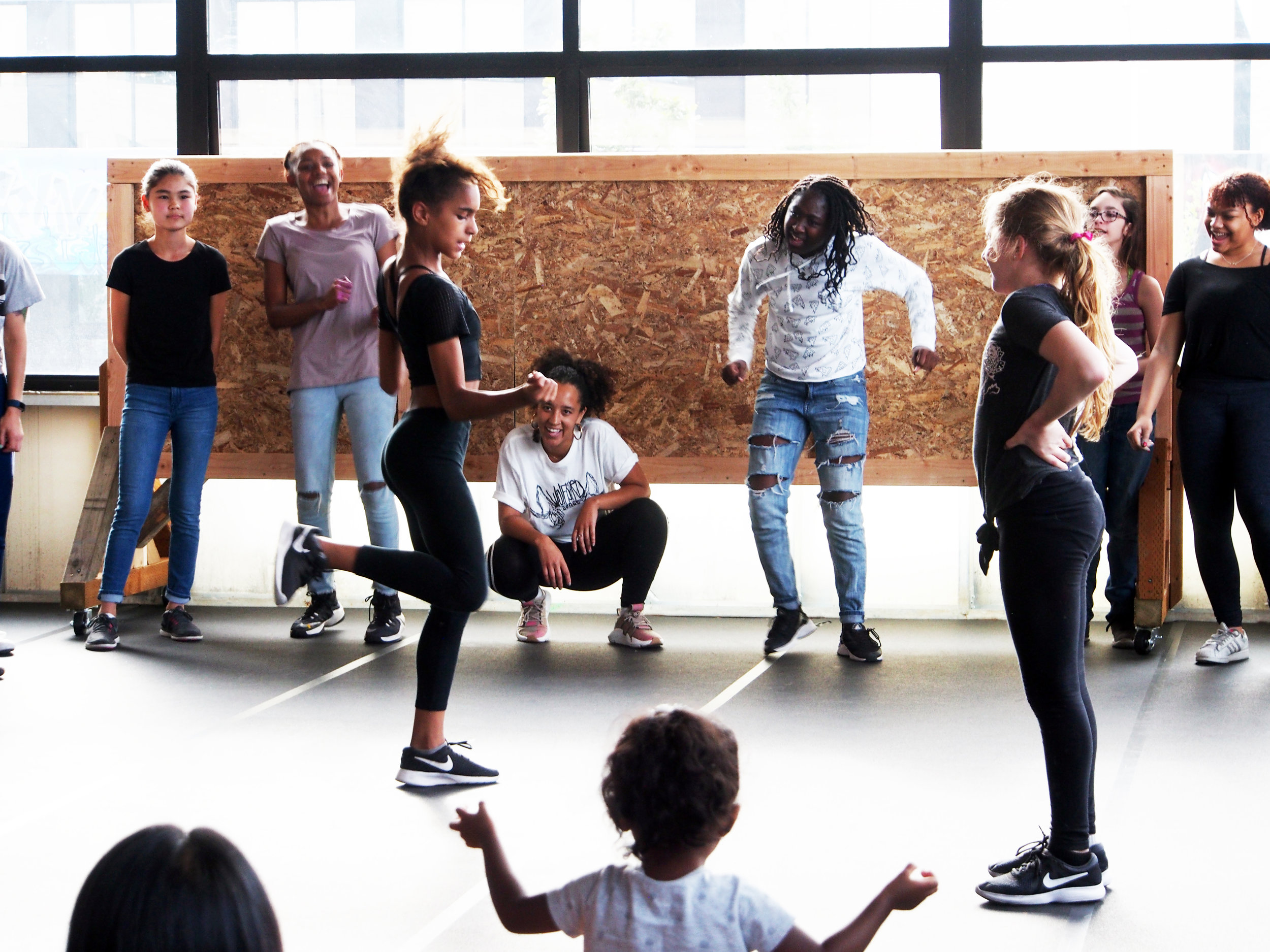
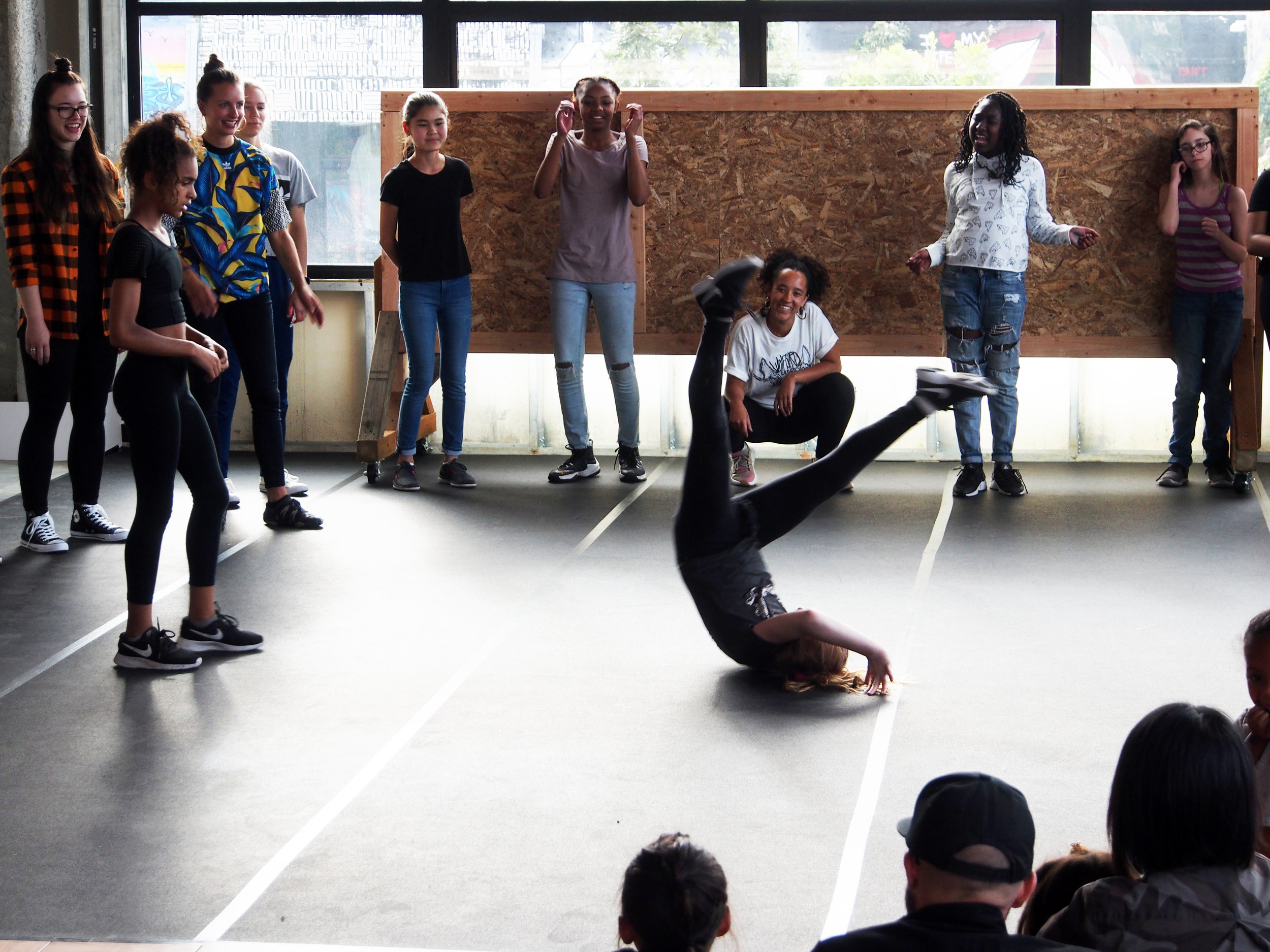
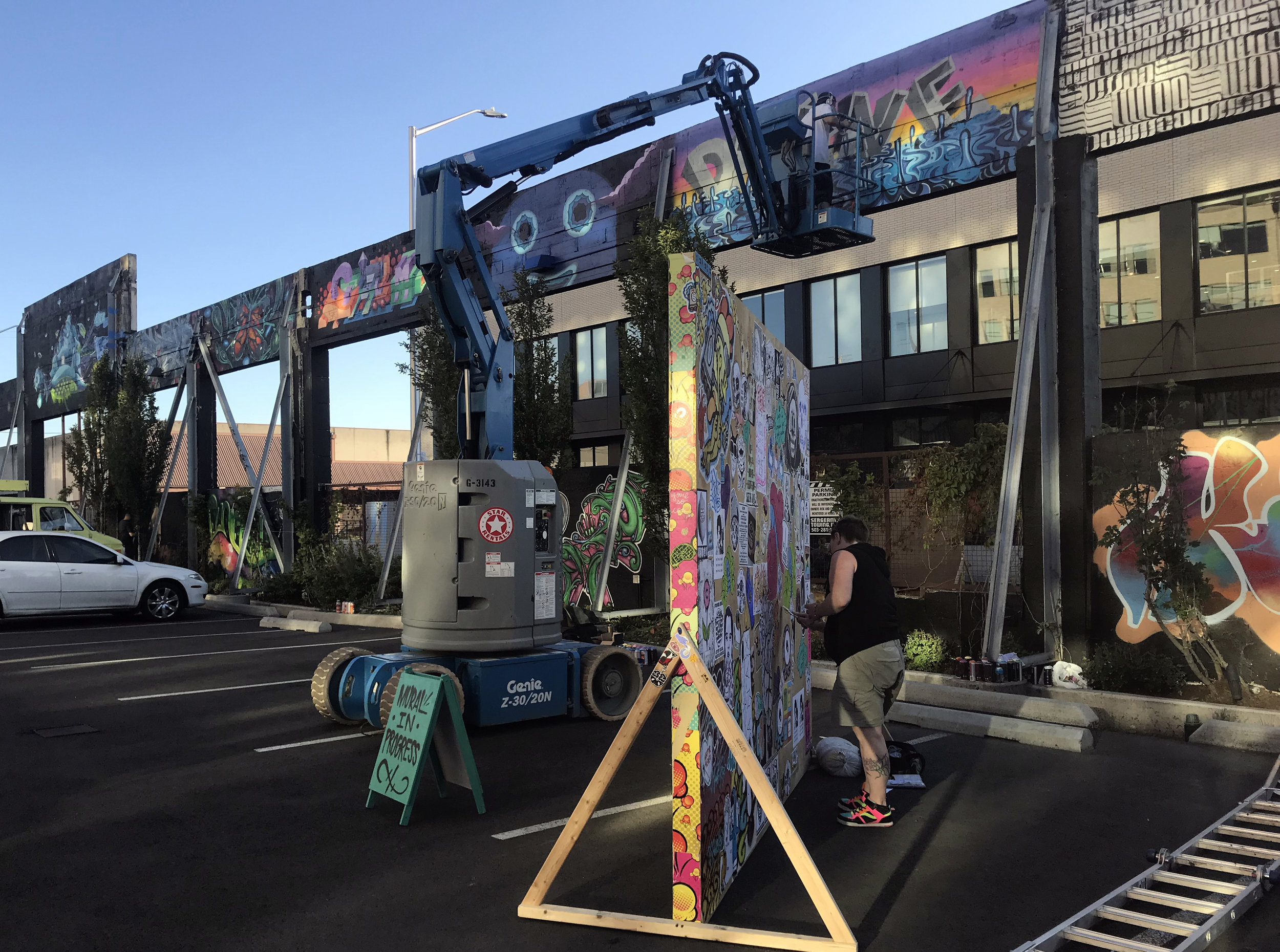
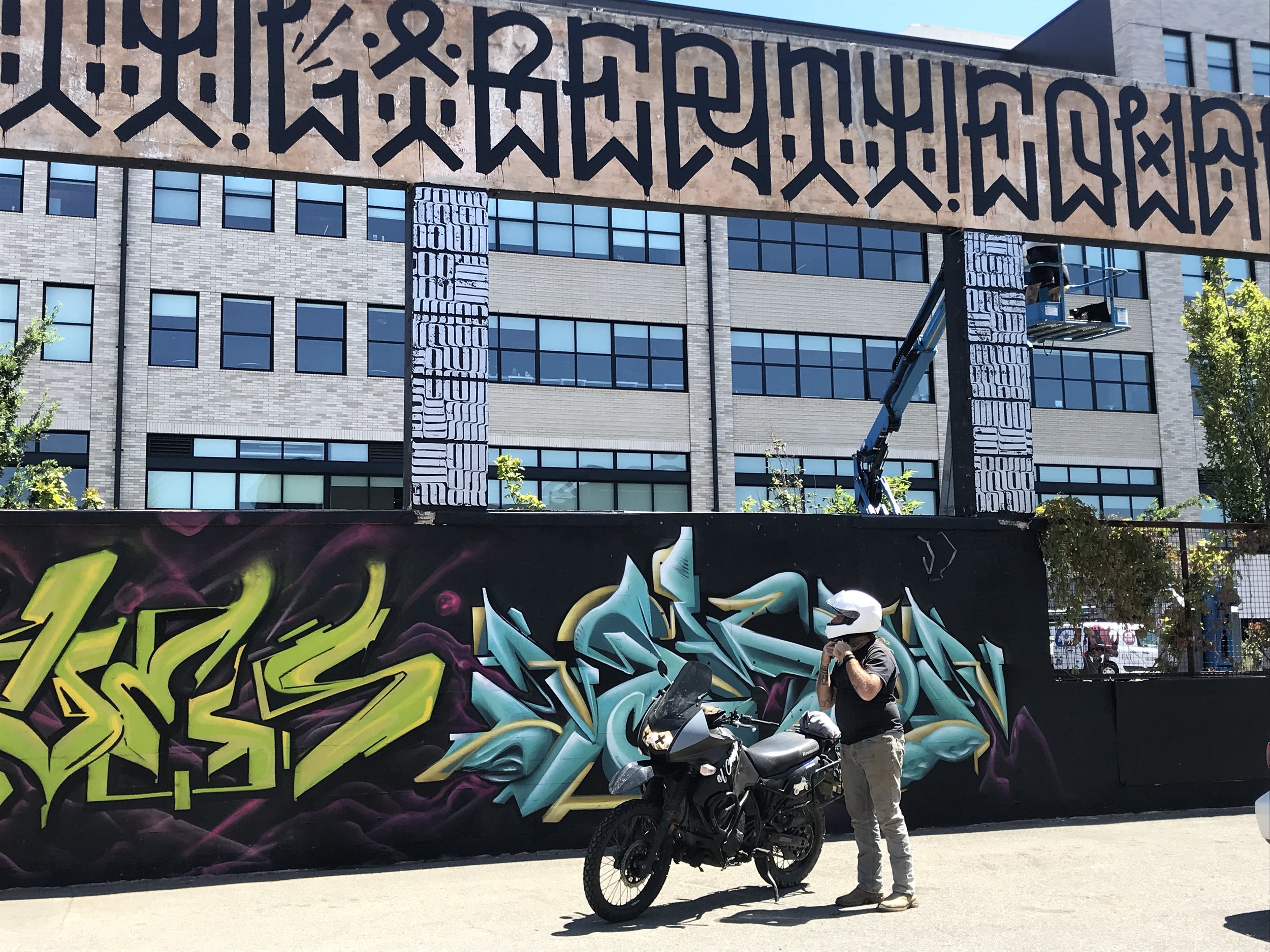
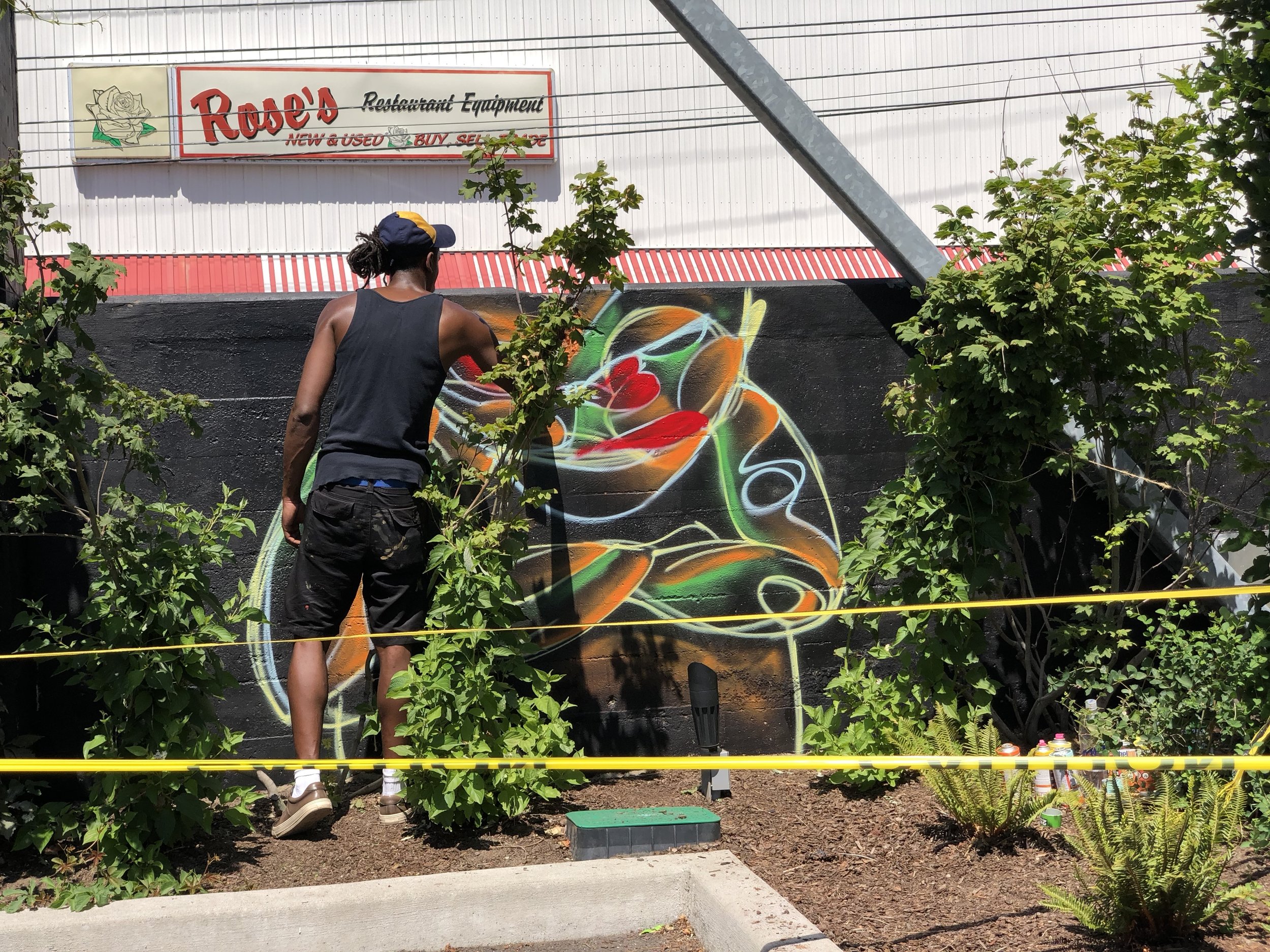
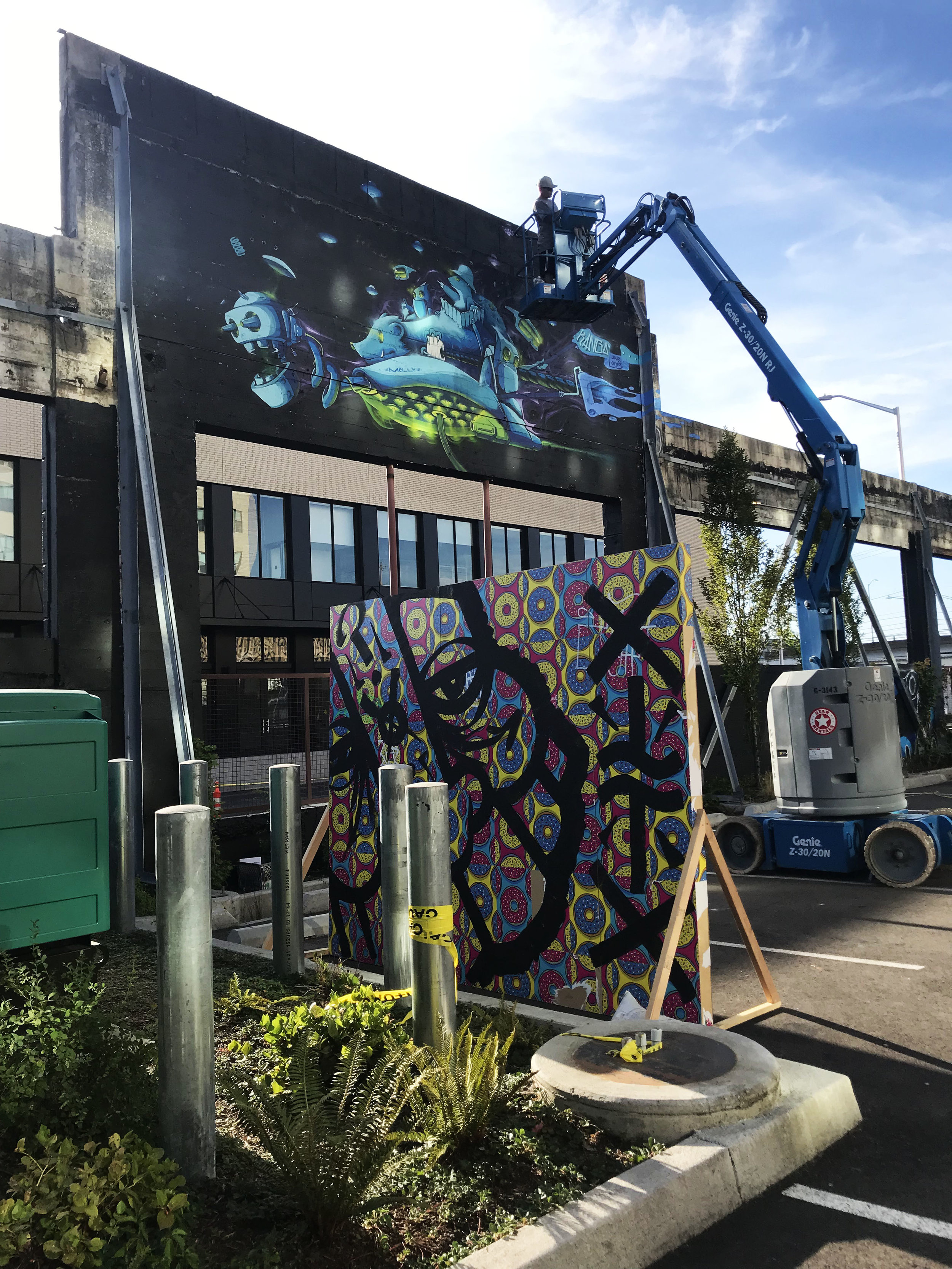
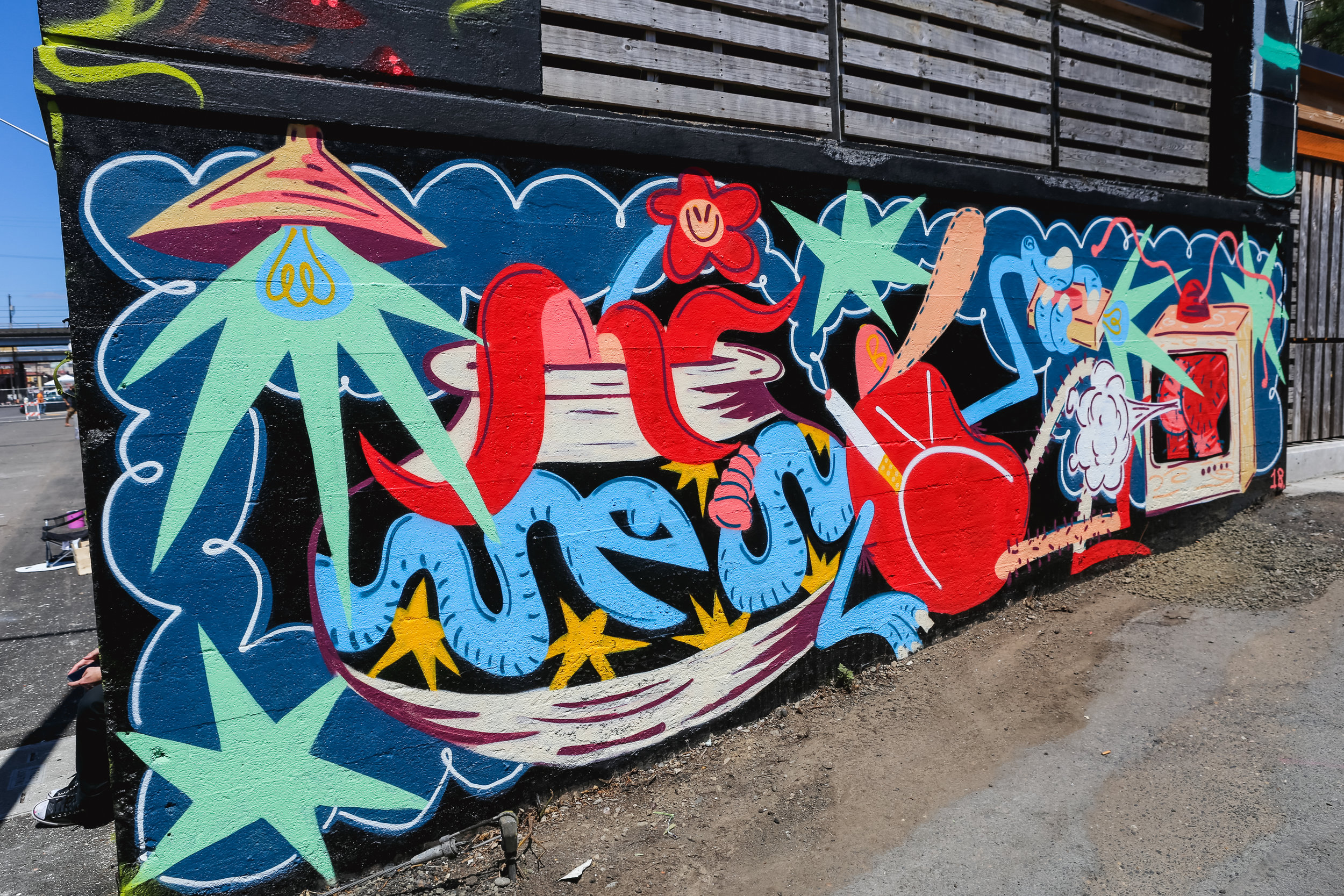
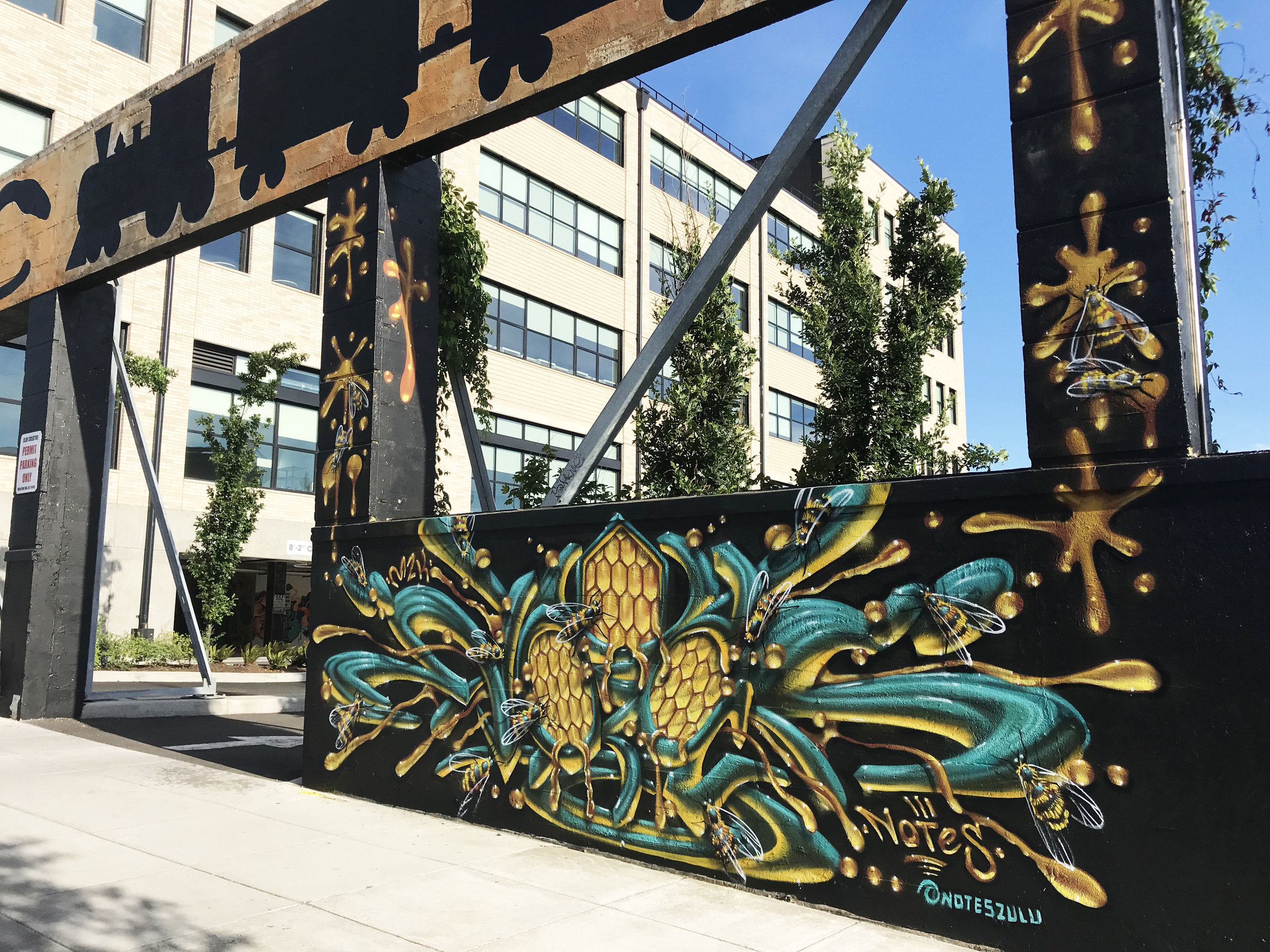
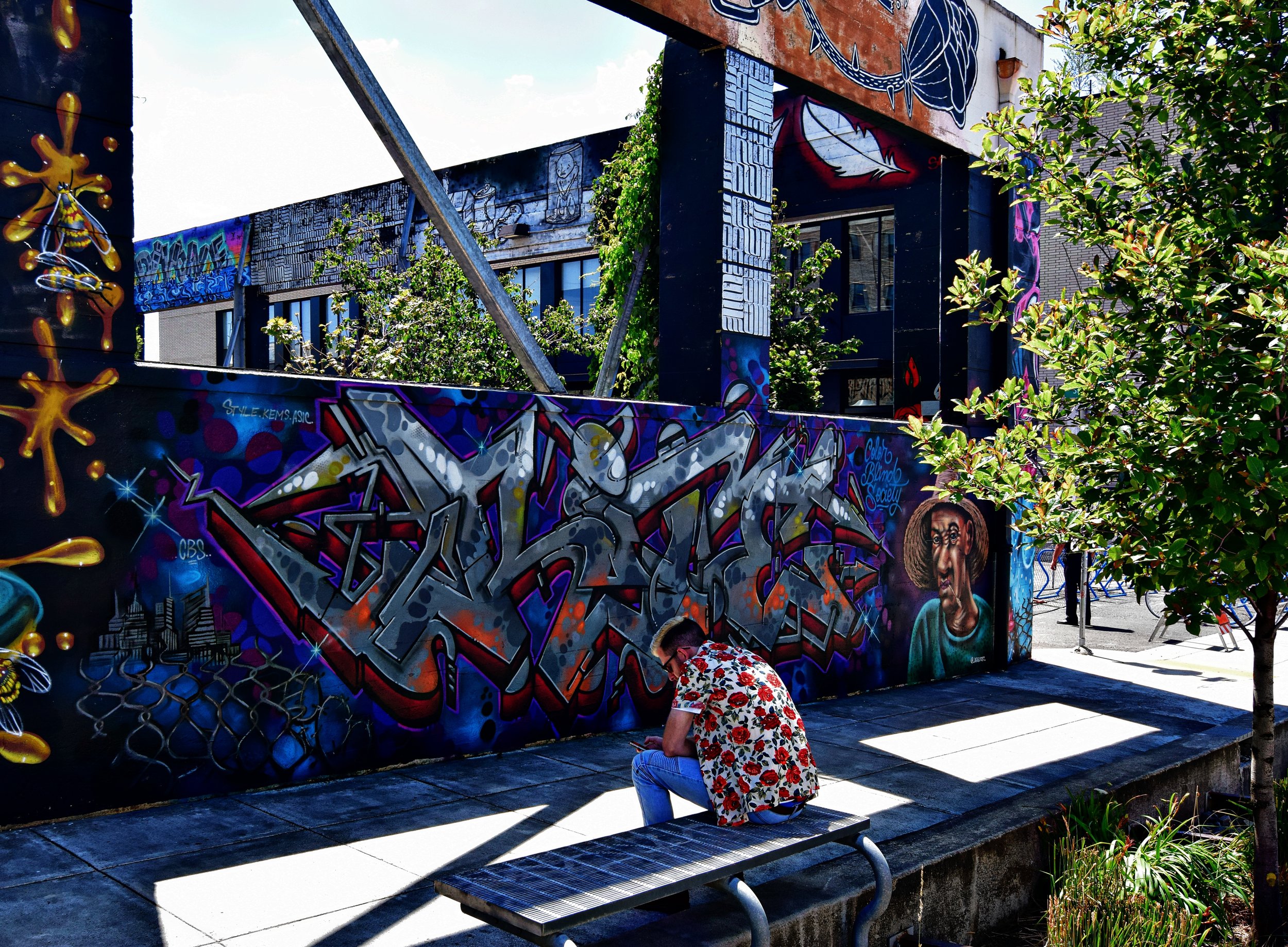
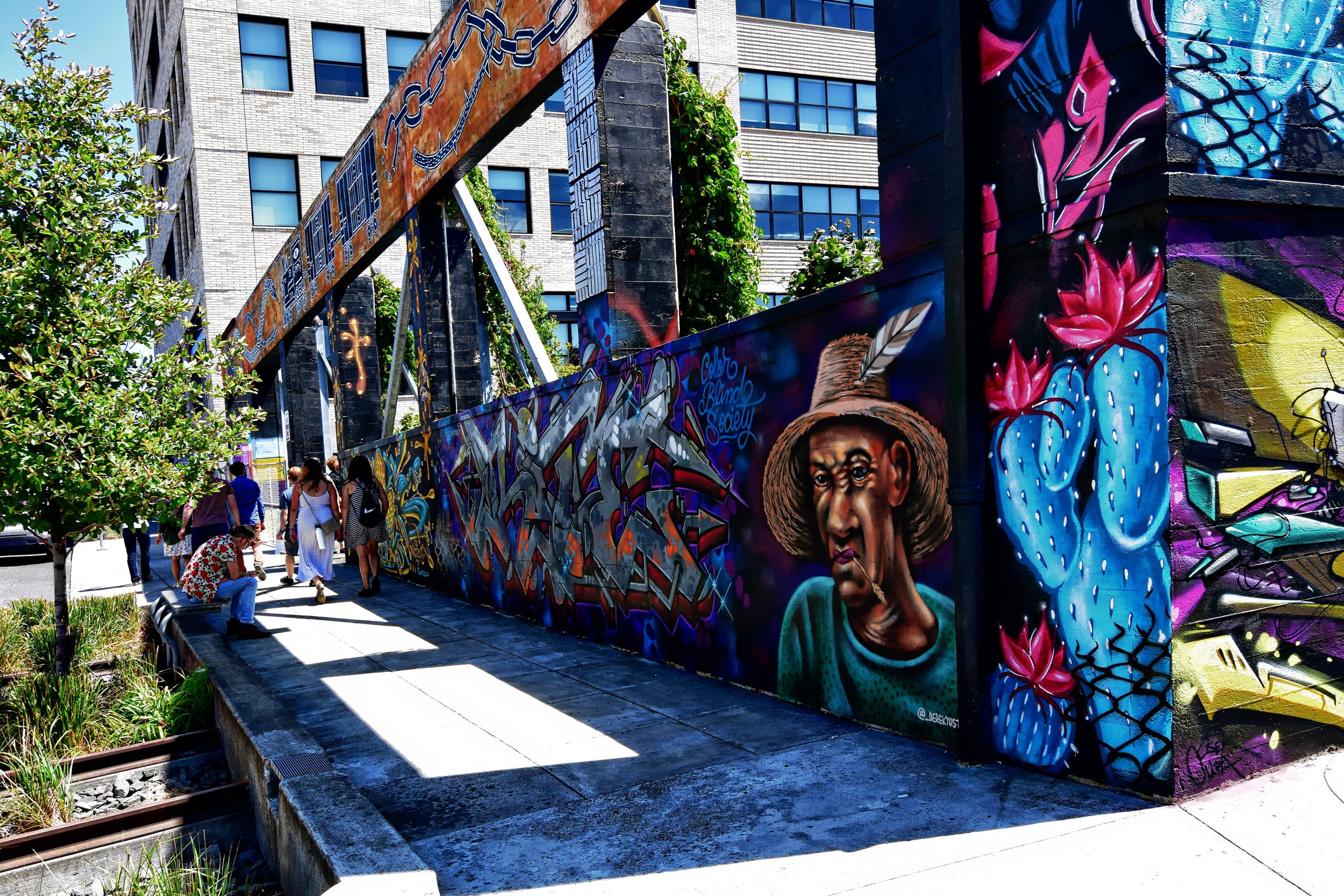
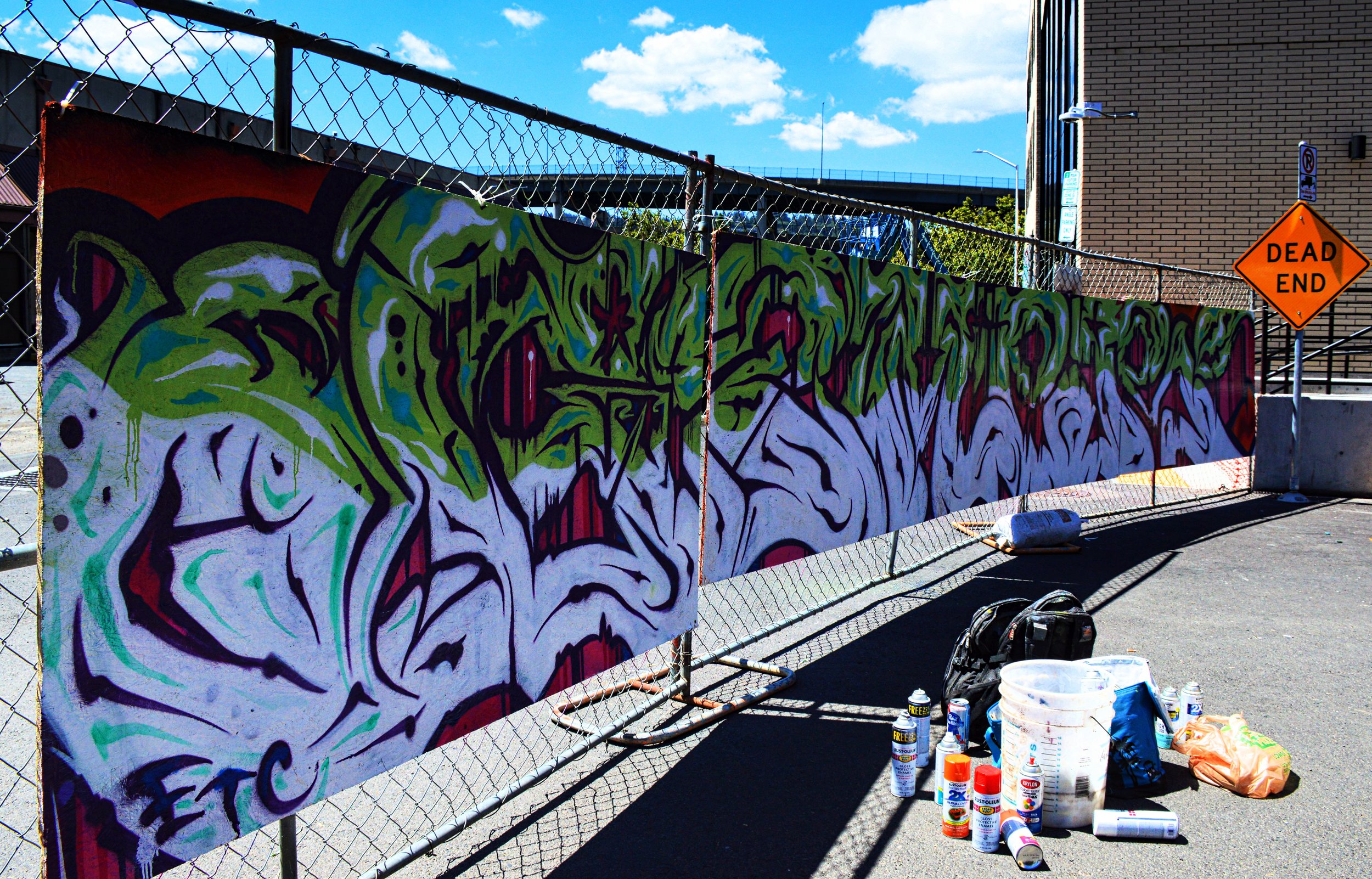
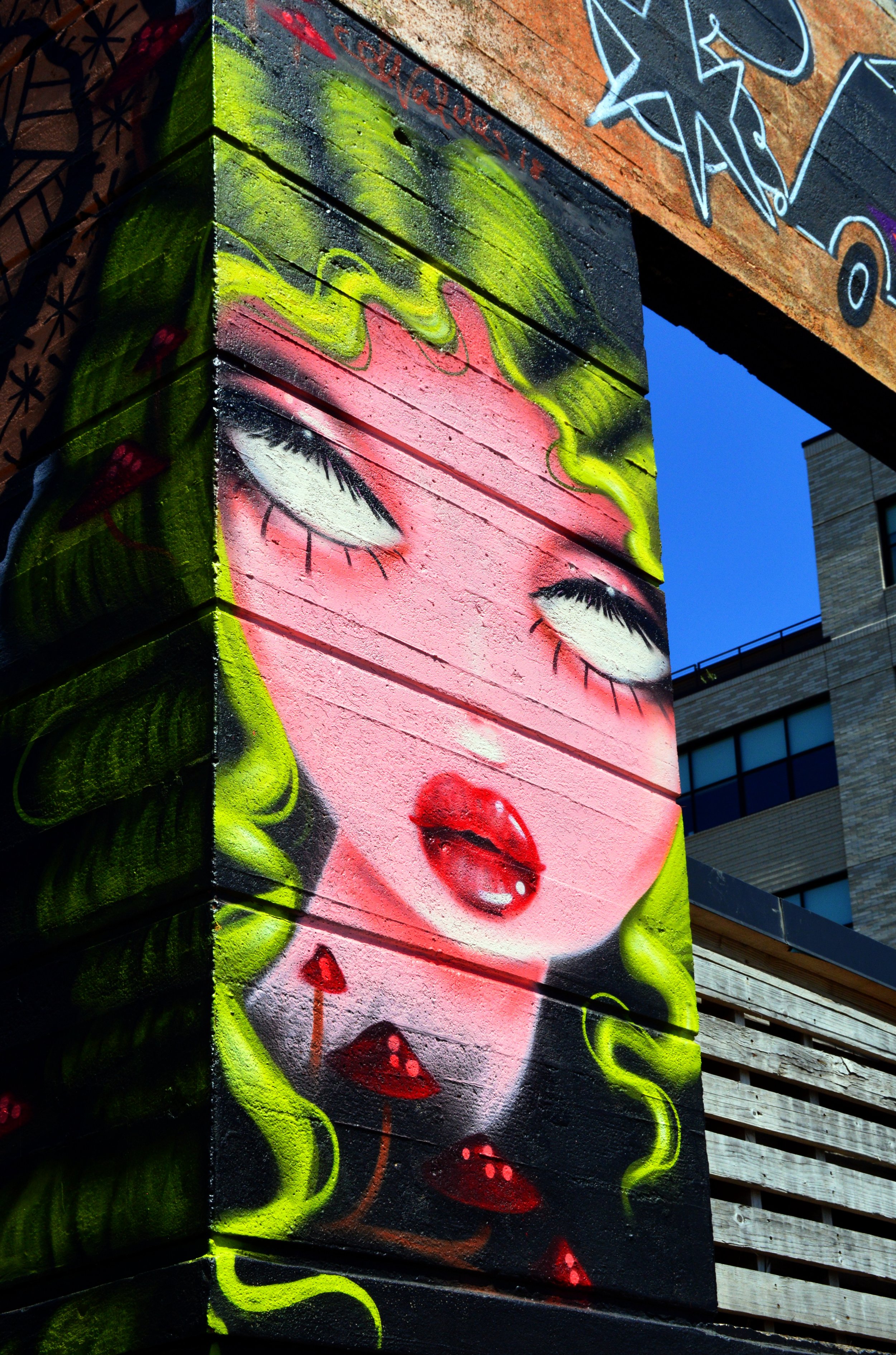
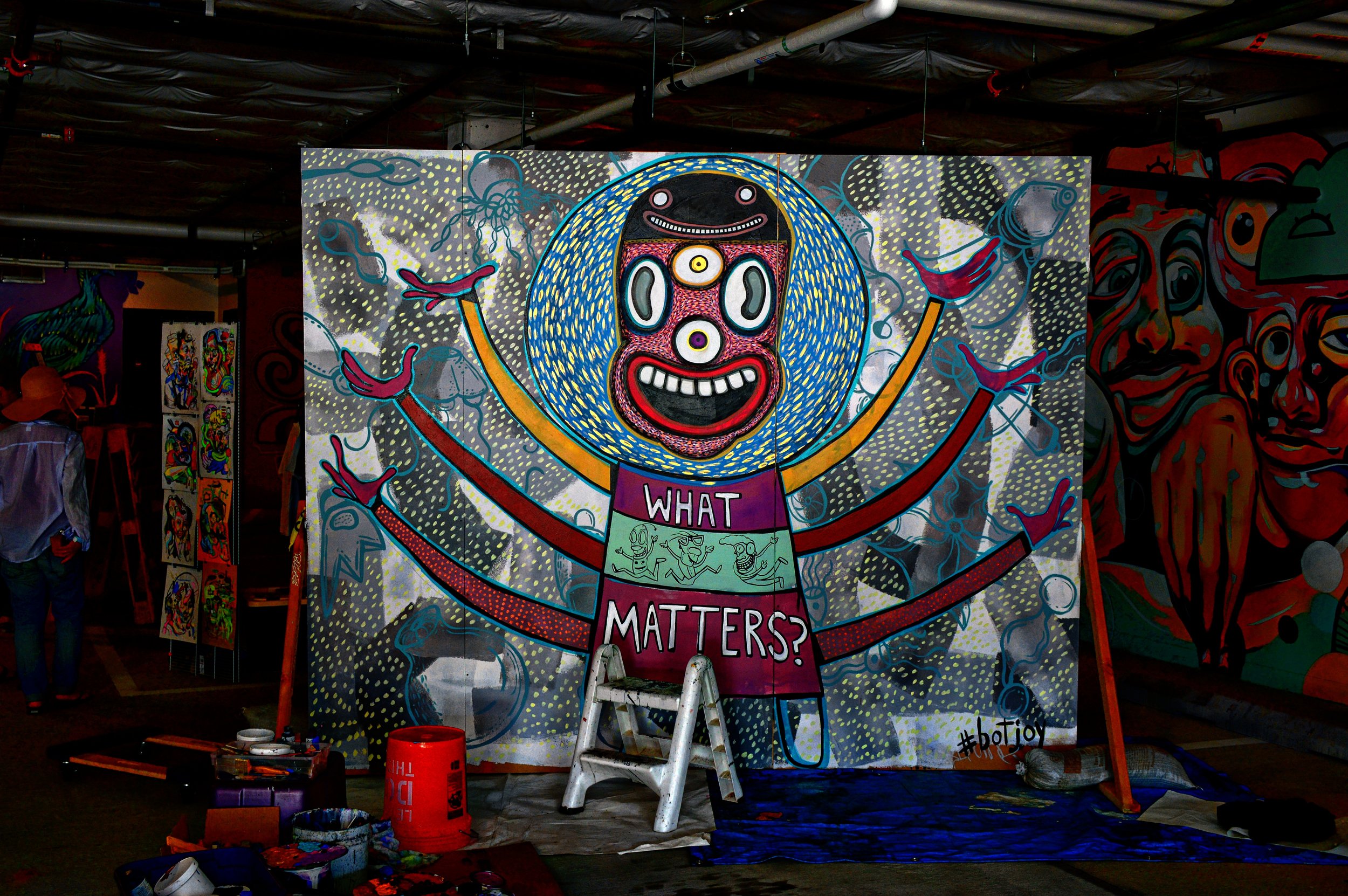
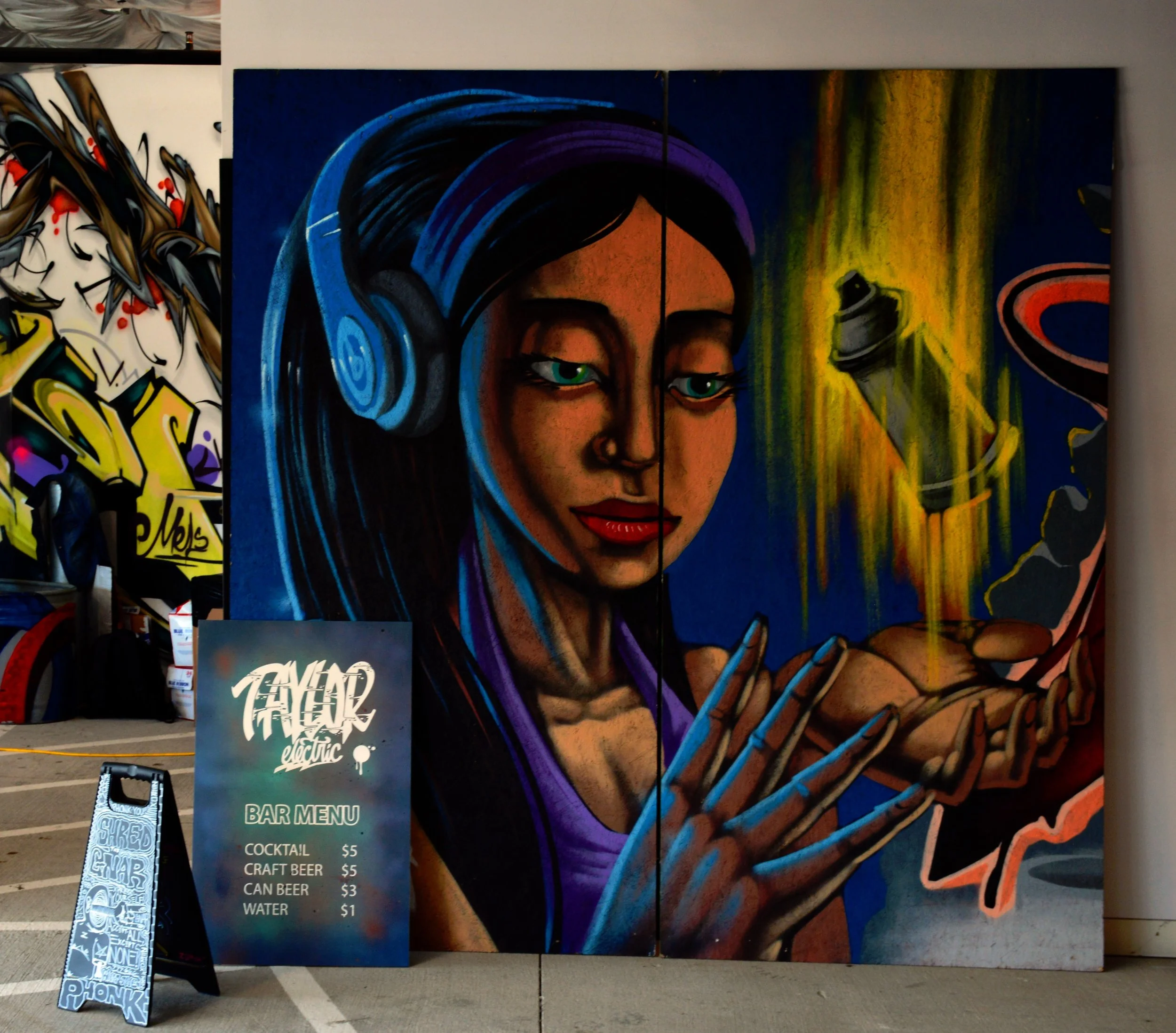
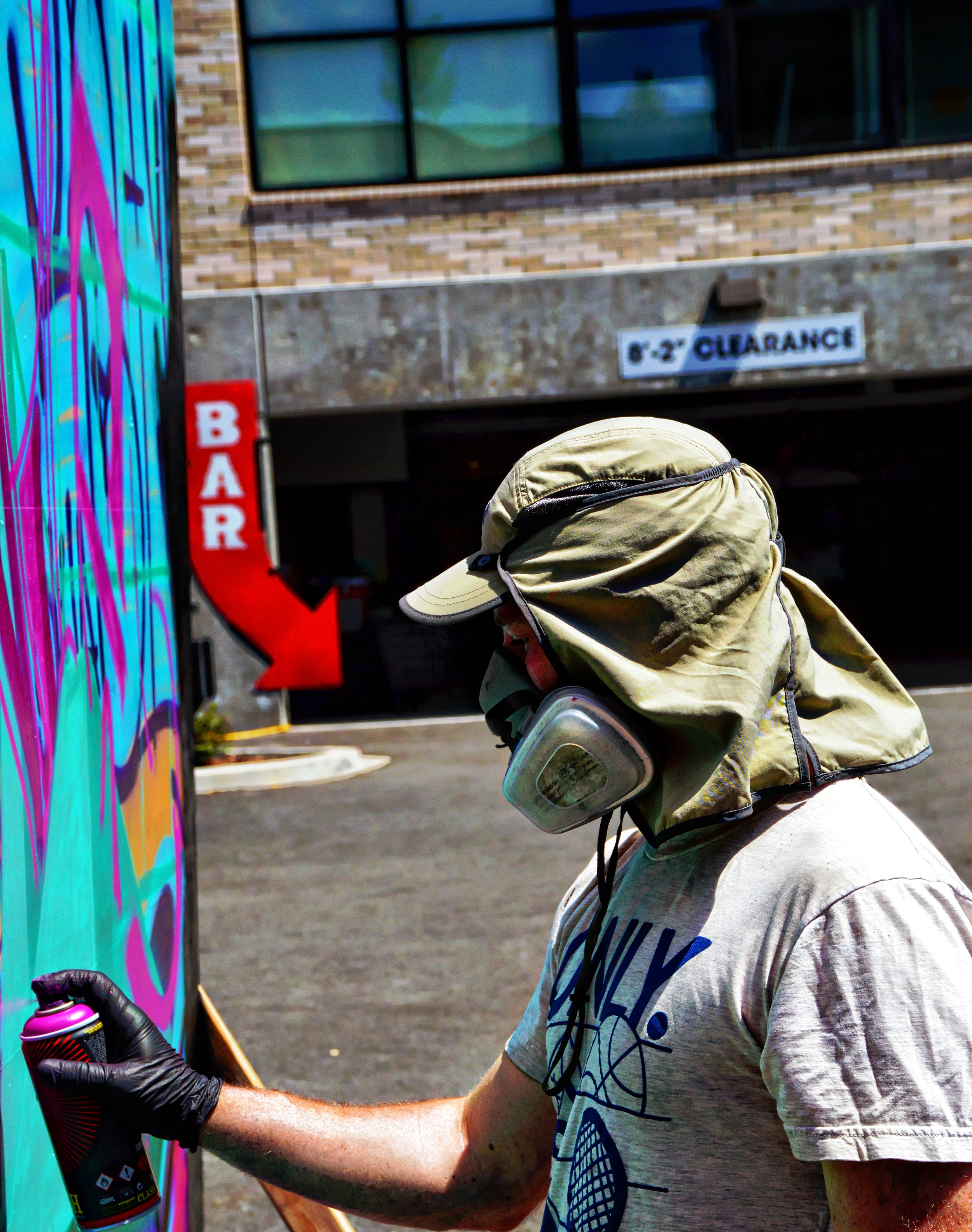
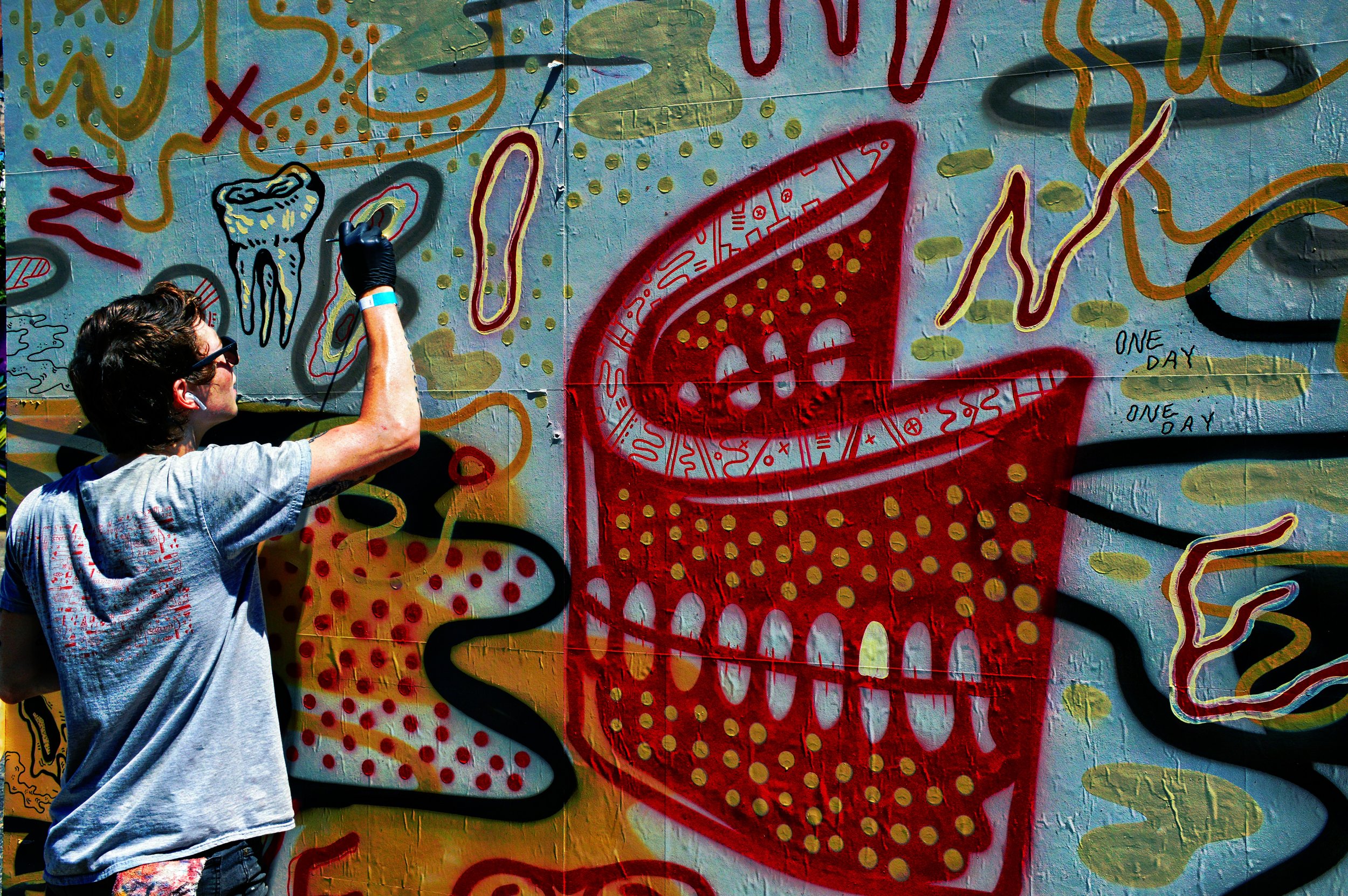
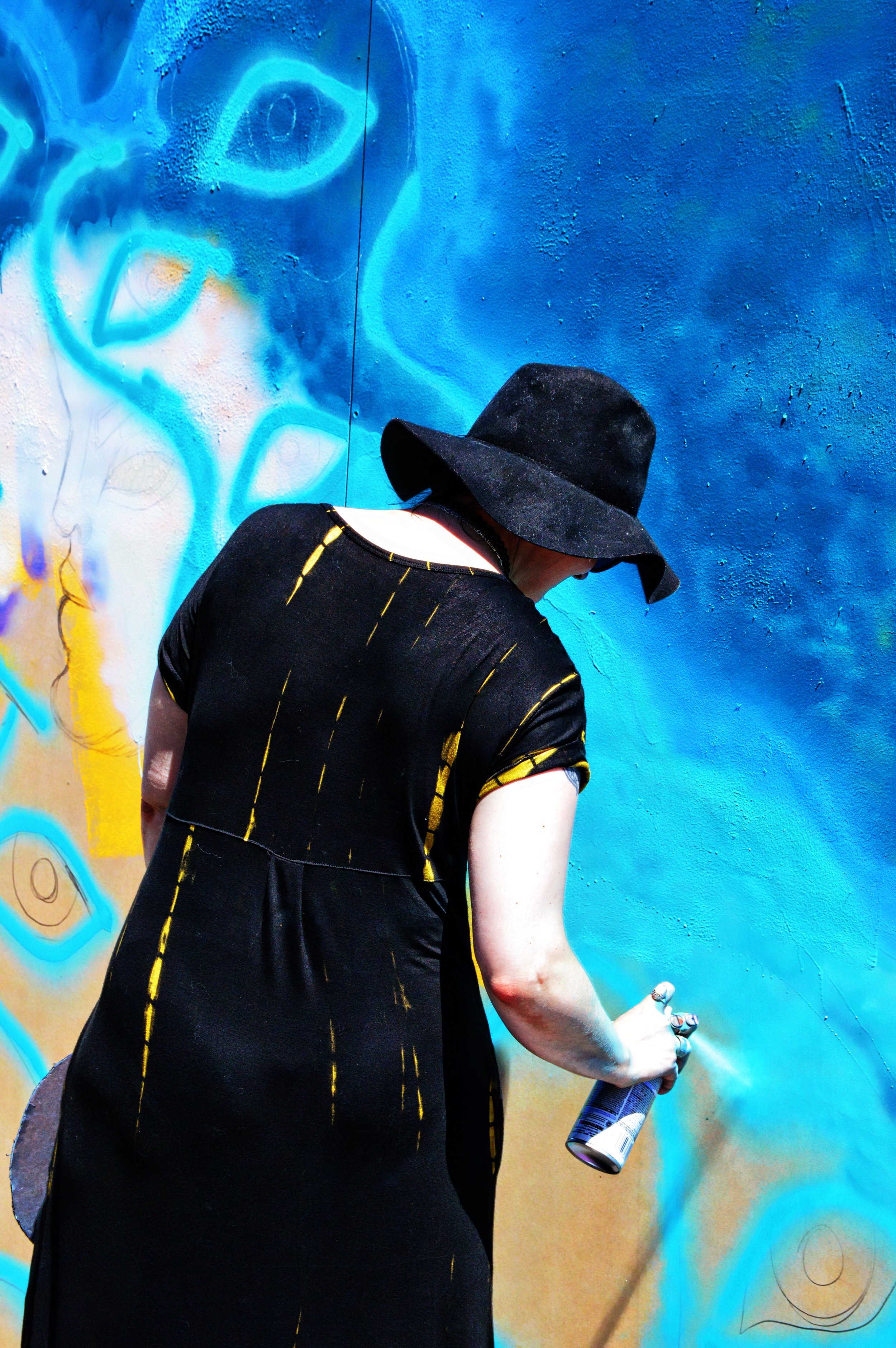
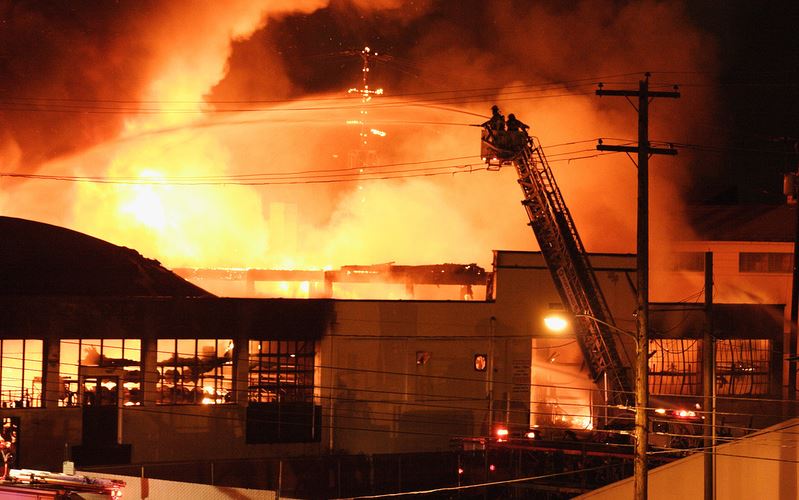
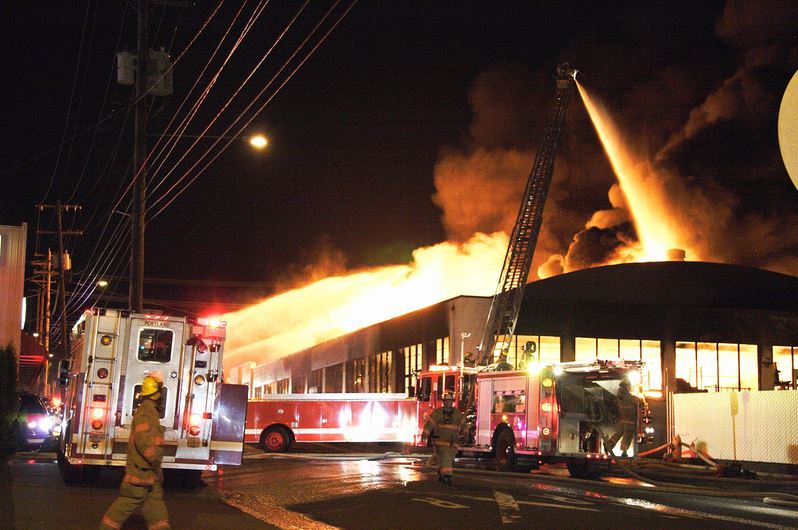
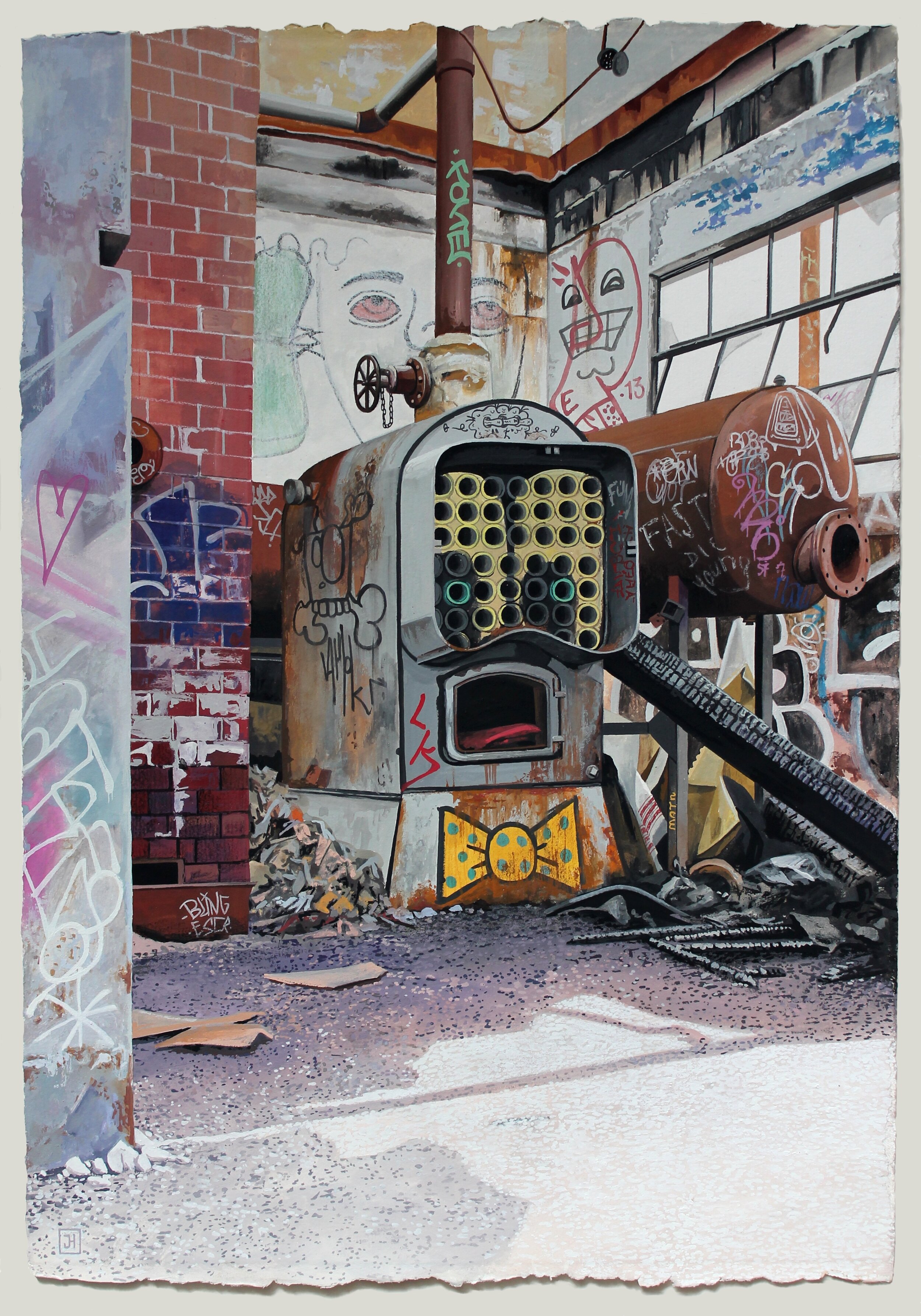
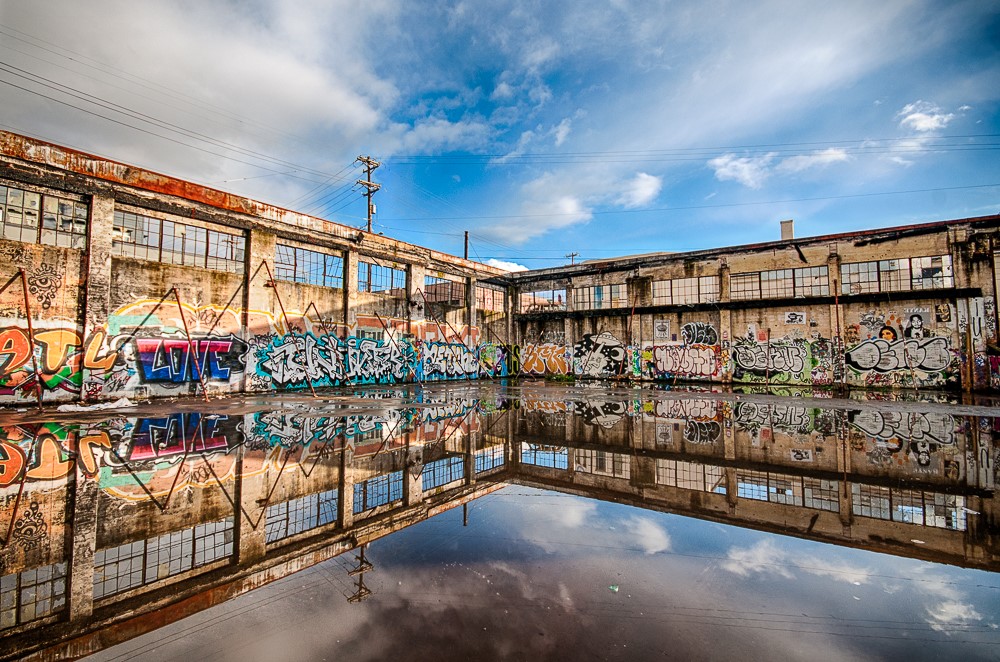
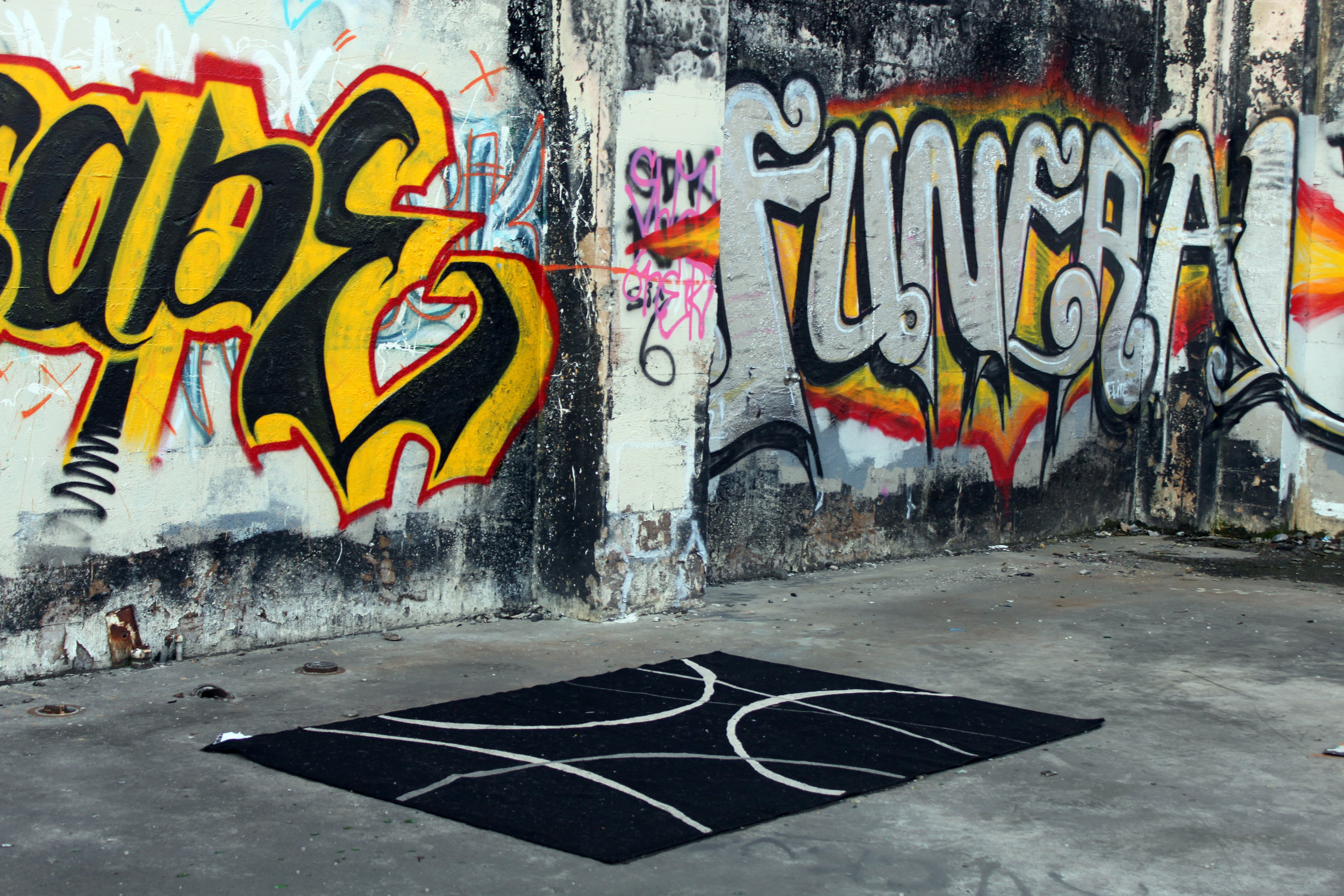
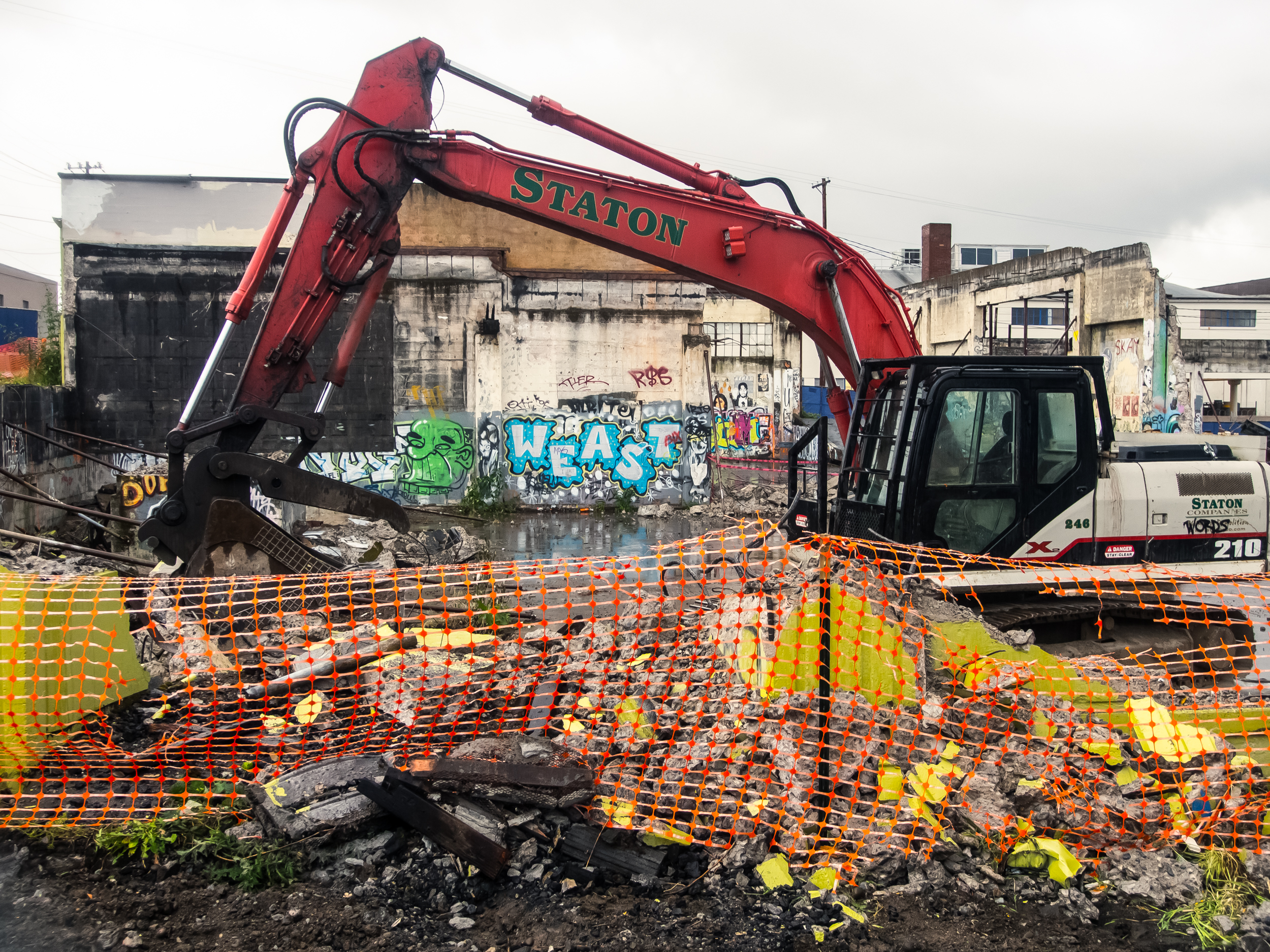
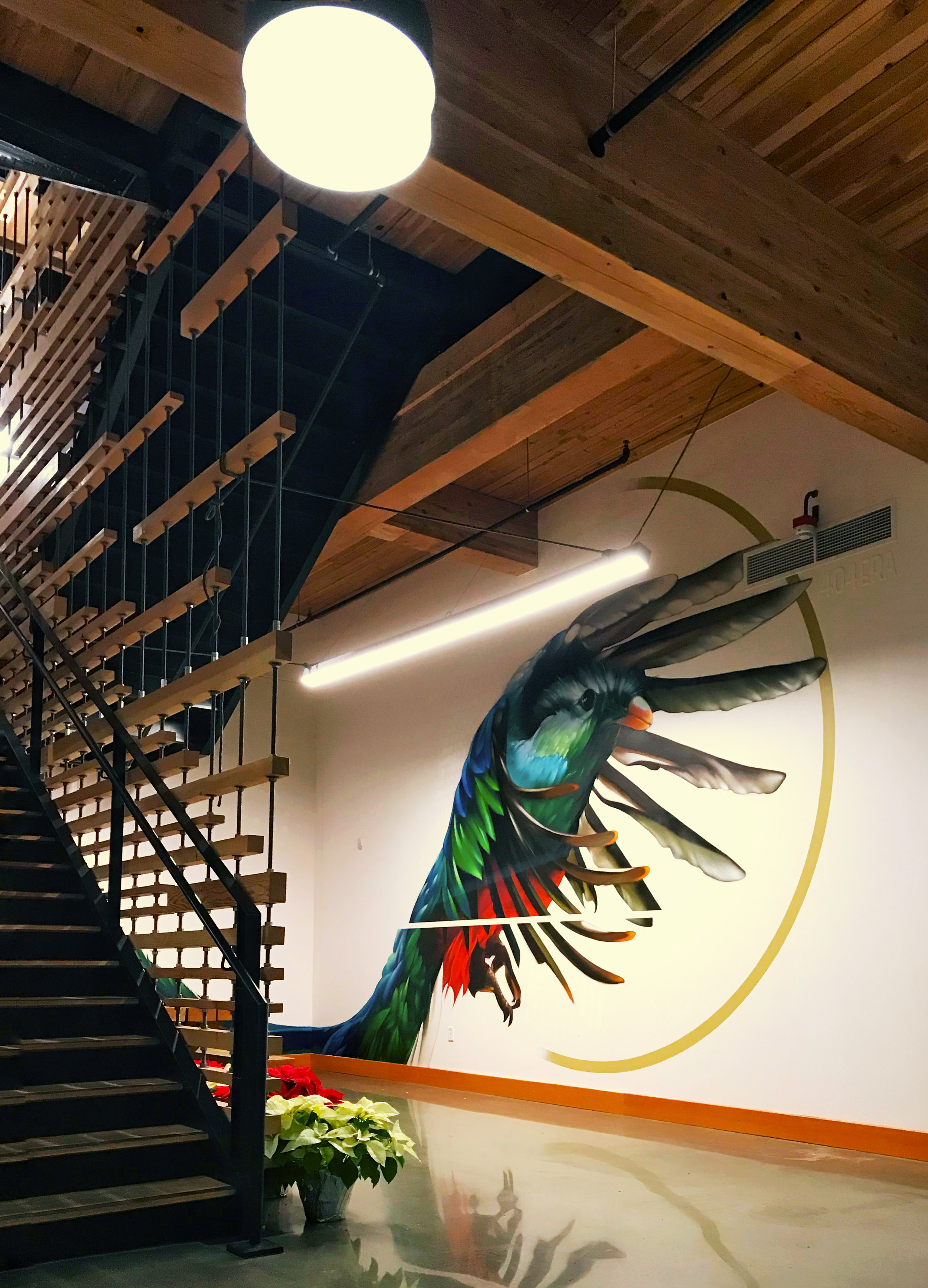
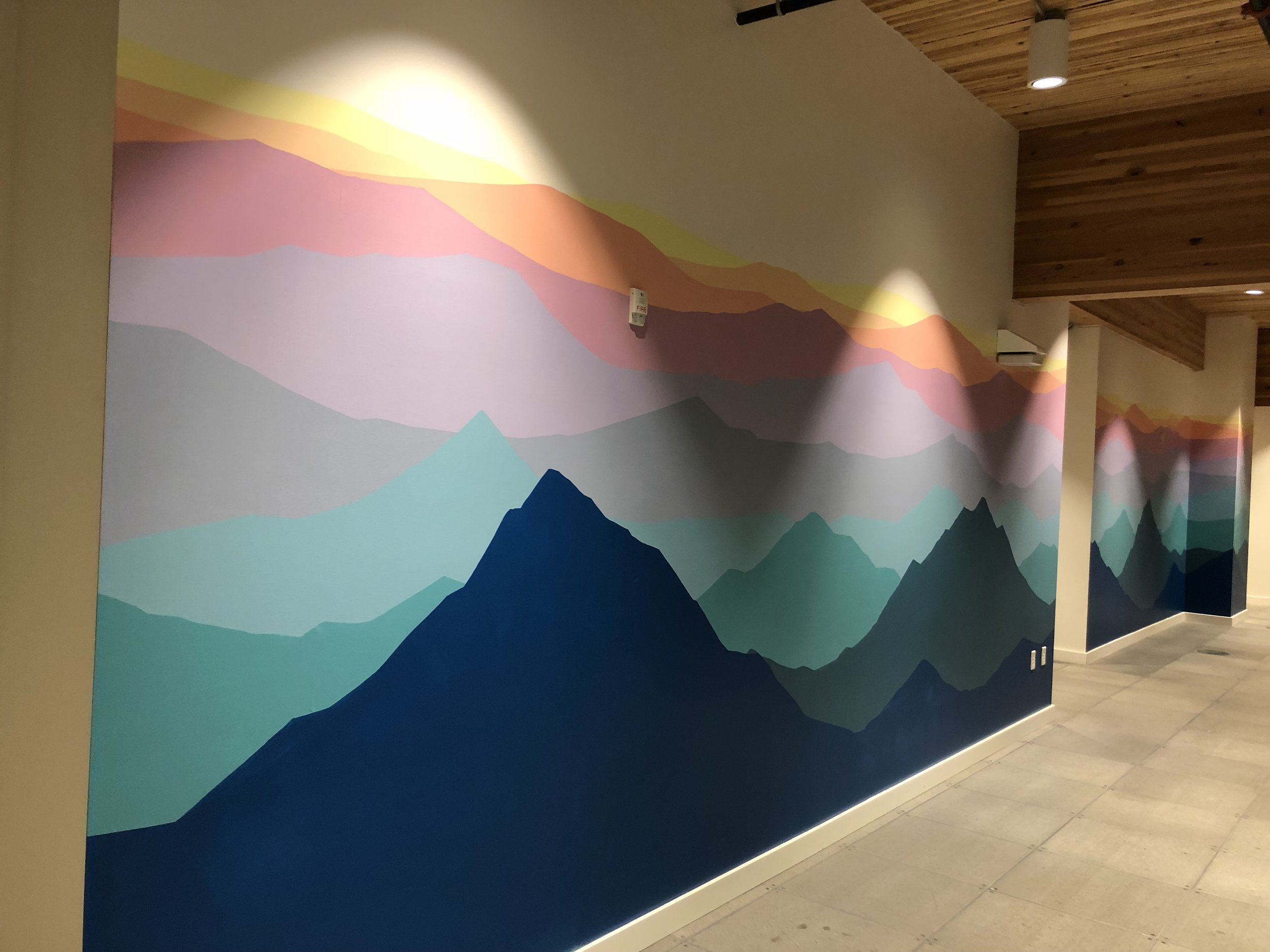
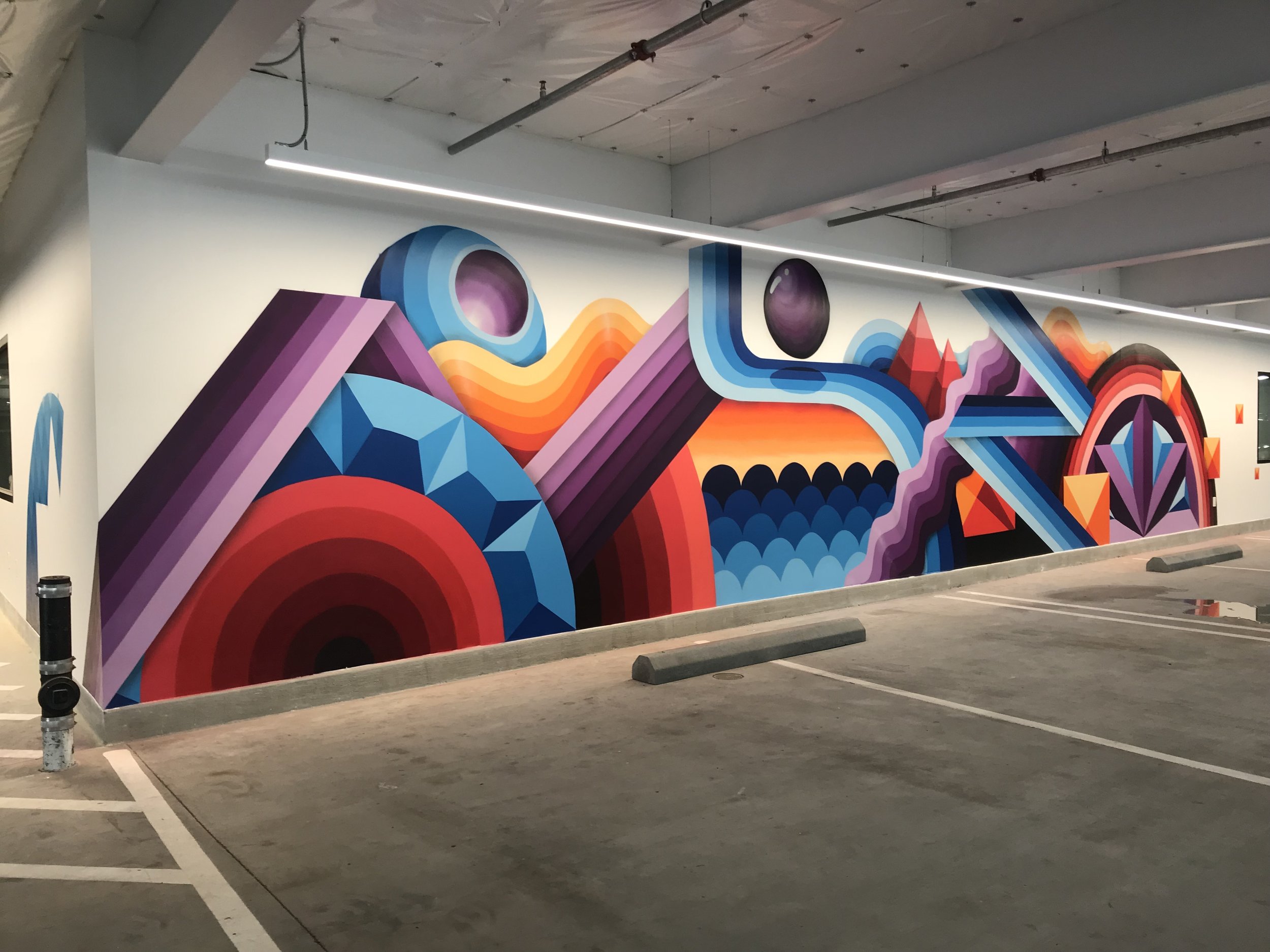
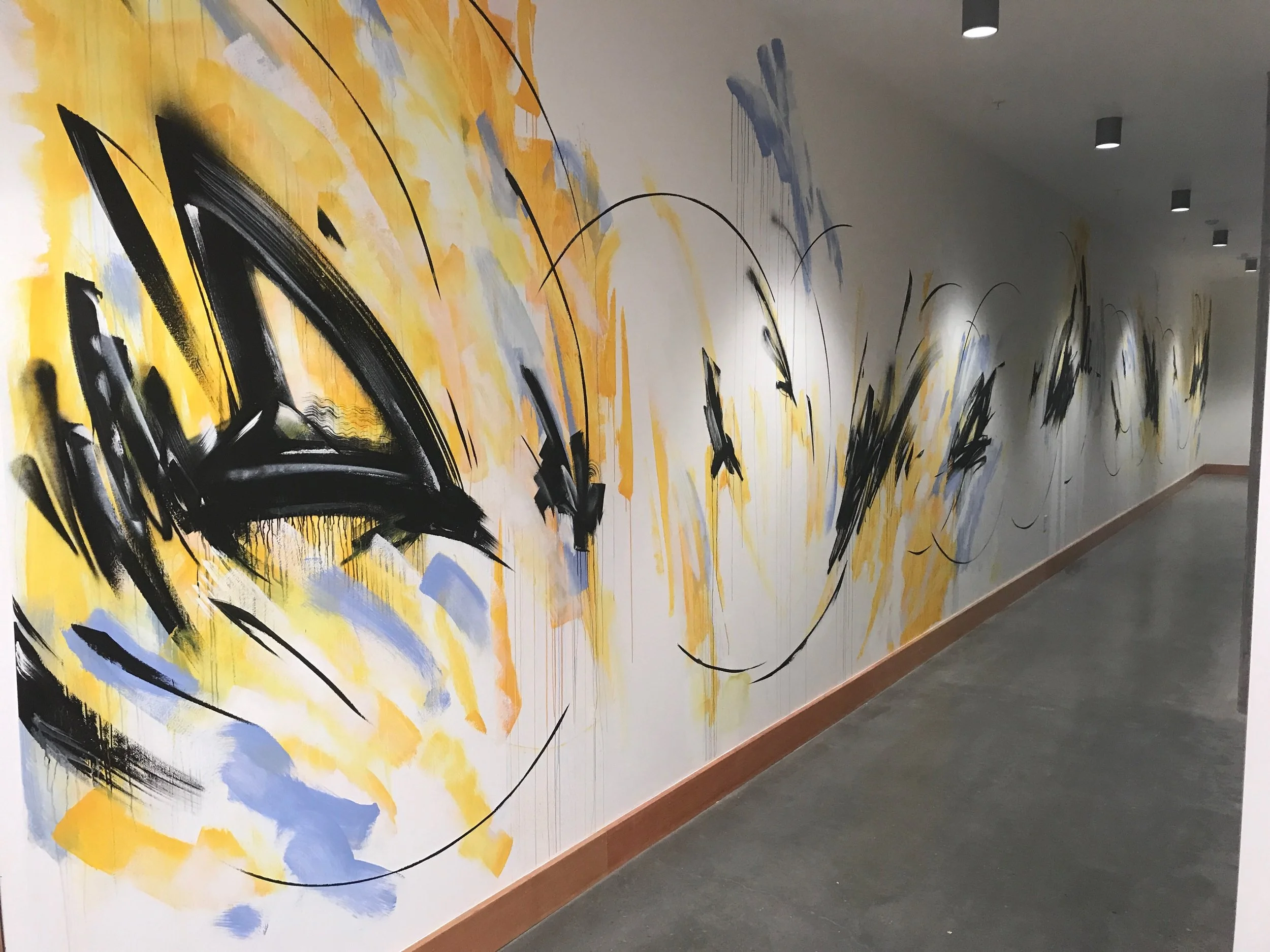
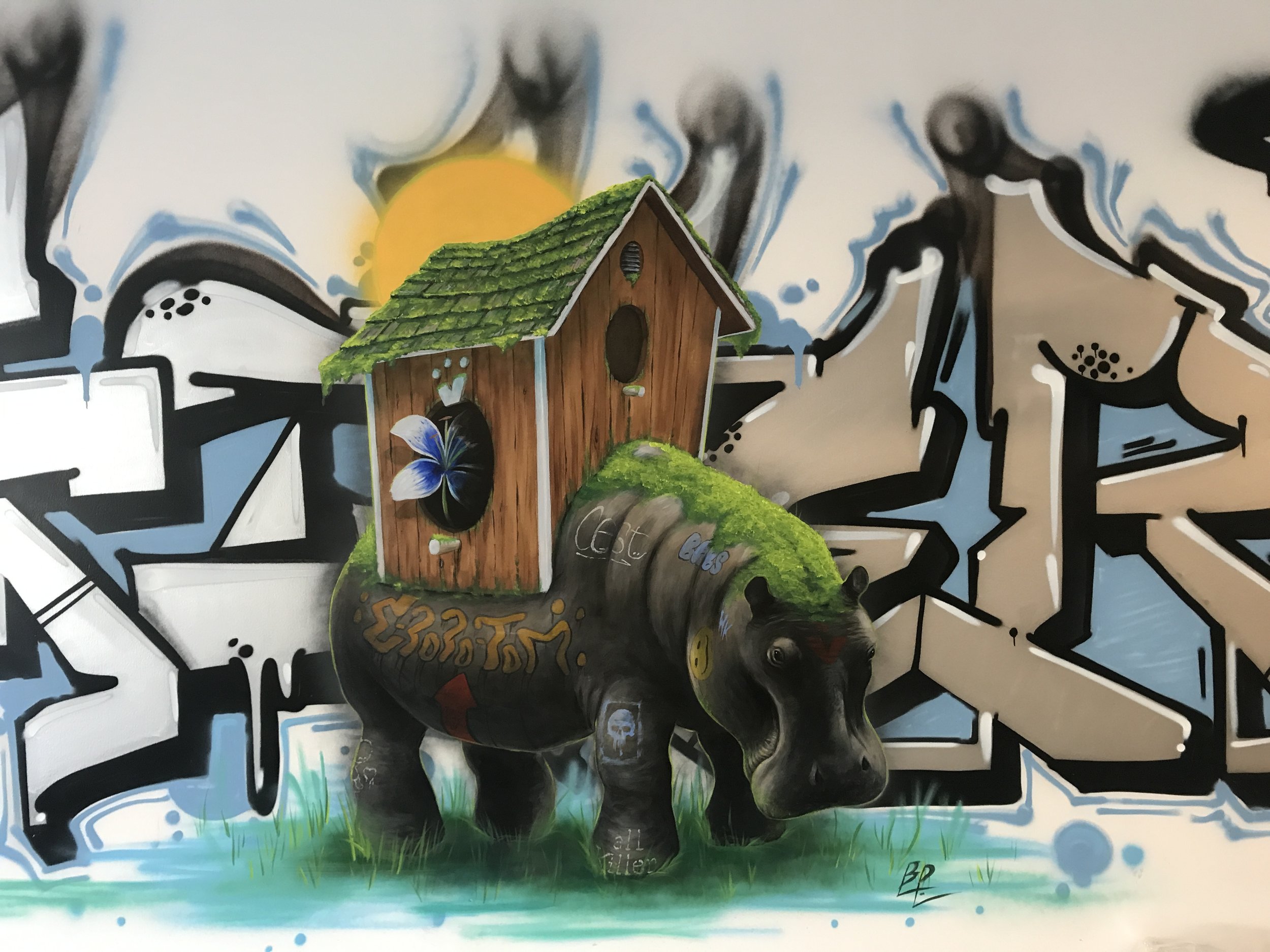
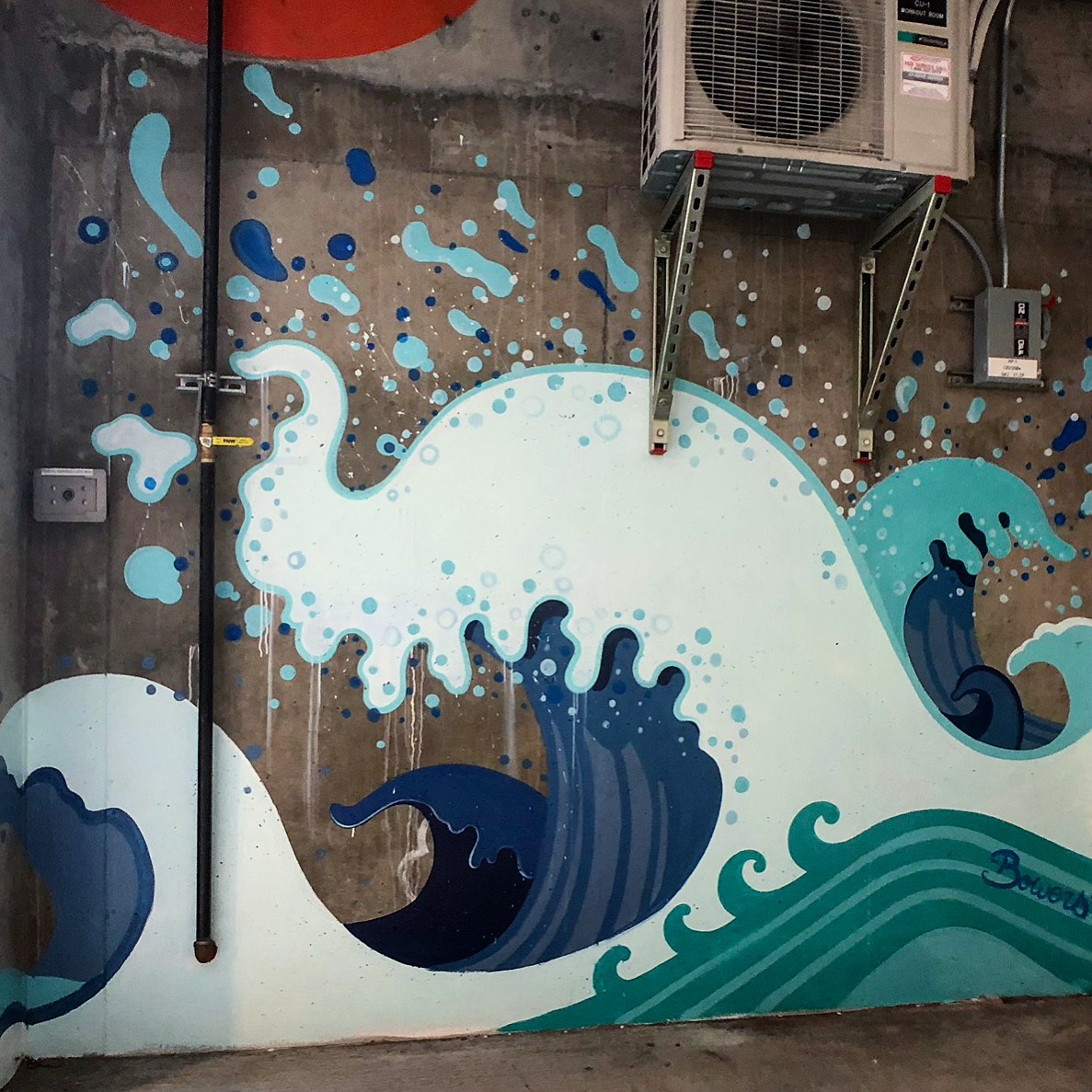
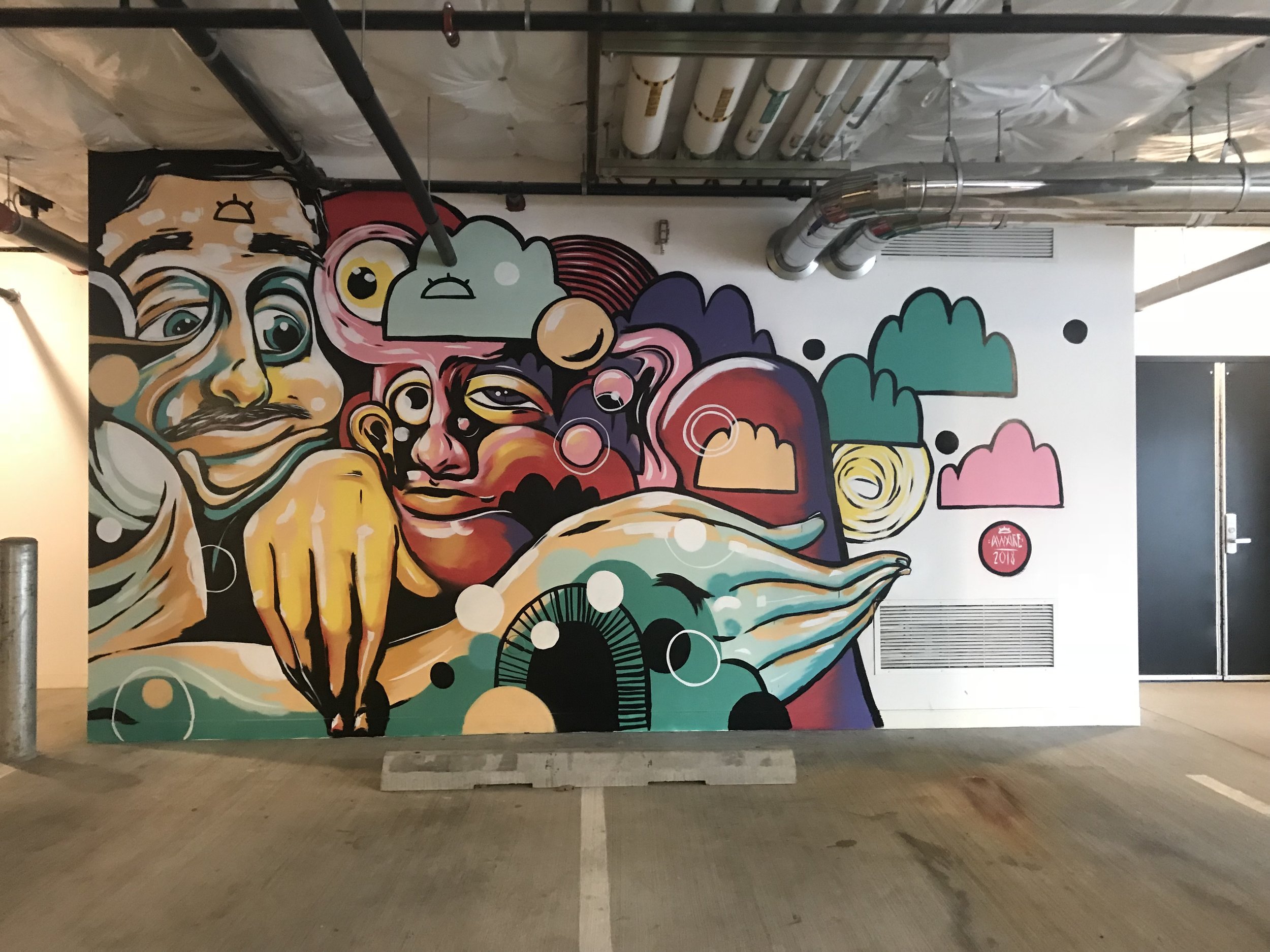
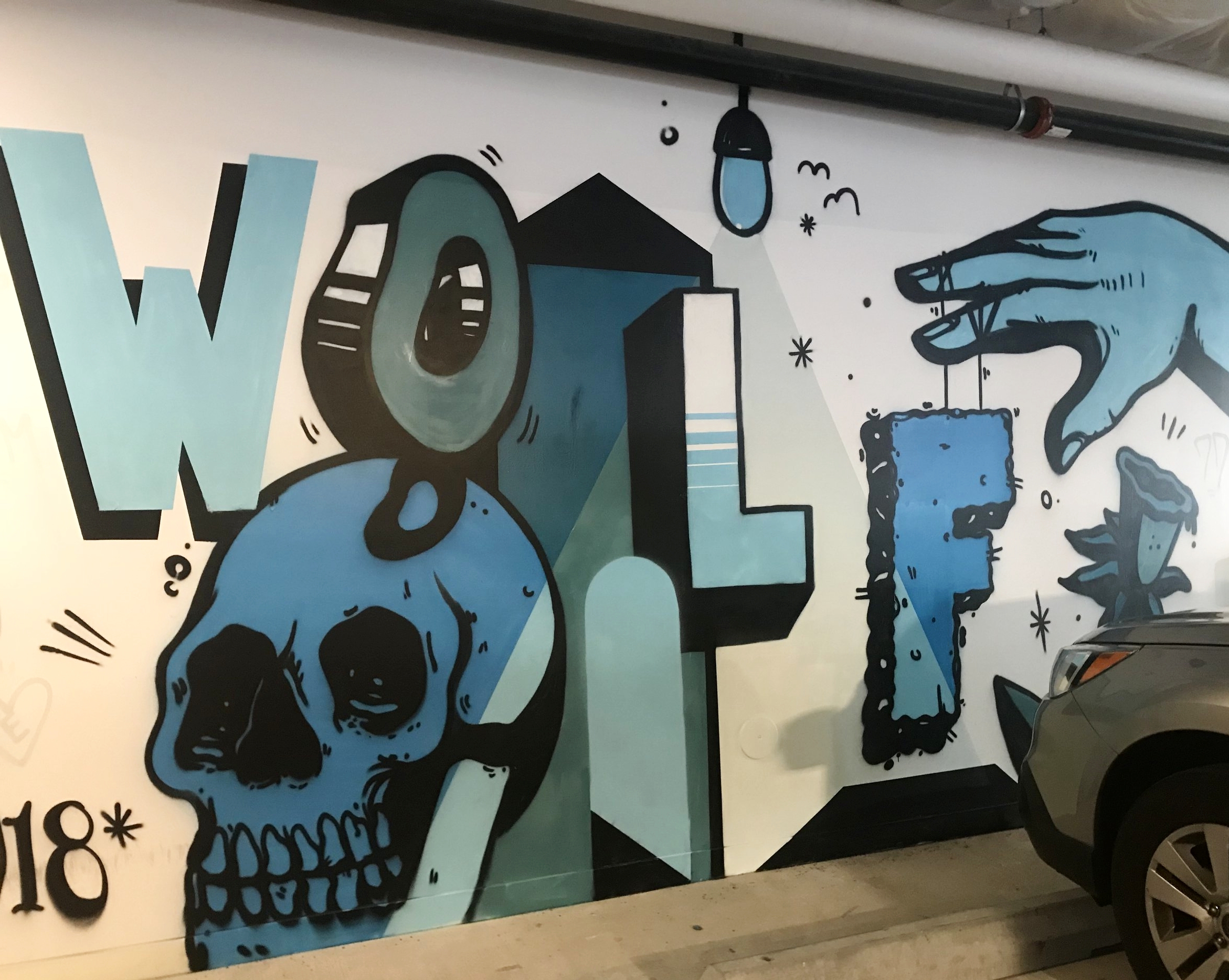
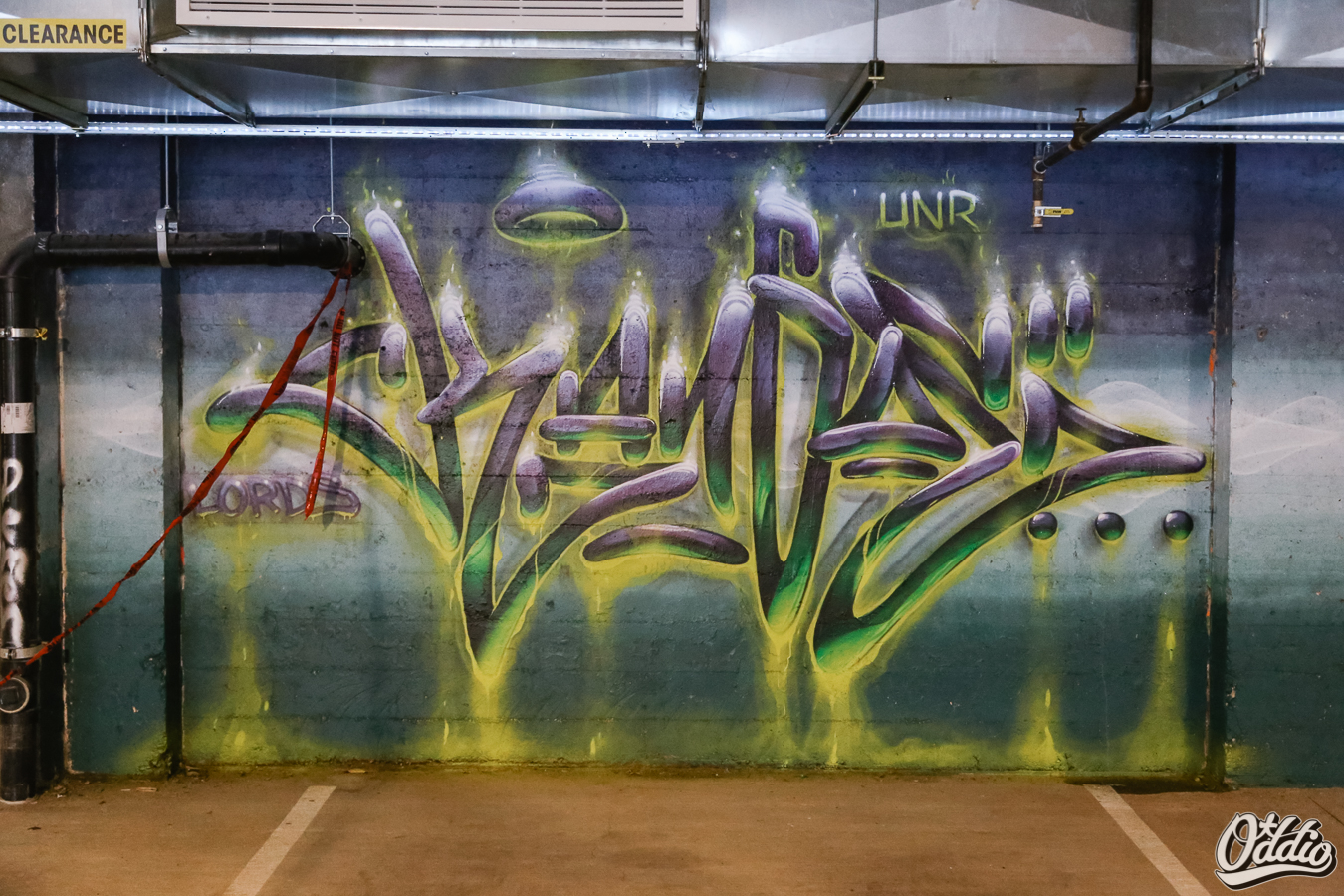
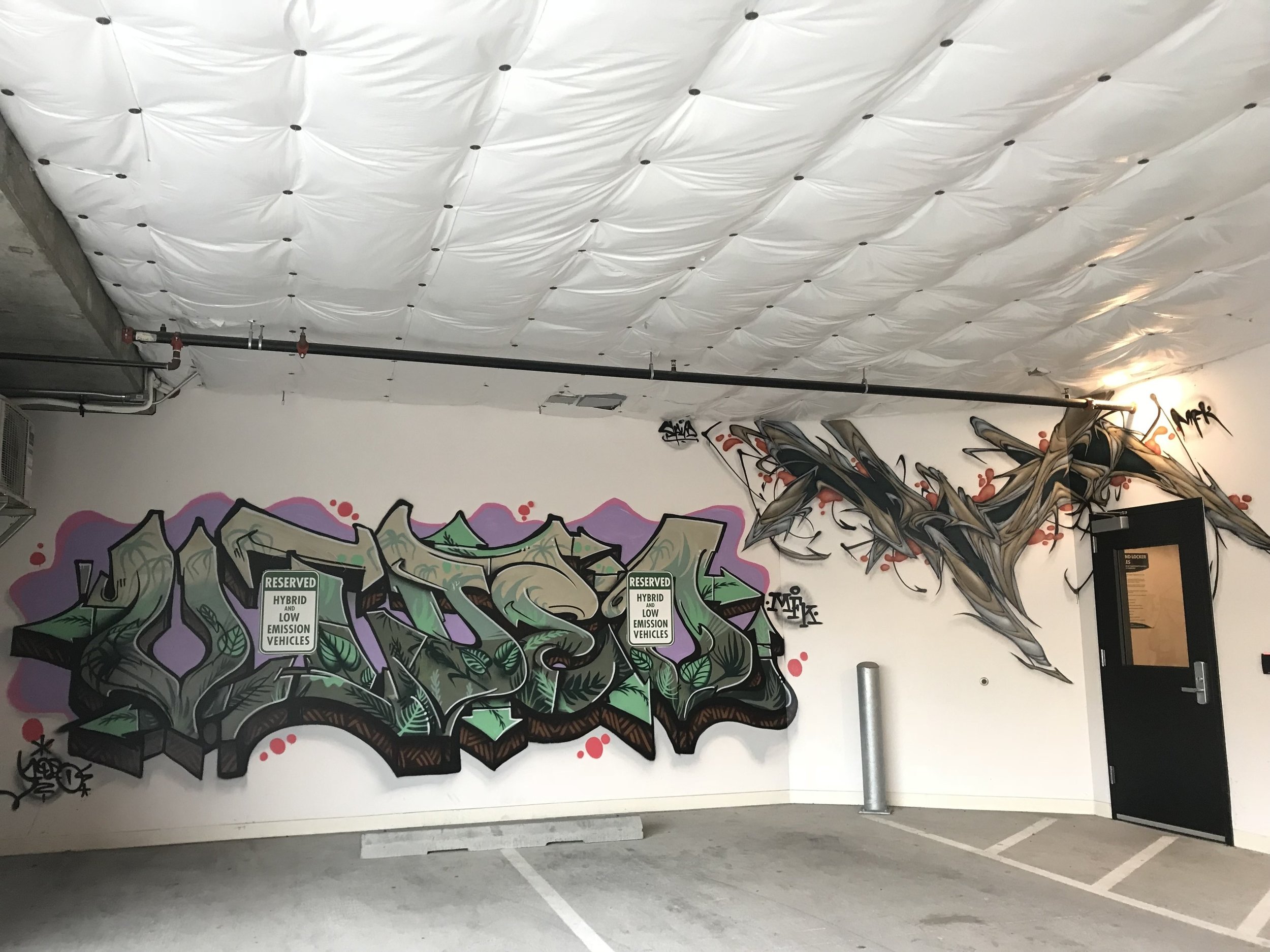
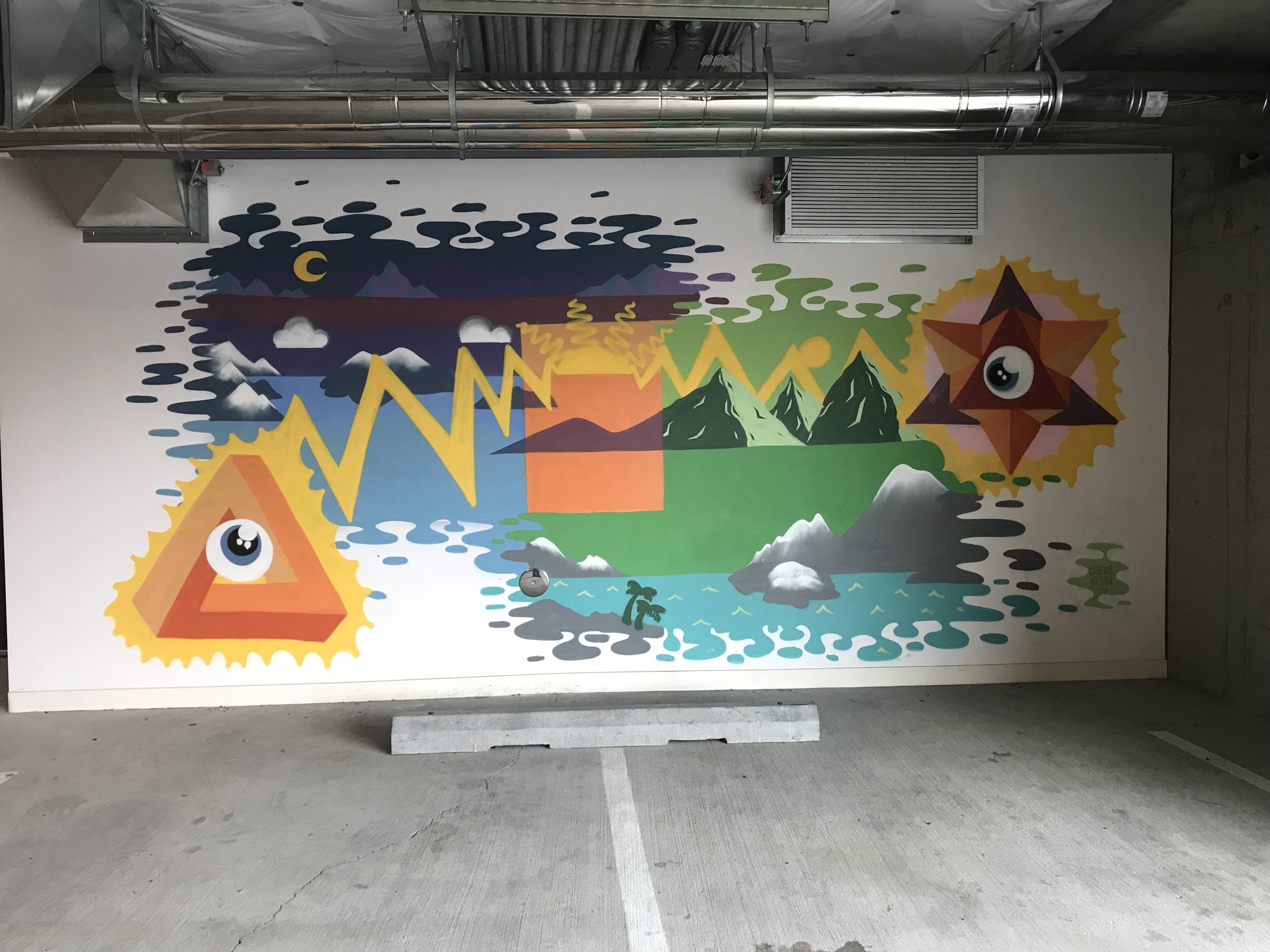












































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































![IMG_E3155[1].JPG](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/54c5d2a7e4b0df35f166e6f8/1521422463076-I80S072851Q1AOE3QO2N/IMG_E3155%5B1%5D.JPG)
![IMG_E3154[1].JPG](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/54c5d2a7e4b0df35f166e6f8/1521422471722-84M1WK0LJYBBLSAJFI2W/IMG_E3154%5B1%5D.JPG)
![IMG_E3153[1].JPG](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/54c5d2a7e4b0df35f166e6f8/1521422479156-GRLX10TIJQ0TYX3DQIXS/IMG_E3153%5B1%5D.JPG)
![IMG_E3152[1].JPG](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/54c5d2a7e4b0df35f166e6f8/1521422495470-OCPRFUPII4WCBQCFGUSK/IMG_E3152%5B1%5D.JPG)
![IMG_E3151[1].JPG](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/54c5d2a7e4b0df35f166e6f8/1521422501581-QWOP17N6HI3BU3023EN9/IMG_E3151%5B1%5D.JPG)
![IMG_3158[1].JPG](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/54c5d2a7e4b0df35f166e6f8/1521422507347-IN63252D6V6CCDKKSBJF/IMG_3158%5B1%5D.JPG)

![IMG_3157[1].JPG](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/54c5d2a7e4b0df35f166e6f8/1521422518114-S8P1TQUSUC7SH9OL2KCF/IMG_3157%5B1%5D.JPG)
![IMG_3156[1].JPG](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/54c5d2a7e4b0df35f166e6f8/1521422530046-19WA4BYRXH3POQ689OMT/IMG_3156%5B1%5D.JPG)
![IMG_3036[1].JPG](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/54c5d2a7e4b0df35f166e6f8/1521422566104-OG2X5SNC0513K7U1NSU3/IMG_3036%5B1%5D.JPG)
![IMG_3097[1].JPG](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/54c5d2a7e4b0df35f166e6f8/1521422596251-WVP89R34PV8OFKI98HHA/IMG_3097%5B1%5D.JPG)
![IMG_E3167[1].JPG](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/54c5d2a7e4b0df35f166e6f8/1521422759806-N06U0I4AVJ6HQ3F7EGD1/IMG_E3167%5B1%5D.JPG)
![IMG_E3166[1].JPG](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/54c5d2a7e4b0df35f166e6f8/1521422768969-T009CJPK22ICXTREH5IM/IMG_E3166%5B1%5D.JPG)
![IMG_3163[1].JPG](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/54c5d2a7e4b0df35f166e6f8/1521422791241-R5KJM4Z6POKT4X6M4RG3/IMG_3163%5B1%5D.JPG)
![IMG_3161[1].JPG](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/54c5d2a7e4b0df35f166e6f8/1521422802945-BUQO11HLI4CBNCAA63KA/IMG_3161%5B1%5D.JPG)
![IMG_3160[1].JPG](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/54c5d2a7e4b0df35f166e6f8/1521422815687-KYQC292C03KVM4AT29K2/IMG_3160%5B1%5D.JPG)